Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding and Utilizing Map Scales
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding and Utilizing Map Scales
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding and Utilizing Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding and Utilizing Map Scales
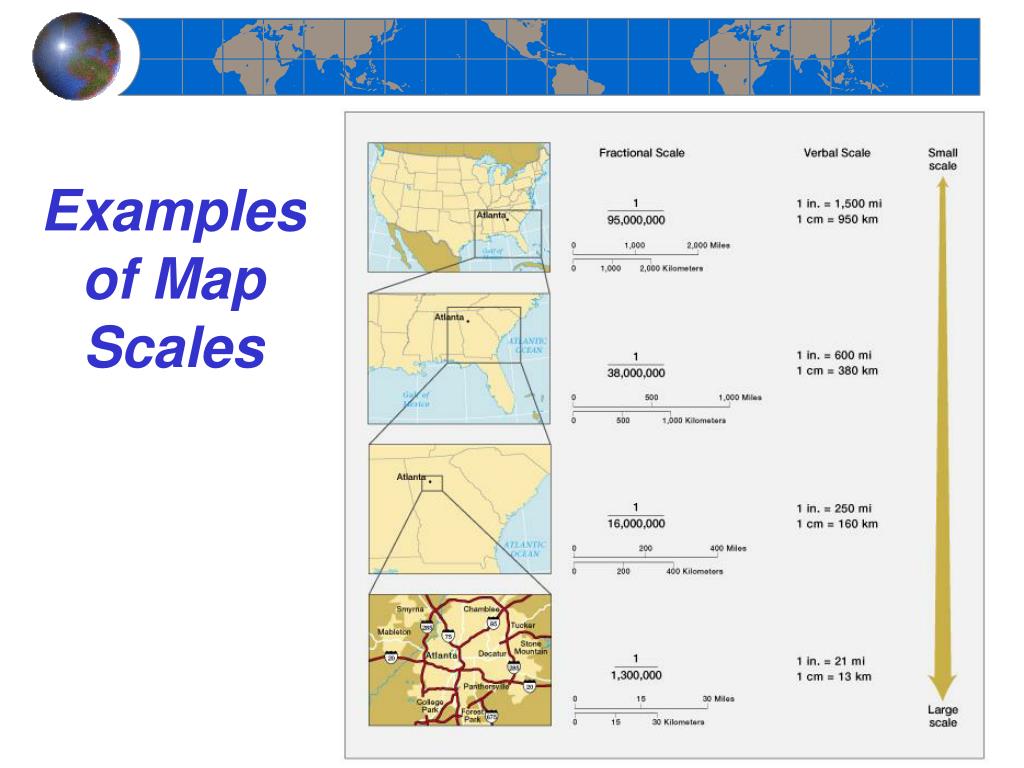
Maps, those ubiquitous tools of navigation and exploration, hold within their lines and symbols a wealth of information about the world. However, to truly comprehend the information a map conveys, one must understand the fundamental concept of map scale. This crucial element provides the key to deciphering the relationship between the map’s representation and the actual dimensions of the real world.
The Essence of Map Scale:
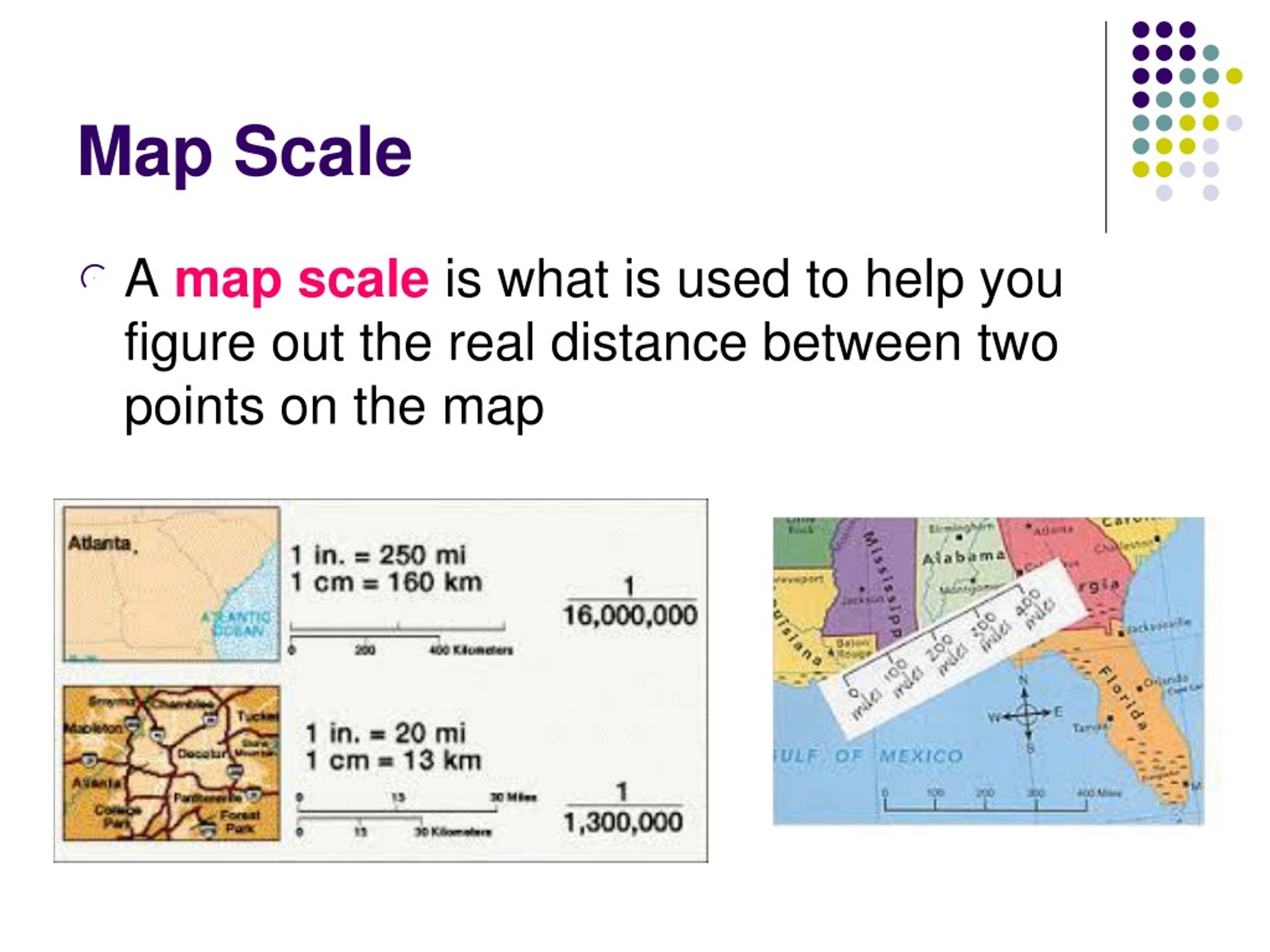
