Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Scale and Map Projections
- 3.2 Methods for Determining Distance from Maps
- 3.3 Calculating Areas from Maps
- 3.4 Factors Affecting Accuracy
- 3.5 Importance and Applications
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Accurate Distance and Area Measurements
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

Maps are powerful tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding the world around us. Beyond simply showing locations, maps can be used to determine distances and areas, crucial information for various applications, from planning travel routes to assessing the impact of development projects. This article delves into the methods for calculating distances and areas directly from maps, exploring the principles behind these calculations and providing practical guidance for accurate results.
Understanding Scale and Map Projections
The foundation of distance and area calculations from maps lies in the concept of scale and map projections.
- Scale: This represents the ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It is typically expressed as a fraction (e.g., 1:100,000) or a verbal statement (e.g., "1 centimeter on the map equals 1 kilometer on the ground"). Understanding the map’s scale is essential for accurate distance calculations.
- Map Projections: The Earth is a sphere, while maps are flat representations. To portray the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane, mapmakers use projections, which distort distances and shapes to some extent. Different projections are designed for specific purposes, and their distortions vary accordingly.
Methods for Determining Distance from Maps
Several methods can be employed to calculate distances from maps, each with its own level of accuracy and complexity:
1. Using a Ruler and Scale:
- Direct Measurement: The simplest approach involves using a ruler to measure the distance between two points on the map and then applying the map’s scale to convert the measurement to real-world distance.
- Example: If the distance between two points on a map with a scale of 1:100,000 measures 5 centimeters, the actual distance on the ground is 5 centimeters x 100,000 = 500,000 centimeters or 5 kilometers.
2. Employing a Map Scale Bar:
- Map Scale Bar: Many maps feature a scale bar, a visual representation of distance on the map corresponding to a specific distance on the ground.
- Direct Comparison: To determine the distance between two points, simply align the scale bar with the distance on the map and read the corresponding real-world distance from the scale bar.
3. Utilizing Online Tools and Software:
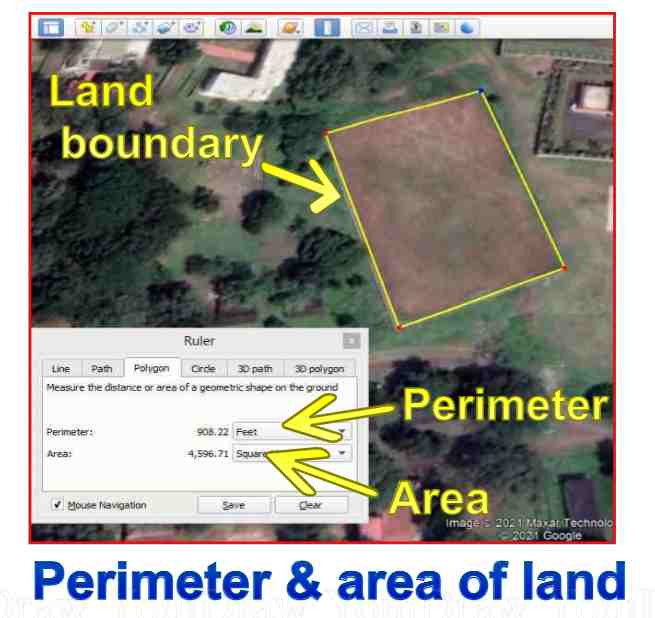
- Digital Maps and GIS: Online mapping services like Google Maps and specialized Geographic Information System (GIS) software offer sophisticated tools for distance calculations.
- Measurement Tools: These tools allow users to draw lines or shapes on the map and obtain precise distance measurements, often accompanied by additional information such as elevation changes and travel time.
Calculating Areas from Maps
Determining areas from maps requires a slightly more involved approach:
1. Grid Method:
- Dividing the Area: This method involves dividing the area on the map into smaller squares or rectangles using a grid overlay.
- Area Calculation: Calculate the area of each individual square or rectangle using the map’s scale and then sum up the areas of all the squares or rectangles to obtain the total area.
