Determining the Scale of a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Determining the Scale of a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Determining the Scale of a Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Determining the Scale of a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
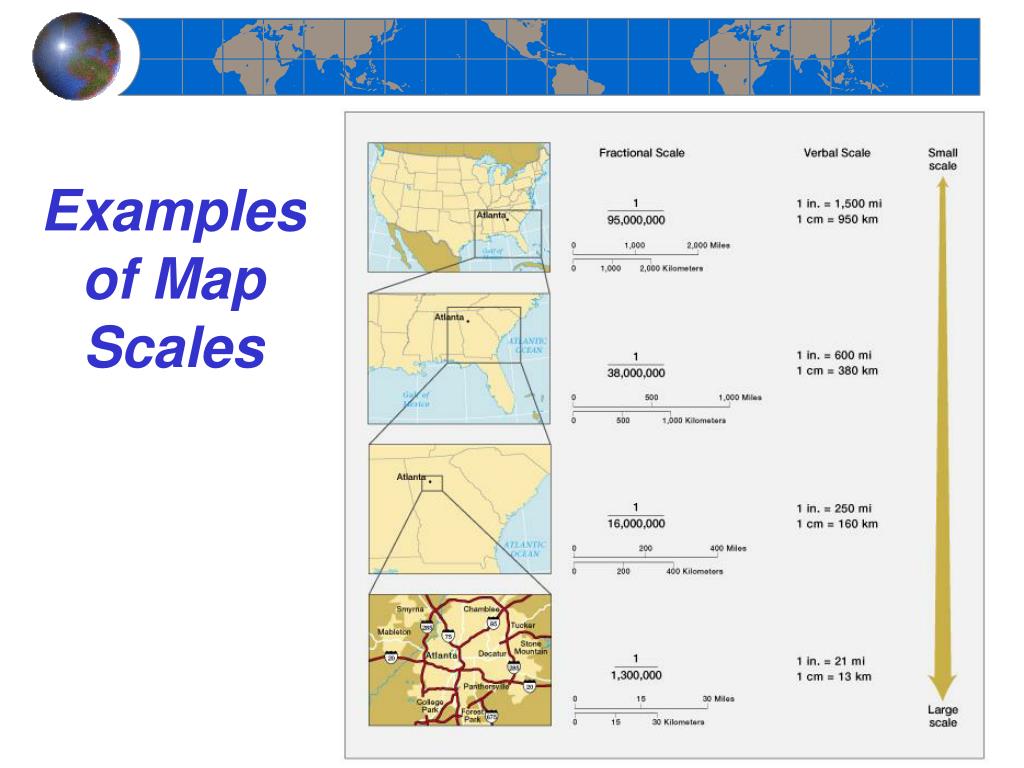
Maps are powerful tools that allow us to visualize and understand the world around us. They shrink vast distances and complex terrains into manageable representations, enabling us to navigate, plan journeys, and comprehend spatial relationships. However, the accuracy and usefulness of a map depend critically on its scale – the ratio that connects distances on the map to their corresponding distances in the real world.
Determining the scale of a map is essential for various purposes, including:
- Accurate Distance Measurement: Knowing the scale allows users to calculate real-world distances between locations directly from the map.
