Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics
- 3.1 The Essence of Map Scale: A Ratio of Reality
- 3.2 The Importance of Map Scale: Navigating the Real World
- 3.3 The Power of Graphic Scale: Visualizing the Relationship
- 3.4 Understanding Graphic Scale: A Visual Guide
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Map Use: Maximizing the Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Our World
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics

Maps, by their very nature, are representations of reality condensed into a manageable format. They enable us to navigate, understand spatial relationships, and visualize complex data. However, the accuracy and usefulness of any map hinge on one crucial element: map scale. Map scale, often depicted through a graphic representation, acts as a bridge between the vastness of the real world and the miniature world of the map. It allows us to interpret distances, understand proportions, and ultimately, to use the map effectively.
The Essence of Map Scale: A Ratio of Reality
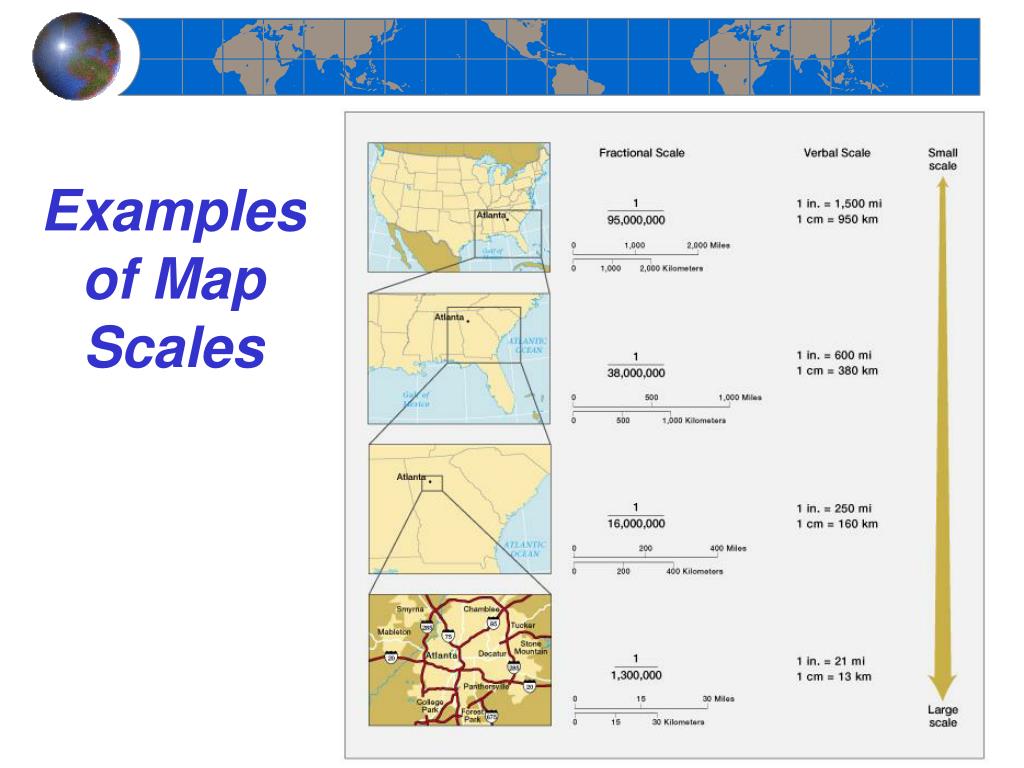
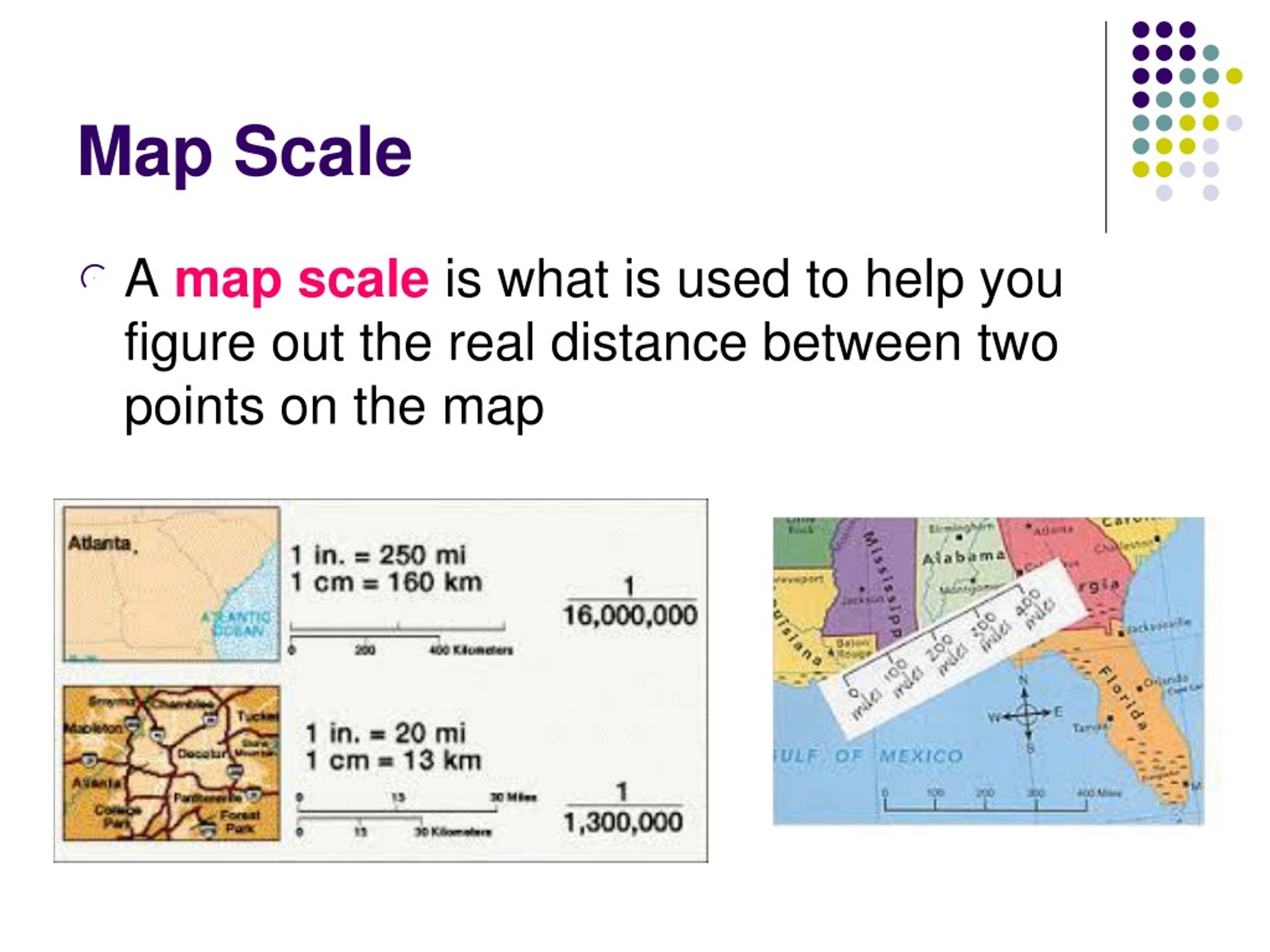
At its core, map scale represents a ratio – a comparison between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is expressed in various ways, each offering a different perspective on the relationship between map and reality:
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method uses words to describe the relationship. For example, "1 inch on the map represents 1 mile on the ground" or "1 centimeter on the map represents 1 kilometer on the ground." This format is intuitive and easy to understand, making it ideal for beginners.
- Representative Fraction (RF): This method expresses the scale as a fraction, typically in the form of 1:X. The numerator "1" represents one unit of measurement on the map, while the denominator "X" represents the corresponding number of the same units on the ground. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map corresponds to 100,000 units on the ground. This format is widely used in cartography due to its accuracy and versatility.
- Graphic Scale: This method uses a visual representation of the scale, typically a bar with marked divisions. The bar represents a specific distance on the map, and the divisions correspond to specific distances on the ground. This format is particularly useful for quick estimations of distances directly from the map.
The Importance of Map Scale: Navigating the Real World
The importance of map scale cannot be overstated. It is the key to bridging the gap between the abstract world of the map and the concrete world we inhabit. Without a clear understanding of map scale, a map becomes a mere illustration, devoid of practical value. Here’s how map scale empowers us:
- Accurate Distance Measurement: Map scale allows us to translate distances measured on the map into real-world distances. This is crucial for navigation, planning routes, and understanding the spatial relationships between locations.