2. Planimeter Method:
- Mechanical Device: A planimeter is a mechanical instrument used to measure areas on maps and other drawings.
- Tracing the Boundary: The planimeter’s tracing arm is moved along the boundary of the area to be measured, and the instrument automatically calculates the area.
3. Digital Tools:
- GIS Software: GIS software provides powerful tools for area calculations, allowing users to define areas using polygons or other shapes and obtain precise area measurements.
- Online Mapping Services: Some online mapping services offer tools to calculate the area enclosed within a drawn shape, facilitating quick and easy area estimations.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
The accuracy of distance and area calculations from maps depends on several factors:
- Map Scale: Smaller scales (e.g., 1:1,000,000) result in greater generalization and distortion, leading to less accurate measurements. Larger scales (e.g., 1:10,000) provide more detail and therefore more precise measurements.
- Map Projection: The specific map projection used influences the distortion of distances and shapes. Understanding the characteristics of the projection is crucial for interpreting the results.
- Measurement Method: The accuracy of different measurement methods varies. For example, using a ruler and scale may be less precise than using a planimeter or digital tools.
- Map Quality: The accuracy of the map itself plays a significant role. Maps with outdated information or errors can lead to inaccurate results.
Importance and Applications
Determining distances and areas from maps holds significant value across various fields:
- Navigation and Travel: Accurate distance calculations are essential for planning travel routes, estimating travel time, and determining fuel consumption.
- Urban Planning and Development: Measuring areas helps in planning land use, assessing the impact of development projects, and estimating population density.
- Environmental Studies: Calculating distances and areas is crucial for mapping ecosystems, monitoring deforestation, and assessing the impact of environmental changes.
- Resource Management: Determining areas is vital for managing natural resources, such as forests, fisheries, and water resources.
- Historical Research: Analyzing maps from different historical periods can provide insights into changes in land use, population distribution, and other historical trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most accurate method for determining distances and areas from maps?
The most accurate methods for determining distances and areas from maps typically involve using digital tools, such as GIS software and online mapping services. These tools offer precise measurements and the ability to work with high-resolution maps, minimizing errors.
2. Can I use a ruler and scale to measure distances and areas on a map with any projection?
While using a ruler and scale is a straightforward method, it is not always accurate for maps with significant distortions, especially those using non-conformal projections. For such maps, specialized tools like planimeters or digital software are recommended.
3. How can I determine the accuracy of my distance and area measurements?
The accuracy of your measurements depends on the factors mentioned earlier, including map scale, projection, measurement method, and map quality. It is crucial to consider these factors and use appropriate tools to minimize errors.
4. Are there any free online tools for calculating distances and areas from maps?
Yes, several free online tools are available for distance and area calculations. Google Maps, for instance, offers a simple measurement tool, while other online mapping services provide more advanced features.
5. How can I improve the accuracy of my distance and area measurements from maps?
To enhance the accuracy of your measurements, use high-resolution maps with appropriate scales and projections. Employ precise measurement tools, such as planimeters or digital software, and consider the potential for distortion in the map projection.
Tips for Accurate Distance and Area Measurements
- Use a Map with an Appropriate Scale: Choose a map scale that provides sufficient detail for your needs.
- Understand the Map Projection: Familiarize yourself with the map projection and its inherent distortions.
- Employ Precise Measurement Tools: Utilize rulers, planimeters, or digital software for accurate measurements.
- Double-Check Your Results: Verify your measurements by using multiple methods or comparing them to known distances and areas.
- Consider the Map’s Accuracy: Be aware of potential inaccuracies in the map itself, such as outdated information or errors.
Conclusion
Determining distances and areas from maps is a valuable skill with applications across various fields. By understanding the principles of scale, map projections, and various measurement methods, individuals can extract accurate information from maps to support informed decision-making in navigation, planning, resource management, and other endeavors. As technology continues to advance, digital tools are becoming increasingly powerful and accessible for distance and area calculations, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/85210081-58b5973d5f9b58604675bafc.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Determining Distance and Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
