A Comparative Study of Maps of Scotland and Ireland: Exploring Historical, Cultural, and Geographic Influences
Related Articles: A Comparative Study of Maps of Scotland and Ireland: Exploring Historical, Cultural, and Geographic Influences
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Study of Maps of Scotland and Ireland: Exploring Historical, Cultural, and Geographic Influences. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Study of Maps of Scotland and Ireland: Exploring Historical, Cultural, and Geographic Influences

This article delves into the fascinating world of maps of Scotland and Ireland, highlighting the diverse influences that shape their representation. From historical cartographic techniques to contemporary digital mapping, the article examines how these maps reflect the unique identities and evolution of these two Celtic nations.
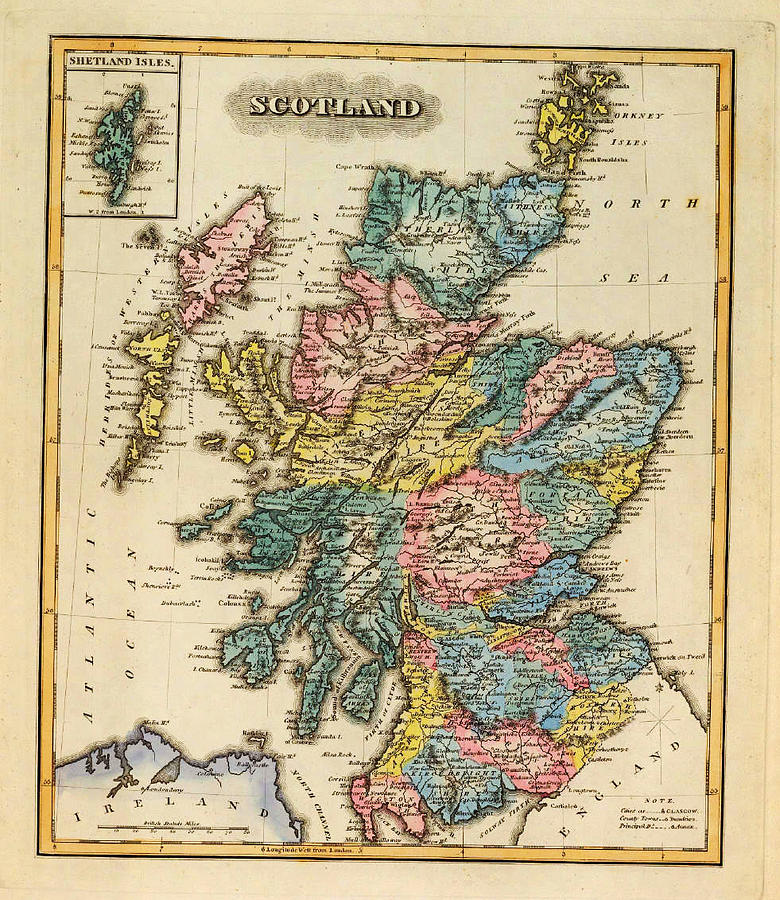
1. Historical Mapping: A Legacy of Exploration and Conquest
The earliest maps of Scotland and Ireland emerged from a combination of practical necessity and intellectual curiosity. Early Celtic societies relied on oral traditions and rudimentary methods of land division, but the arrival of Roman cartographers in the 1st century AD introduced a more systematic approach. Roman maps, though often limited in detail, provided valuable insights into the geography and resources of these regions.
1.1. Early Medieval Mapping: The Dawn of Religious and Political Influence
The Middle Ages witnessed a shift in mapping practices, driven by the influence of the Church and the rise of powerful kingdoms. Monasteries played a crucial role in preserving ancient knowledge, including cartographic traditions. The development of the "T-O" map, a common medieval map design featuring a circular world with Jerusalem at its center, reflects the profound influence of religious beliefs on mapmaking.
1.2. The Renaissance and the Emergence of Detailed Mapping
The Renaissance saw a renewed interest in exploration and scientific inquiry, leading to significant advancements in cartography. The development of the printing press facilitated the mass production of maps, making them more accessible to wider audiences. This period witnessed the emergence of more accurate and detailed maps of Scotland and Ireland, incorporating new discoveries and observations.
1.3. The Enlightenment and the Rise of Scientific Cartography
The 18th century Enlightenment ushered in a scientific revolution, further transforming cartography. The focus shifted towards precision and objectivity, with mathematicians and surveyors employing new techniques to produce increasingly accurate maps. This era saw the creation of detailed topographic maps, capturing the physical features of the land in unprecedented detail.
