Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of map
- 3.2 Delving Deeper: Implementation and Usage
- 3.3 Practical Applications: Real-World Scenarios
- 3.4 FAQs about map Function in C++
- 3.5 Tips for Using map Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++
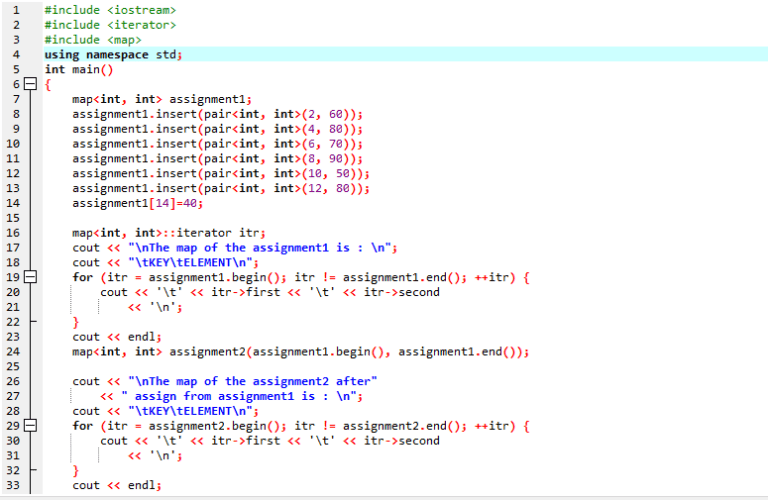
The map function in C++ is a powerful tool for developers, offering a highly efficient and organized way to store and access data. It provides a unique blend of functionality, seamlessly integrating the concepts of key-value pairs, ordered storage, and search capabilities, making it an indispensable component of many C++ applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the map function, exploring its core features, implementation details, and practical applications.
Understanding the Essence of map
At its core, the map function in C++ operates as an associative container. This means it stores elements in the form of key-value pairs, where each key is associated with a specific value. The key plays a crucial role in organizing the data within the map, ensuring efficient retrieval and manipulation.
Key Features of the map Function:
-
Ordered Storage: Unlike other containers like
vectororlist, themapfunction maintains a sorted order of its elements based on the keys. This inherent ordering simplifies searching and iteration, allowing for efficient access to desired data. -
Unique Keys: Each key within a
mapmust be unique. This constraint guarantees that there is a one-to-one relationship between keys and their corresponding values, facilitating unambiguous data retrieval. -
Efficient Search and Retrieval: The ordered nature of the
mapallows for logarithmic time complexity for search operations, making it highly efficient for retrieving specific values based on their associated keys. -
Dynamic Resizing: The
mapcontainer automatically resizes as needed to accommodate new elements, eliminating the need for manual memory management and ensuring optimal performance.
Delving Deeper: Implementation and Usage
The map function is implemented using a balanced binary search tree (BST) data structure, typically a red-black tree. This underlying structure ensures efficient insertion, deletion, and search operations, making it a suitable choice for applications requiring fast data access.
Key Operations and Functionality:
-
Insertion: To add a new key-value pair to a
map, theinsert()function is used. It takes a pair containing the key and its associated value as input. -
Retrieval: Accessing the value associated with a specific key is achieved using the
operator[]or theat()function. Both methods allow retrieval based on the key, providing a convenient way to access stored information. -
Deletion: Removing a key-value pair from the
mapis done using theerase()function. It accepts either a key or an iterator pointing to the element to be removed. -
Iteration: The
mapfunction allows for easy iteration over its elements using iterators. These iterators provide a sequential traversal of the key-value pairs, enabling efficient processing of the stored data.
Practical Applications: Real-World Scenarios
The map function finds widespread application in various programming scenarios, demonstrating its versatility and efficiency:
-
Storing and Retrieving Configuration Data: The
mapcan effectively store application configuration settings, allowing for easy access and modification of key parameters. Each key can represent a configuration option, and the associated value holds its corresponding setting. -
Implementing Dictionaries and Hash Tables: The key-value pair structure of the
mapmakes it ideal for implementing dictionaries and hash tables, allowing for fast lookup of data based on specific keys. -
Managing Game Data: In game development, the
mapcan store game objects, player attributes, and other relevant data, enabling efficient access and manipulation of game state information. -
Creating Symbol Tables: The
mapfunction can be used to create symbol tables, which map identifiers to their corresponding values or addresses, facilitating efficient code compilation and execution.
FAQs about map Function in C++
Q1: What is the difference between map and unordered_map?
A1: The map container maintains a sorted order of elements based on the keys, while the unordered_map uses a hash table for storage, providing faster average access times but sacrificing sorted order.
Q2: Can I use custom data types as keys in a map?
A2: Yes, you can use custom data types as keys in a map, but you need to define a comparison operator (operator <) for the custom type to ensure that the map can maintain its sorted order.
Q3: How do I handle collisions in a map?
A3: The map function internally handles collisions using a balanced BST, ensuring efficient resolution without requiring explicit collision handling from the user.
Q4: What are the time complexities of different operations on a map?
A4: The time complexities for typical operations on a map are as follows:
- Insertion: O(log n)
- Deletion: O(log n)
- Search: O(log n)
- Iteration: O(n)
Q5: When should I use a map over other container types?
A5: Use a map when you need efficient key-based access, sorted storage, and the ability to handle unique keys. If you require faster average access times and don’t need sorted order, consider using unordered_map.
Tips for Using map Effectively
-
Choose appropriate key types: Select keys that are suitable for comparison and ordering, ensuring efficient search and retrieval operations.
-
Use iterators for efficient traversal: Iterators provide a convenient and efficient way to process the elements of a
map, enabling you to access and modify data as needed. -
Consider using
unordered_mapfor specific scenarios: If you prioritize faster average access times and don’t need sorted order,unordered_mapcan offer better performance. -
Leverage the
map‘s functionalities: Explore the various operations provided by themapfunction, includinginsert(),erase(),find(),count(), andat(), to optimize your code and enhance its readability.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map
The map function in C++ is a powerful tool for developers, offering a highly efficient and organized way to store and access data. Its ordered storage, unique keys, and efficient search capabilities make it a valuable asset for various programming tasks. By understanding its core features, implementation details, and practical applications, developers can leverage the power of the map function to create robust, efficient, and well-organized C++ applications.
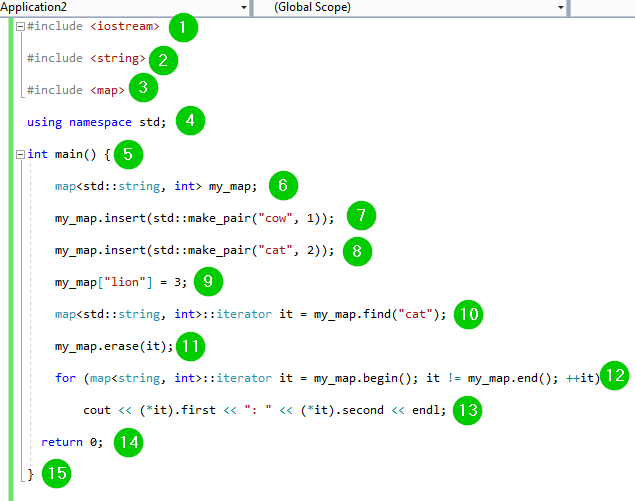






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to the map Function in C++. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