Map scale is the ratio that defines the relationship between a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially acts as a conversion factor, allowing us to translate distances measured on the map to their real-world equivalents. This ratio can be expressed in various ways, each offering a distinct approach to understanding the scale:
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method states the relationship directly, for example, "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This mathematical expression uses a colon to separate the map distance from the ground distance, both in the same units. A common example is 1:100,000, meaning one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
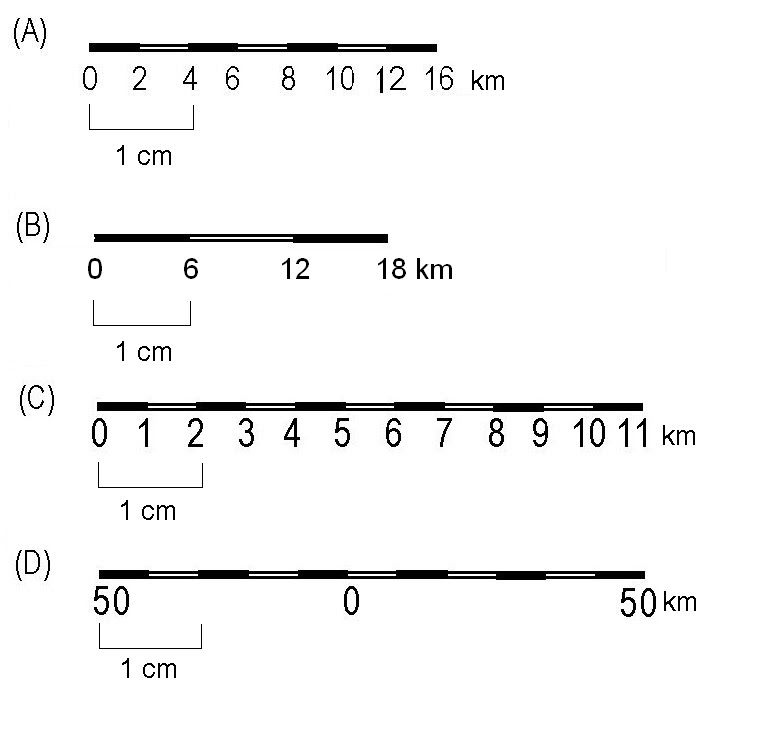
- Graphic Scale: This visual representation uses a line segment marked with specific distances, allowing for direct measurement of distances on the map and their corresponding real-world equivalents.
