Defining and Exploring the Concept of a Radius on a Map
Related Articles: Defining and Exploring the Concept of a Radius on a Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Defining and Exploring the Concept of a Radius on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining and Exploring the Concept of a Radius on a Map
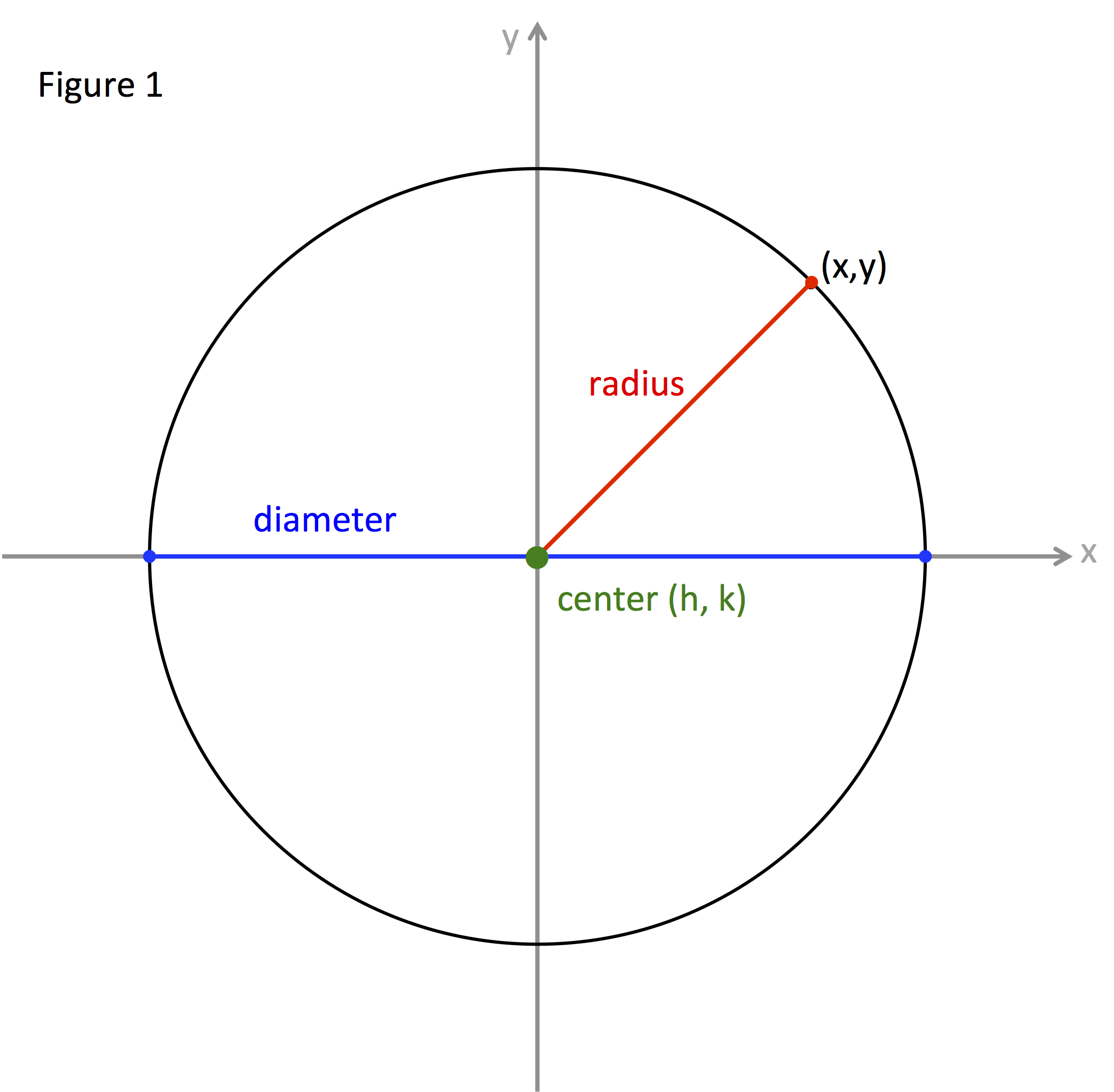
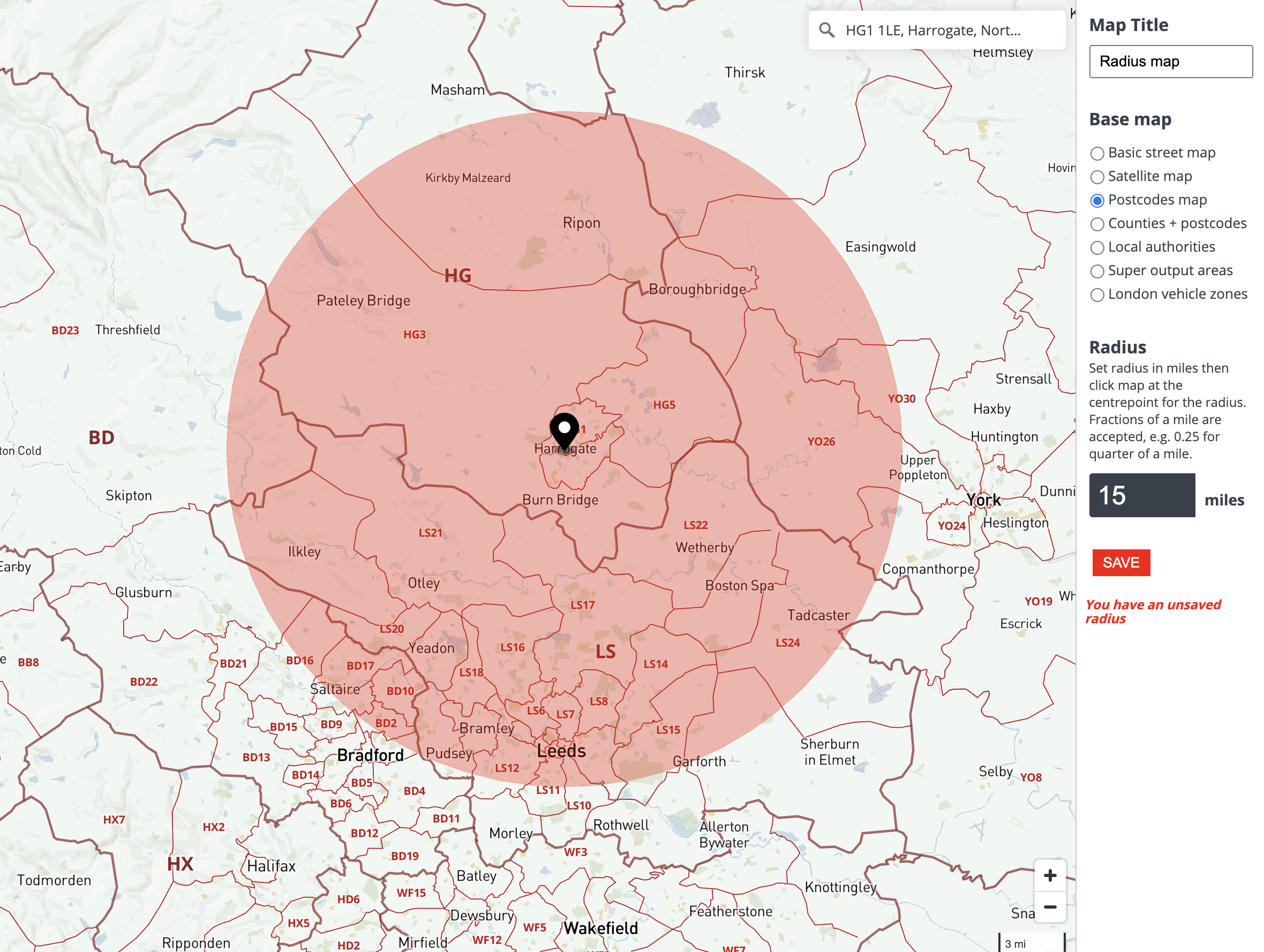
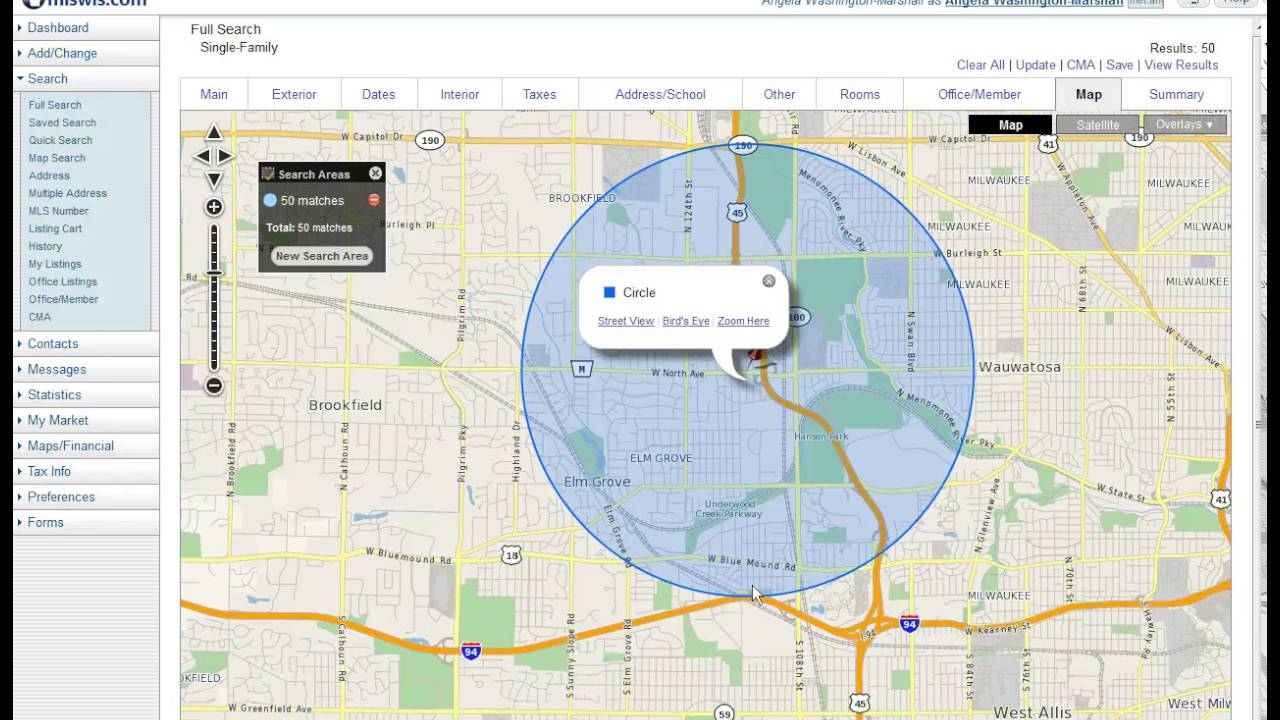
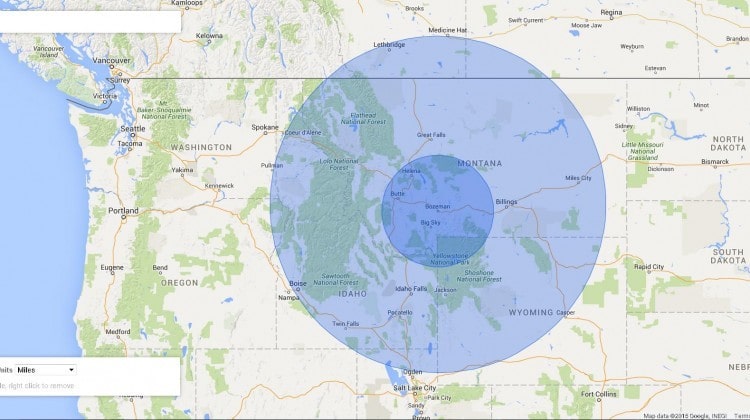
The concept of a radius on a map, often visualized as a circle drawn around a central point, is a fundamental tool in various fields. It allows for the visualization and quantification of spatial relationships, providing a clear understanding of distances and areas within a defined boundary. This article will explore the multifaceted nature of a radius on a map, examining its applications, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding the Radius Concept:
At its core, a radius is a line segment extending from the center of a circle to its circumference. On a map, this concept is applied to define a circular area around a specific location, known as the center point. This area, bounded by the circumference, represents all points that are within a certain distance from the center. The distance is measured in units like kilometers, miles, or nautical miles, depending on the context and scale of the map.
Applications of a Radius on a Map:
The application of a radius on a map is diverse, spanning various disciplines:
1. Geographic Analysis:
- Proximity Analysis: Identifying locations within a certain distance from a specific point, such as determining the number of schools within a 5-kilometer radius of a residential area.
- Market Analysis: Understanding the geographic reach of a business or service, identifying potential customers within a defined radius.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the impact of a specific event or phenomenon on surrounding areas, such as assessing the influence of a pollution source within a 10-mile radius.