- Spatial Proportionality: Map scale ensures that the relative size and distances between features on the map accurately reflect their real-world counterparts. This is essential for understanding geographical relationships, visualizing the distribution of features, and making informed decisions based on spatial information.
- Data Interpretation: Map scale influences the level of detail that can be represented on a map. A larger scale map, with a smaller denominator in the RF, can depict more intricate features, while a smaller scale map, with a larger denominator, offers a broader overview. This allows us to tailor our map selection to the specific information we need.
The Power of Graphic Scale: Visualizing the Relationship
While all three scale representations are valuable, the graphic scale stands out for its intuitive and visual nature. It offers a direct, tangible representation of the scale, making it easier to grasp the relationship between the map and reality.
Benefits of Graphic Scale:
- Direct Measurement: Graphic scales enable us to measure distances on the map directly using the provided bar. This eliminates the need for complex calculations and facilitates quick estimations.
- Visual Clarity: The visual representation of the scale makes it easier to grasp the relationship between map and ground distances. This is particularly helpful for individuals with limited mathematical skills or for those who prefer visual learning.
- Flexibility: Graphic scales can be easily adjusted to accommodate different map sizes and orientations. This ensures that the scale remains relevant even when the map is reproduced or resized.
- Universality: Graphic scales are widely used in various types of maps, making them a familiar and easily understood tool for a wide audience.
Understanding Graphic Scale: A Visual Guide
Graphic scales typically consist of a straight line with marked divisions. The line represents a specific distance on the map, and the divisions correspond to specific distances on the ground. The scale can be linear, meaning the divisions are evenly spaced, or it can be non-linear, with divisions that vary according to the map’s scale.
Interpreting Graphic Scale:
- Identify the Scale Bar: Locate the graphic scale on the map. It is usually found in the map’s margin or legend.
- Determine the Units: Note the units of measurement used on the scale bar. This could be inches, centimeters, miles, kilometers, or other units.
- Measure the Distance: Use a ruler or other measuring tool to measure the distance between two points on the map.
- Compare to the Scale Bar: Match the measured distance on the map to the corresponding division on the scale bar. This will reveal the actual distance between the two points on the ground.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. What is the difference between large-scale and small-scale maps?
A large-scale map depicts a smaller area with more detail, while a small-scale map covers a larger area with less detail. Large-scale maps have a smaller denominator in the representative fraction, while small-scale maps have a larger denominator.
2. How do I choose the right map scale for my needs?
The appropriate map scale depends on the specific purpose of the map. For detailed navigation, a large-scale map is preferable. For broader overviews, a small-scale map is more suitable.
3. Can I convert between different scale representations?
Yes, it is possible to convert between verbal, representative fraction, and graphic scales. However, it is essential to ensure consistency in the units of measurement.
4. What are some common examples of map scales?
Common map scales include 1:100,000, 1:250,000, and 1:1,000,000. The smaller the denominator, the larger the scale and the greater the detail.
5. How accurate is graphic scale?
Graphic scales offer a good approximation of distances. However, their accuracy is limited by the precision of the map’s production and the measuring tools used.
Tips for Effective Map Use: Maximizing the Potential
- Understand the Scale: Always take the time to understand the scale of the map before using it. This will help you interpret distances and make informed decisions.
- Choose the Right Map: Select a map with an appropriate scale for your specific needs. If you require detailed information, choose a large-scale map. For a broader overview, opt for a small-scale map.
- Use a Ruler: Utilize a ruler or measuring tool to accurately measure distances on the map. This will ensure more precise estimations of real-world distances.
- Be Aware of Distortion: Remember that all maps distort reality to some extent. Understand the type of projection used in the map and how it might affect distances and shapes.
- Practice: The best way to become proficient with map scale is to practice using it in different scenarios. This will help you develop an intuitive understanding of the relationship between map and reality.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Our World
Map scale graphics, though seemingly simple, play a crucial role in our understanding of maps. They provide the vital link between the abstract representations on a map and the complex reality we inhabit. By understanding map scale, we can navigate effectively, interpret spatial data, and make informed decisions based on the information presented. The ability to decipher the language of maps, empowered by the clarity of map scale graphics, is a valuable skill in our increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale Graphics. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
