Deciphering the Language of Distance: Understanding Map Scales
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Distance: Understanding Map Scales
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Distance: Understanding Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Distance: Understanding Map Scales
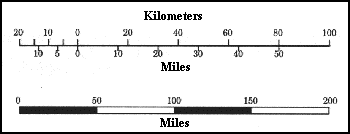
Maps are powerful tools, allowing us to navigate unfamiliar landscapes, visualize vast distances, and comprehend the spatial relationships between different locations. A crucial element in map interpretation is the scale, which establishes the relationship between distances on the map and their real-world counterparts. This article delves into the significance of a map scale expressed as "2cm : 1000km", explaining its implications and highlighting its importance in various applications.
Understanding the Ratio:
The statement "2cm : 1000km" represents a ratio that signifies a specific relationship between the map and the real world. It indicates that every 2 centimeters measured on the map correspond to 1000 kilometers in reality. This ratio forms the basis for understanding the scale of the map and its implications for interpreting distances.
Visualizing the Scale:
To grasp the magnitude of this scale, consider the following:
- A 1cm line on the map represents 500km in the real world. This means that a distance of 500 kilometers on the ground is compressed to a mere 1 centimeter on the map.
- A distance of 1000 kilometers on the ground would be represented by a 2cm line on the map. This emphasizes the significant reduction in size achieved by the map.
Implications of the Scale:
The chosen scale has profound implications for the map’s intended purpose and its effectiveness in conveying information:
- Level of Detail: A scale of 2cm : 1000km is considered a small-scale map, meaning it represents a large area with a high level of generalization. While suitable for displaying broad geographic patterns, it lacks the detail to show intricate features or smaller settlements.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of distances measured on the map is directly influenced by the scale. Due to the significant reduction in size, small errors in measurement on the map can translate into significant discrepancies in the real world.
-
Applications: Maps with this scale are commonly used for:
- Global or continental maps: They provide a concise overview of vast geographical regions.
- Long-distance travel planning: They help visualize major routes and distances for journeys spanning hundreds or thousands of kilometers.
- Geographical studies: They facilitate the analysis of large-scale phenomena such as climate patterns, tectonic plate movements, or population distribution.
The Importance of Scale:
The scale of a map is a critical factor in its effectiveness and usefulness. It determines the amount of information that can be displayed, the level of detail achievable, and the accuracy of measurements. Understanding the scale allows users to:
- Interpret distances accurately: By applying the scale ratio, users can convert distances measured on the map into their real-world equivalents.
- Compare relative sizes: The scale helps in visually comparing the sizes of different geographical features and understanding their relative importance.
- Select the appropriate map: Different tasks require maps with different scales. Understanding the scale helps users choose the map best suited for their specific needs.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map represents a smaller area with greater detail. It has a larger scale ratio, such as 1cm : 100 meters, meaning that 1 centimeter on the map represents 100 meters in reality. Conversely, a small-scale map represents a larger area with less detail, using a smaller scale ratio like 2cm : 1000km.
Q: How can I determine the distance between two points on a map with a scale of 2cm : 1000km?
A: Measure the distance between the two points on the map in centimeters. Divide this measurement by 2 (as 2cm represents 1000km). Multiply the result by 1000 to obtain the real-world distance in kilometers.
Q: Are there different types of map scales?
A: Yes, there are three common types of map scales:
- Verbal scale: This expresses the scale using words, for example, "1 centimeter represents 1000 kilometers."
- Representative fraction (RF): This expresses the scale as a ratio, for example, 1:100,000. This means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world.
- Graphic scale: This uses a visual representation, typically a line divided into segments representing real-world distances.
Tips for Using Maps with a Scale of 2cm : 1000km:
- Read the scale carefully: Ensure you understand the relationship between map distances and real-world distances.
- Use a ruler: Accurately measure distances on the map using a ruler.
- Consider the map’s purpose: Choose a map with a scale appropriate for your needs.
- Be aware of distortion: Maps with small scales often distort the shapes and sizes of geographical features, especially at higher latitudes.
Conclusion:
Maps with a scale of 2cm : 1000km play a crucial role in understanding large-scale geographical patterns and facilitating long-distance travel planning. By comprehending the relationship between map distances and real-world distances, users can effectively interpret information, make informed decisions, and gain valuable insights into the vastness of our planet. Understanding the language of scale unlocks a deeper understanding of maps and their ability to convey information about the world around us.





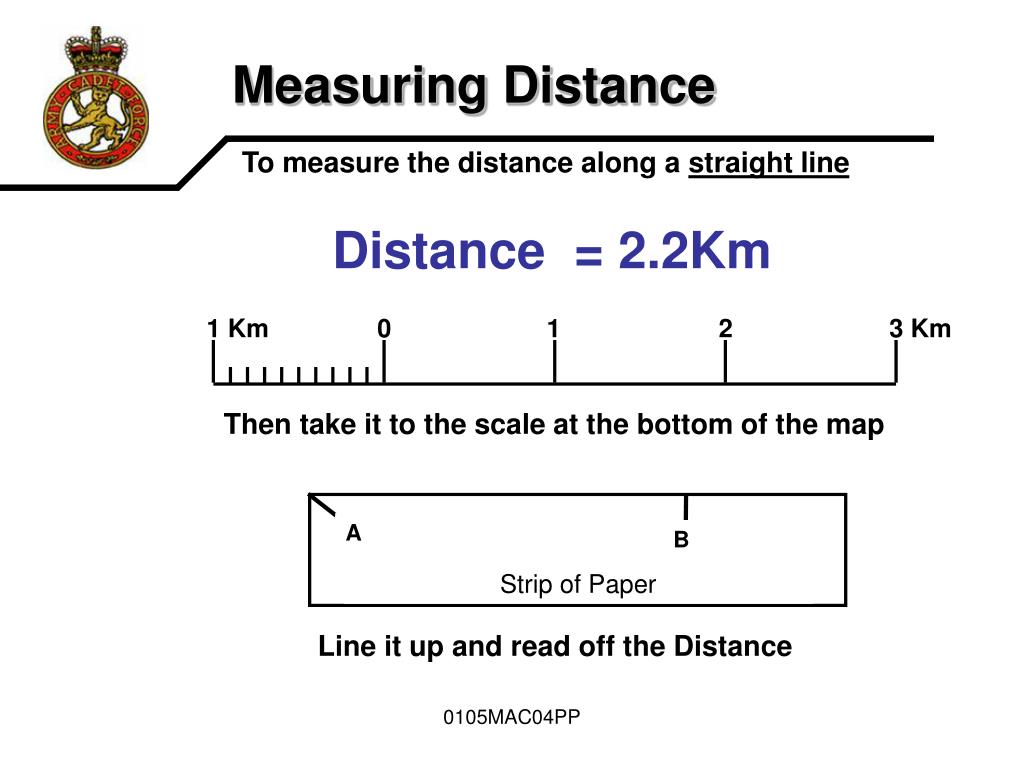

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Distance: Understanding Map Scales. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