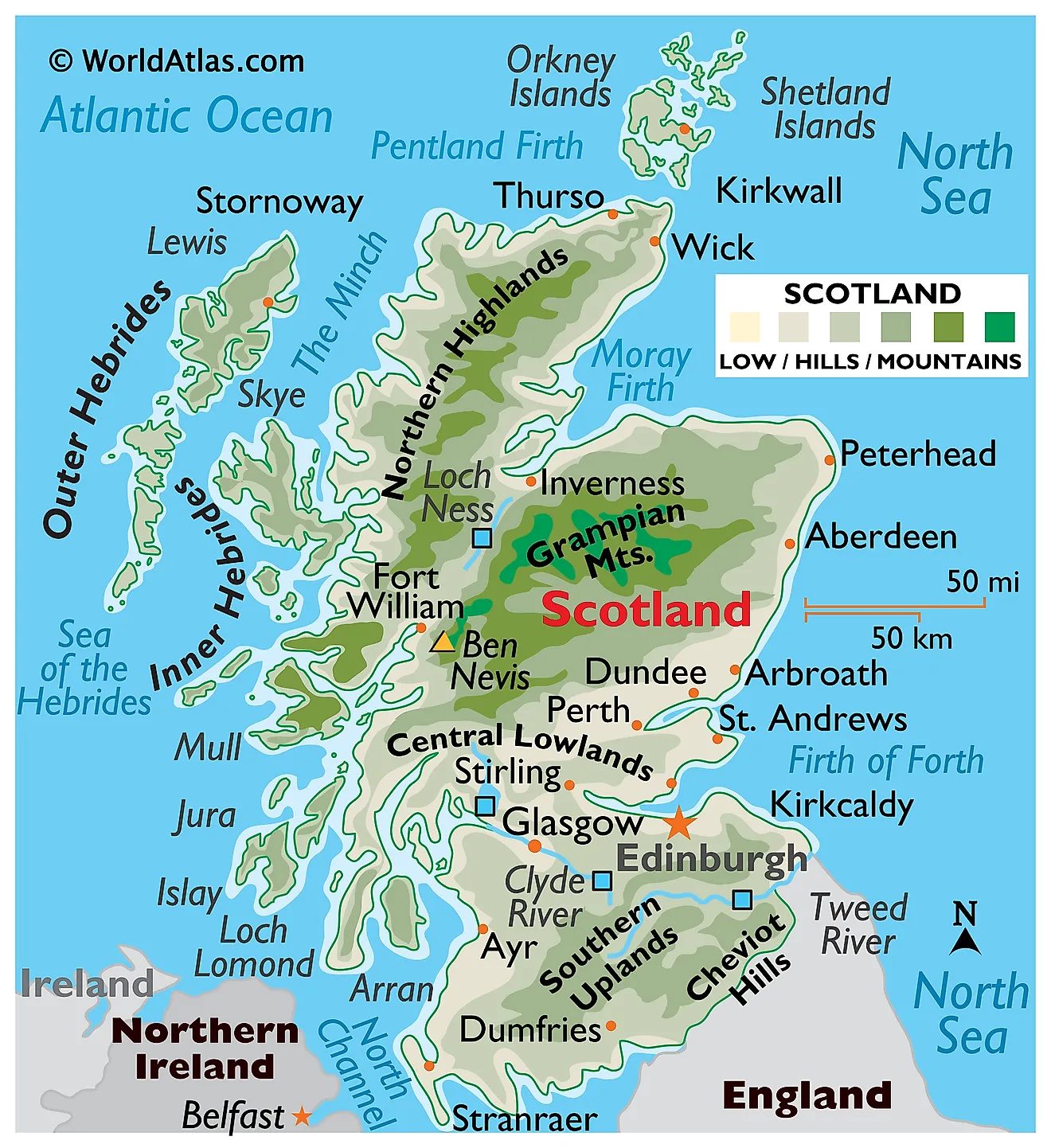
2. Modern Mapping: From Analogue to Digital
The 20th century witnessed a dramatic shift from analogue to digital mapping. The advent of aerial photography and satellite imagery revolutionized the process of mapmaking, allowing for unprecedented levels of detail and accuracy. Digital mapping platforms, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, have further democratized access to geographic information, providing users with interactive and dynamic maps.
2.1. Thematic Mapping: Unveiling Underlying Patterns and Trends
Modern mapping extends beyond simply representing physical features. Thematic maps, which focus on specific themes such as population density, economic activity, or environmental factors, provide valuable insights into the social, economic, and environmental characteristics of Scotland and Ireland.