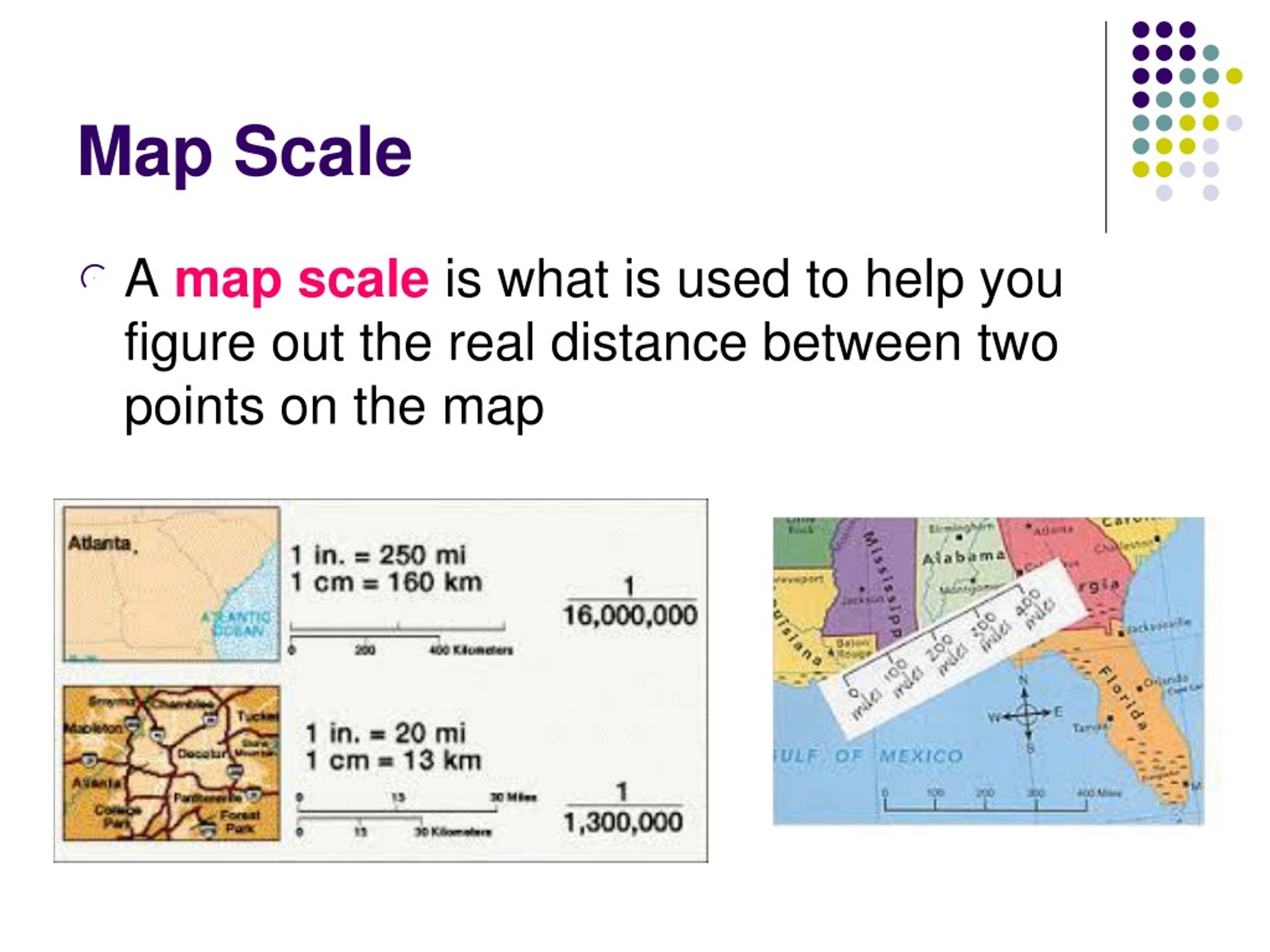
- Understanding Map Detail: A larger scale (e.g., 1:10,000) indicates more detail and finer features than a smaller scale (e.g., 1:100,000).
- Comparing Maps: Different maps of the same area might use varying scales, impacting the level of detail and the appearance of features.
Understanding Map Scales
Map scales are typically expressed in three primary forms:
- Verbal Scale: This expresses the relationship between map distance and real-world distance in words, such as "1 centimeter equals 1 kilometer."
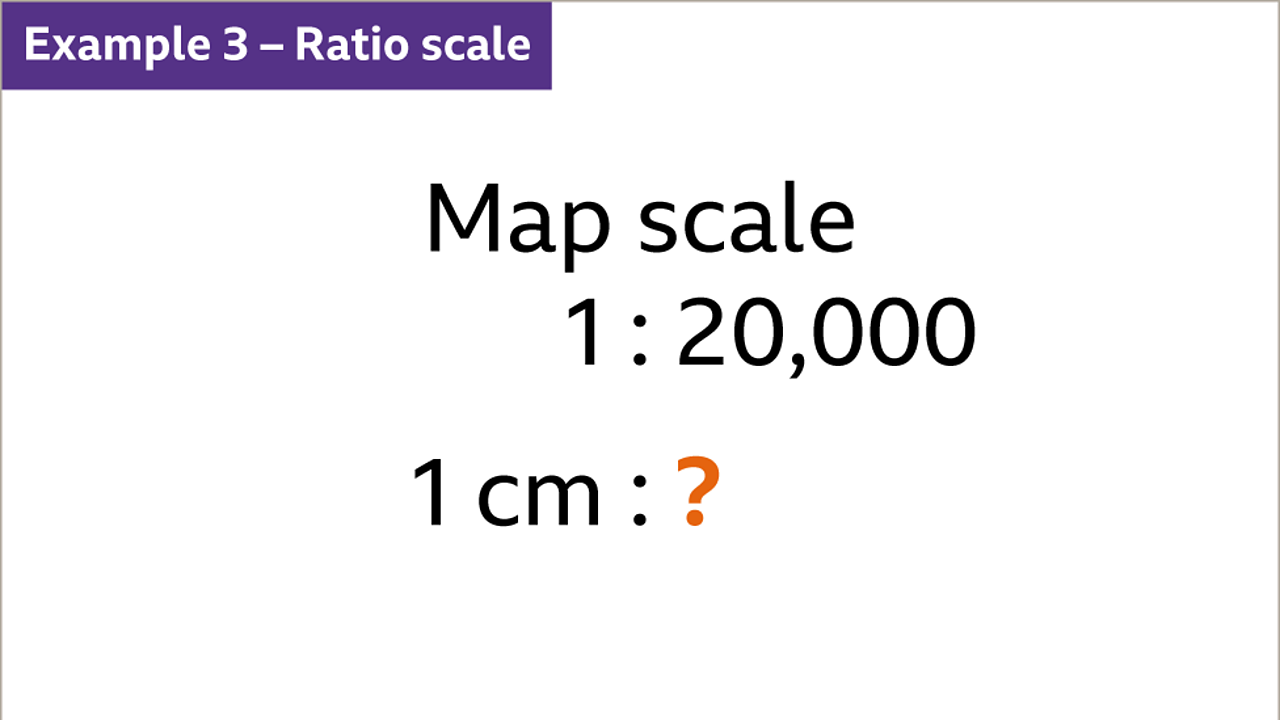
- Representative Fraction (RF): This is a ratio representing the map distance to the corresponding real-world distance, written as 1:X, where X is a number representing the real-world distance. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 means 1 unit on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world.
- Graphic Scale: This is a visual representation of the scale using a line divided into segments representing specific distances. This allows for quick estimations of distances directly on the map.
Calculating the Scale of a Map
To determine the scale of a map, you need two pieces of information:
- A measured distance on the map: This can be any identifiable feature on the map, such as a road, river, or border.
- The corresponding real-world distance: This can be obtained from reliable sources like atlases, online mapping tools, or GPS measurements.
Once you have these two pieces of information, you can calculate the scale using the following steps:
- Convert both distances to the same units: Ensure that the map distance and real-world distance are expressed in the same unit (e.g., centimeters, meters, miles).
- Divide the real-world distance by the map distance: This will give you the representative fraction (RF) of the map.
- Express the RF in a clear and concise way: You can use the standard 1:X format or convert it to a verbal scale.
Example
Let’s say you measure a road on a map to be 4.2 inches long. You know that the actual distance of this road is 21 miles. To determine the map scale:
- Convert distances to the same units: 21 miles is equal to 33,792 inches (21 miles x 63,360 inches/mile).
