Mapping the World: Three Ways to Express Scale
Related Articles: Mapping the World: Three Ways to Express Scale
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the World: Three Ways to Express Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the World: Three Ways to Express Scale

Maps are powerful tools, offering a visual representation of our world, condensed and accessible. They allow us to understand spatial relationships, navigate unfamiliar terrain, and glean insights into the distribution of natural and human phenomena. However, to accurately interpret a map and derive meaningful information from it, understanding its scale is paramount. Scale, in cartography, refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the Earth’s surface. This ratio, crucial for accurately depicting the real world on a map, can be expressed in three primary ways:
1. Verbal Scale:
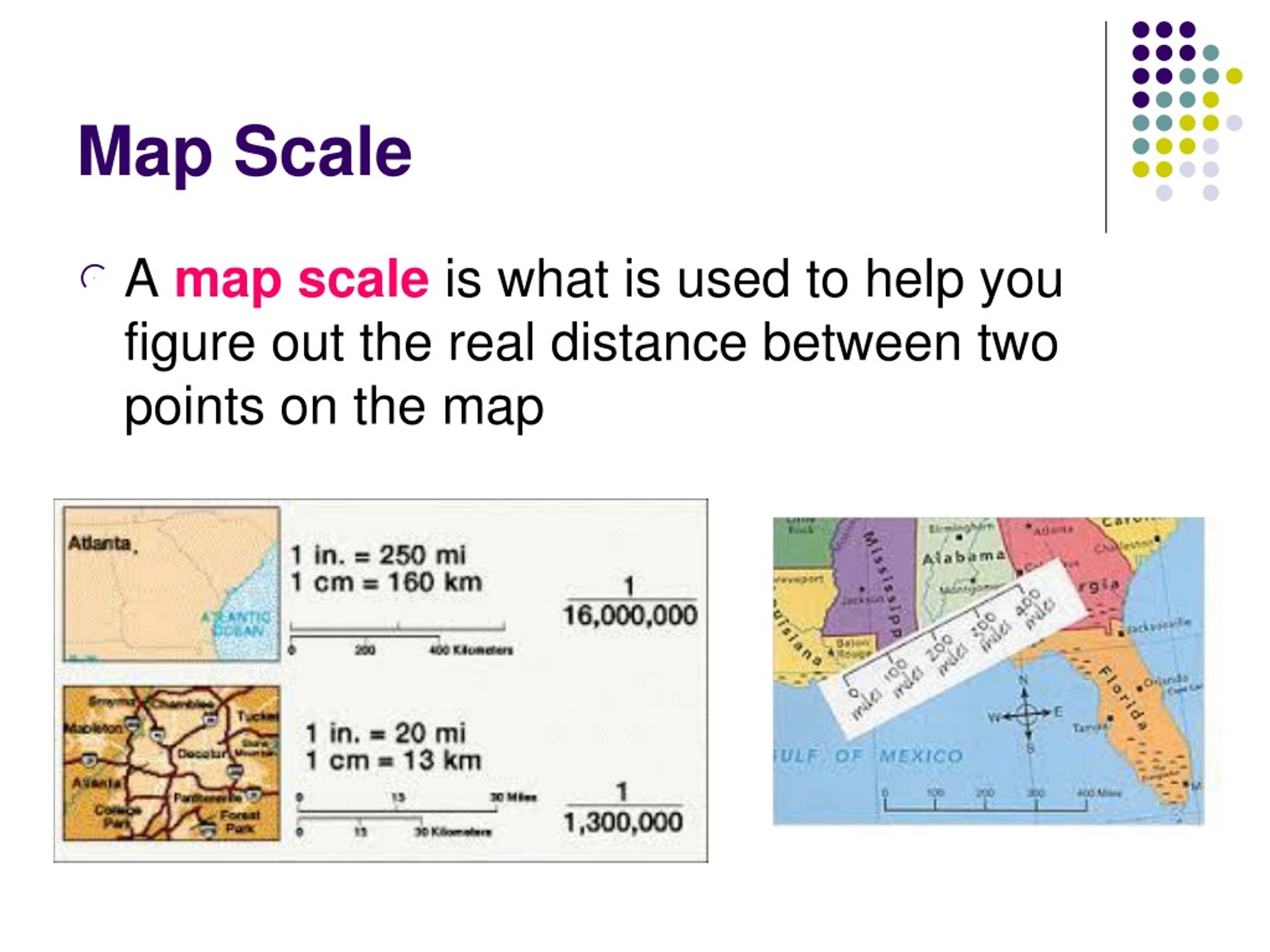
The verbal scale, often the most intuitive for the general public, expresses the relationship between map distance and real-world distance in words. This method typically utilizes a phrase like "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers," or "1 inch equals 10 miles." This straightforward statement clearly conveys the proportional relationship between map and reality.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: The verbal scale is easily understood by individuals without prior cartographic knowledge. Its clear, direct language makes it accessible and user-friendly.
- Flexibility: This method allows for a wide range of scales to be expressed easily, making it adaptable to various map types and purposes.