2. Navigation and Transportation:
- Route Planning: Determining the shortest or most efficient route between two points, considering the radius around obstacles or areas of interest.
- Traffic Management: Analyzing traffic patterns within a defined radius, identifying congestion points and optimizing traffic flow.
- Emergency Response: Establishing a search and rescue zone around a disaster area, ensuring efficient deployment of resources.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use Planning: Defining development zones based on distance from infrastructure or designated areas.
- Urban Design: Designing public spaces and amenities within a radius of residential areas, promoting walkability and accessibility.
- Infrastructure Planning: Evaluating the feasibility of new infrastructure projects, considering their impact on surrounding areas.
4. Security and Surveillance:
- Surveillance Zones: Establishing monitored areas around critical infrastructure or sensitive locations.
- Crime Analysis: Identifying crime hotspots within a defined radius, enabling targeted security measures.
- Border Control: Monitoring and controlling movement within a specific radius along national borders.
Benefits of Utilizing a Radius on a Map:
The application of a radius on a map offers several key benefits:
- Visual Clarity: Provides a clear and intuitive representation of spatial relationships, facilitating understanding of distances and areas.
- Quantitative Analysis: Enables precise measurement of distances and areas, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Optimizes resource allocation based on proximity to specific points, maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
- Improved Decision-Making: Facilitates informed decision-making by providing a comprehensive understanding of spatial context.
- Enhanced Communication: Simplifies communication by providing a common visual language for understanding spatial relationships.
Challenges and Limitations:
While the radius concept offers significant advantages, it also presents certain challenges:
- Scale and Resolution: The accuracy of radius measurements is dependent on the scale and resolution of the map. Fine-grained analysis requires high-resolution maps.
- Terrain and Obstacles: Actual distances may vary from map-based radii due to terrain features, obstacles, and accessibility limitations.
- Data Availability: The effectiveness of radius analysis depends on the availability of accurate and comprehensive data for the specific location.
- Oversimplification: The circular shape of a radius may oversimplify complex spatial relationships, potentially leading to inaccurate conclusions.
- Bias and Interpretation: The definition of the radius and the interpretation of results can be influenced by subjective factors and biases.
FAQs Regarding Radius on a Map:
1. How is a radius on a map calculated?
A radius on a map is calculated using distance formulas and the coordinates of the center point. Geographic information systems (GIS) software typically employs algorithms to calculate distances based on the chosen unit of measurement and map projection.
2. What are the different types of radii on a map?
Radii on a map can be classified based on their shape, purpose, and application. Common types include:
- Circular Radius: A standard circle with a fixed radius around a central point.
- Buffer Zone: A polygon-shaped radius that accounts for terrain features and obstacles.
- Isodistance Lines: Lines connecting points equidistant from a specific location.
3. How does the scale of the map affect the radius?
The scale of the map directly impacts the accuracy and interpretation of the radius. Smaller-scale maps, representing larger areas, will have less precise radius measurements compared to large-scale maps.
4. What are the limitations of using a radius on a map?
The limitations of using a radius on a map include:
- Terrain and Obstacles: Actual distances may vary from map-based radii due to terrain features, obstacles, and accessibility limitations.
- Data Availability: The effectiveness of radius analysis depends on the availability of accurate and comprehensive data for the specific location.
- Oversimplification: The circular shape of a radius may oversimplify complex spatial relationships, potentially leading to inaccurate conclusions.
Tips for Effectively Utilizing a Radius on a Map:
- Choose the appropriate map scale and resolution: Select a map that provides sufficient detail for the desired analysis.
- Consider terrain and obstacles: Factor in terrain features and obstacles when interpreting radius measurements.
- Verify data accuracy: Ensure the data used for radius calculations is accurate and reliable.
- Use appropriate units of measurement: Select units of measurement relevant to the analysis and scale of the map.
- Interpret results critically: Consider the limitations of the radius concept and interpret results with caution.
Conclusion:
The concept of a radius on a map is a powerful tool for visualizing and quantifying spatial relationships. It enables efficient analysis of proximity, facilitates resource allocation, and supports informed decision-making in various fields. However, it is crucial to be aware of the limitations and potential biases associated with this concept and to interpret results critically. By understanding the intricacies of radius application, we can leverage its potential to enhance our understanding of the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining and Exploring the Concept of a Radius on a Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