- Divide the real-world distance by the map distance: 33,792 inches / 4.2 inches = 8,046.
- Express the RF: The scale of the map is 1:8,046. This means 1 inch on the map represents 8,046 inches (or 0.128 miles) in the real world.
FAQs
-
Q: What are the common scales used in maps?
- A: Common map scales vary depending on the purpose of the map. Large-scale maps (1:10,000 or larger) are used for detailed city plans or local areas. Medium-scale maps (1:100,000 to 1:1,000,000) are suitable for regional planning or national parks. Small-scale maps (1:1,000,000 or smaller) are often used for world maps or global overviews.
-
Q: How can I determine the real-world distance from a map?
-
A: You can use a variety of resources to find the real-world distance, including:
- Online mapping tools: Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap offer distance measurement tools.
- Atlases: Many atlases include scale bars or detailed distance information.
- GPS devices: These can provide accurate measurements of distances between points.
-
A: You can use a variety of resources to find the real-world distance, including:
-
Q: Can I change the scale of a map?
- A: While you cannot directly change the scale of a printed map, you can use scaling software or online tools to create a new map with a different scale based on the original data.
Tips
- Use a ruler or measuring tape for accurate map distance measurements.
- Double-check the units of measurement for both map distance and real-world distance.
- Always refer to reliable sources for real-world distances.
- Consider the purpose of the map and choose a scale that is appropriate for your needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the scale of a map is crucial for extracting meaningful information and making accurate interpretations. By using the methods described above, you can confidently determine the scale of any map and apply it to measure distances, compare different maps, and make informed decisions based on the spatial relationships depicted.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Determining the Scale of a Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!