Mastering the Art of Map Scale Interpretation:
To effectively utilize a map scale, one must first understand the specific representation used. Once identified, the scale can be employed to determine actual distances, calculate areas, and gain a comprehensive understanding of the map’s depiction of the world.
Calculating Distances:
- Verbal Scale: If the verbal scale states "1 centimeter represents 10 kilometers," and you measure a distance of 5 centimeters on the map, the corresponding distance on the ground would be 50 kilometers (5 centimeters x 10 kilometers/centimeter).
- Representative Fraction (RF): Using the RF 1:100,000, a distance of 2 centimeters on the map corresponds to 200,000 centimeters (2 centimeters x 100,000) or 2 kilometers on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: Using a graphic scale, simply align the distance measured on the map with the scale line. The corresponding distance on the ground can be directly read from the scale markings.
Calculating Areas:
- Determining Area from a Map: The scale can be used to calculate the area of a region depicted on the map. For example, if a square on the map measures 5 centimeters by 5 centimeters, and the scale is 1:50,000, the actual area on the ground would be 250,000 square meters (5 centimeters x 5 centimeters x 50,000 x 50,000).
- Understanding Area Distortions: It’s important to note that map scales often introduce area distortions, particularly in maps depicting large areas. The further away from the equator a region is, the greater the distortion. This is because maps are flat representations of a curved surface, leading to inaccuracies in area calculations.
The Importance of Map Scale:
The map scale is not merely a technical detail; it is the cornerstone of accurate map interpretation. Without it, maps would be little more than abstract representations, devoid of any real-world significance. Understanding the scale allows us to:
- Comprehend the Map’s Representation: The scale provides the crucial link between the map’s dimensions and the actual size of features on the ground.
- Measure Distances Accurately: Whether planning a journey or studying geographic patterns, map scale enables precise distance calculations.
- Assess the Accuracy of the Map: The scale provides an indication of the level of detail and precision captured in the map. A larger scale (smaller representative fraction) typically indicates a higher level of detail, while a smaller scale (larger representative fraction) portrays a broader view with less detail.
- Evaluate the Suitability of the Map for Specific Purposes: A map with a large scale might be ideal for navigating a city, while a map with a small scale would be more appropriate for understanding global patterns.
FAQs about Map Scale:
Q: What is the difference between a large scale map and a small scale map?
A: A large scale map has a smaller representative fraction, meaning that a unit on the map represents a smaller unit on the ground. This results in a higher level of detail and is suitable for depicting smaller areas, like city maps or topographic maps. A small scale map has a larger representative fraction, meaning that a unit on the map represents a larger unit on the ground. This provides a broader view with less detail and is suitable for depicting larger areas, like world maps or regional maps.
Q: Why is it important to choose the right map scale for a specific task?
A: Choosing the appropriate map scale ensures that the map provides the necessary level of detail and accuracy for the intended purpose. For instance, a map with a large scale would be essential for navigating a city, while a small scale map would be more suitable for understanding global patterns.
Q: Can map scales be converted from one form to another?
A: Yes, map scales can be converted between different forms. For example, a verbal scale can be converted to a representative fraction by expressing the ratio of the map distance to the ground distance in the same units. Similarly, a graphic scale can be used to determine the representative fraction by measuring the distance on the scale line and comparing it to the corresponding distance on the ground.
Q: What are some common examples of map scales?
A: Common map scales include:
- Large Scale: 1:10,000, 1:25,000, 1:50,000 (used for city maps, topographic maps)
- Medium Scale: 1:100,000, 1:250,000 (used for regional maps, national parks)
- Small Scale: 1:1,000,000, 1:10,000,000 (used for world maps, continental maps)
Tips for Utilizing Map Scale:
- Always check the scale before using a map. The scale is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool for precise distance measurements.
- Consider the purpose of the map when choosing a scale. A map with a larger scale might be necessary for detailed navigation, while a smaller scale map would be sufficient for a general overview.
- Be aware of potential distortions in area measurements. Maps, especially those depicting large areas, often introduce distortions in area calculations.
- Practice using map scales with different examples. Familiarity with various representations and calculations will enhance your understanding.
Conclusion:
Mastering the art of map scale interpretation is essential for anyone who seeks to navigate, explore, or simply understand the world around them. By comprehending the relationship between the map’s representation and the real world, we can unlock the full potential of these valuable tools, gaining insights into distances, areas, and geographic patterns with greater accuracy and clarity. From planning a hiking trip to analyzing global trends, map scales empower us to navigate the world with confidence and understanding.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding and Utilizing Map Scales. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!