2.2. Interactive Mapping: Engaging with Geographic Information
Interactive maps, often found on websites and mobile applications, allow users to explore geographic data in a dynamic and interactive way. Users can zoom in and out, pan across the map, and access detailed information about specific locations. This interactive approach enhances the understanding and engagement with geographic information.
3. The Importance of Maps in Understanding Scotland and Ireland
Maps are not mere static representations of the land; they are powerful tools for understanding the historical, cultural, and geographic complexities of Scotland and Ireland.
3.1. Historical Perspective: Tracing the Footprints of the Past
Maps provide a visual narrative of historical events, tracing the movements of people, armies, and trade routes. They reveal the evolution of settlements, the impact of political boundaries, and the influence of past conflicts. Examining historical maps allows us to understand the shaping of the landscape and the development of cultural identities.
3.2. Cultural Understanding: Exploring the Diversity of Landscapes and Traditions
Maps highlight the diverse landscapes, languages, and cultural traditions that define Scotland and Ireland. They reveal the influence of geographical features on cultural development, showcasing the distinct characteristics of each region. Maps can be used to explore the rich tapestry of folklore, music, and literature that have shaped these nations.
3.3. Geographic Insights: Unveiling the Natural and Human-Made Features
Maps provide a comprehensive overview of the physical features of Scotland and Ireland, from rugged mountains and rolling hills to coastal inlets and fertile valleys. They reveal the impact of climate and geology on the landscape, and they highlight the distribution of natural resources. Maps are essential tools for understanding the environmental challenges and opportunities facing these nations.
4. FAQs on Maps of Scotland and Ireland
4.1. What are the most significant historical maps of Scotland and Ireland?
Some of the most significant historical maps include the "T-O" maps from the medieval period, which provide insights into the early understanding of these regions. The maps created during the Renaissance by cartographers like Mercator and Ortelius offered more detailed and accurate representations. The maps produced during the Enlightenment, such as the Ordnance Survey maps of Scotland and Ireland, established the foundation for modern cartography.
4.2. How have maps of Scotland and Ireland evolved over time?
Maps of Scotland and Ireland have evolved from simple, schematic representations to highly detailed and accurate depictions. Early maps were often influenced by religious beliefs and political agendas, while later maps embraced scientific principles and objective observation. The advent of aerial photography and satellite imagery in the 20th century revolutionized mapping, allowing for unprecedented levels of detail and accuracy.
4.3. What are the different types of maps used to represent Scotland and Ireland?
There are numerous types of maps used to represent Scotland and Ireland, including:
- Topographic maps: Depicting physical features such as elevation, rivers, and roads.
- Political maps: Showcasing administrative boundaries, cities, and regions.
- Thematic maps: Focusing on specific themes like population density, economic activity, or environmental factors.
- Historical maps: Illustrating historical events, settlements, and political boundaries.
- Cultural maps: Highlighting cultural traditions, languages, and folklore.
4.4. How can maps be used to promote tourism and economic development in Scotland and Ireland?
Maps play a crucial role in promoting tourism and economic development by providing visitors with essential information about attractions, transportation, and accommodation. They can also be used to highlight the unique cultural and natural features of specific regions, attracting visitors and encouraging investment.
5. Tips for Using Maps of Scotland and Ireland
5.1. Explore Different Types of Maps: Utilize various map types to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
5.2. Consult Historical Maps: Examine historical maps to trace the evolution of the landscape and cultural identity.
5.3. Consider Thematic Maps: Explore thematic maps to understand specific aspects of the region, such as population distribution or economic activity.
5.4. Utilize Interactive Maps: Engage with interactive maps to explore geographic data in a dynamic and engaging way.
5.5. Combine Maps with Other Resources: Integrate maps with other resources, such as travel guides, historical accounts, and cultural information, to enhance your understanding.
6. Conclusion
Maps of Scotland and Ireland offer a rich tapestry of information, revealing the historical, cultural, and geographic influences that have shaped these nations. From early medieval maps reflecting religious beliefs to modern digital maps showcasing intricate detail, these representations provide invaluable insights into the unique identities and evolving landscapes of these Celtic lands. Understanding the history and evolution of maps allows us to appreciate the complexity and dynamism of these regions, fostering a deeper appreciation for their past, present, and future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Study of Maps of Scotland and Ireland: Exploring Historical, Cultural, and Geographic Influences. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