2. Representative Fraction (RF):
The representative fraction, often denoted as a ratio, presents the scale in a more mathematically precise manner. It expresses the relationship between map distance and real-world distance as a fraction, where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the corresponding distance on the Earth’s surface. For example, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
Benefits:
- Precision: The RF offers a more precise and unambiguous representation of the scale compared to the verbal scale. It eliminates any ambiguity associated with language variations.
- Mathematical Clarity: The fractional representation facilitates calculations and allows for easy conversion between different units of measurement.
3. Graphic Scale:
The graphic scale, also known as a bar scale, utilizes a visual representation to depict the scale. It typically consists of a line divided into segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground. This visual representation allows users to directly measure distances on the map and correlate them with real-world distances.
Benefits:
- Visual Clarity: The graphic scale provides an immediate and intuitive understanding of the map’s scale. It allows users to visually assess distances without needing to refer to numerical values.
- Independence from Units: Unlike verbal or fractional scales, the graphic scale remains accurate regardless of the units of measurement used on the map.
Understanding the Importance of Scale:
The accurate depiction of scale is crucial for several reasons. It allows for:
- Accurate Measurement: Scale enables users to measure distances, areas, and other spatial properties on a map and accurately correlate them to real-world values.
- Accurate Representation: Scale ensures that the map accurately reflects the relative sizes and shapes of geographic features, preventing distortions and misinterpretations.
- Comparison and Analysis: Maps with consistent scales enable the comparison of different areas and features, facilitating spatial analysis and understanding of geographic relationships.
- Navigation and Planning: Accurate scale is essential for navigation and planning, allowing users to determine distances, routes, and travel times.
FAQs:
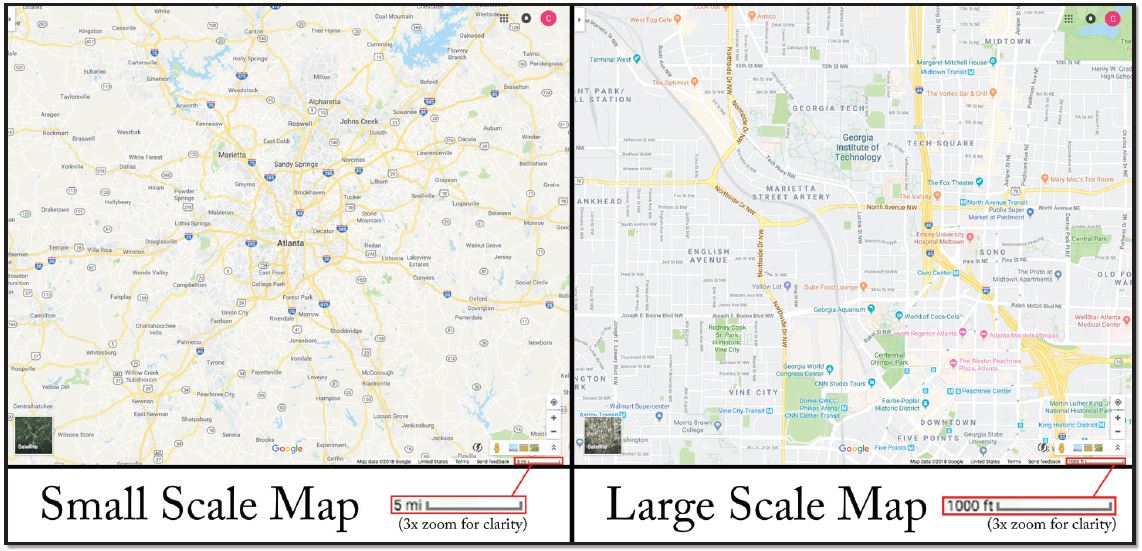
Q: What is the difference between a large scale and a small scale map?
A: A large-scale map portrays a smaller area in greater detail, using a larger ratio (e.g., 1:10,000). Conversely, a small-scale map represents a larger area with less detail, utilizing a smaller ratio (e.g., 1:10,000,000).
Q: Why is it important to understand the scale of a map?
A: Understanding the scale allows you to interpret the map accurately. It helps you determine the distance between locations, the size of features, and the level of detail provided.
Q: Can a map have multiple scales?
A: Yes, some maps may employ multiple scales to represent different aspects of the same area. For instance, a map depicting a city might use a larger scale for the city center and a smaller scale for its surrounding suburbs.
Tips:
- Always check the scale before using a map. Ensure that the scale is appropriate for your intended use.
- Pay attention to the units of measurement used on the map. Ensure that you understand the relationship between the units on the map and the units in the real world.
- Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure distances on the map. This will help you to accurately determine distances in the real world.
- Consider the purpose of the map when interpreting its scale. Different scales are suitable for different purposes. For example, a map designed for navigation will likely have a larger scale than a map designed to show the distribution of population.
Conclusion:
The accurate representation of scale is fundamental to the effectiveness and usefulness of maps. By understanding the different ways in which scale can be expressed, users can confidently interpret map information, make accurate measurements, and gain valuable insights from these visual representations of our world. Whether expressed verbally, as a representative fraction, or through a graphic scale, scale remains an essential element in the language of cartography, ensuring that maps effectively convey the complexities of our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the World: Three Ways to Express Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
