Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Radius Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Radius Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Radius Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Radius Maps
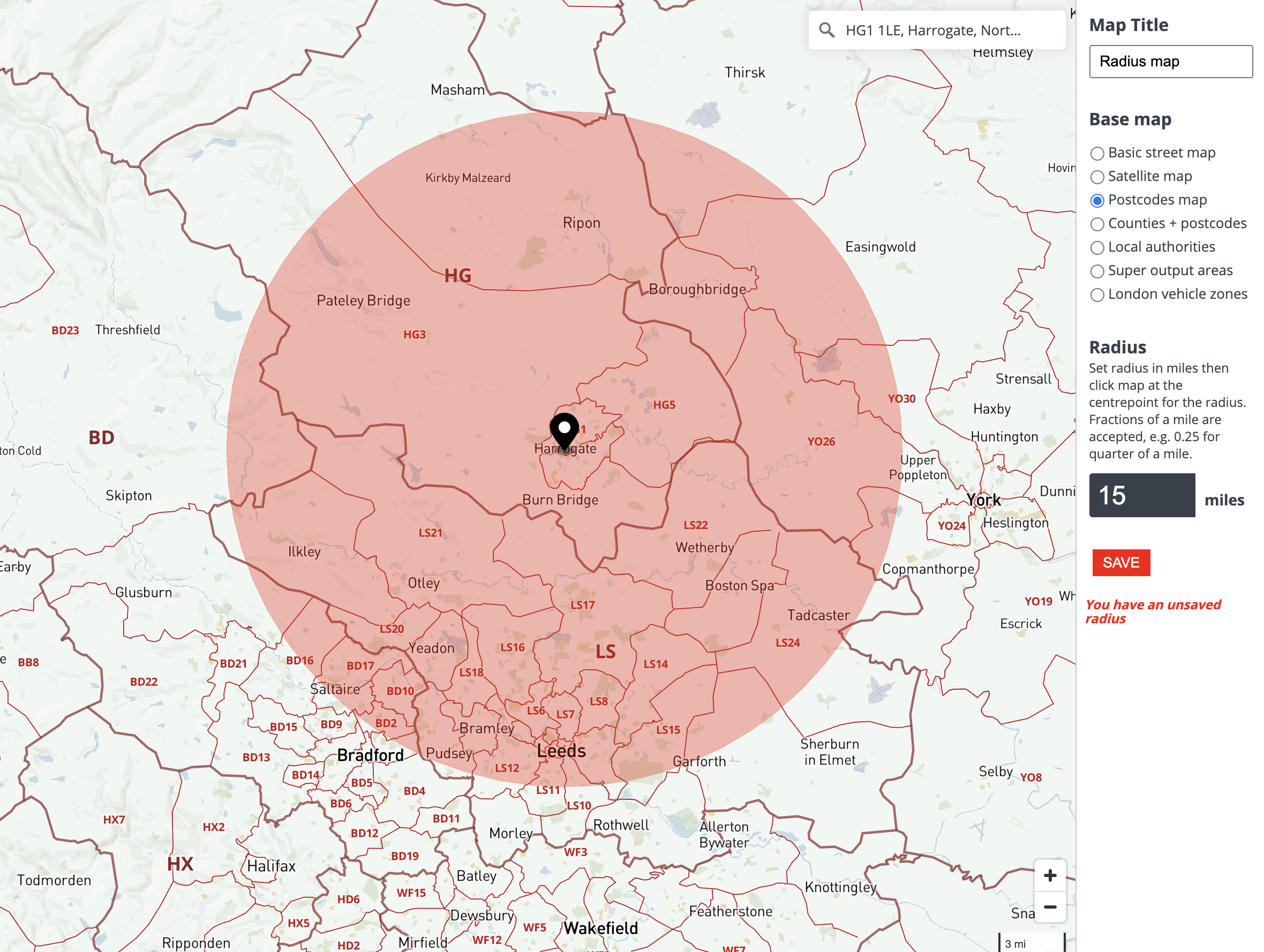
Interactive radius maps have emerged as indispensable tools in a variety of fields, offering a powerful way to visualize and analyze spatial data. These maps allow users to explore the world around a specific point, revealing a range of information within a defined radius. This capability has revolutionized decision-making in industries ranging from retail and logistics to healthcare and urban planning.
Understanding the Concept of Radius Maps
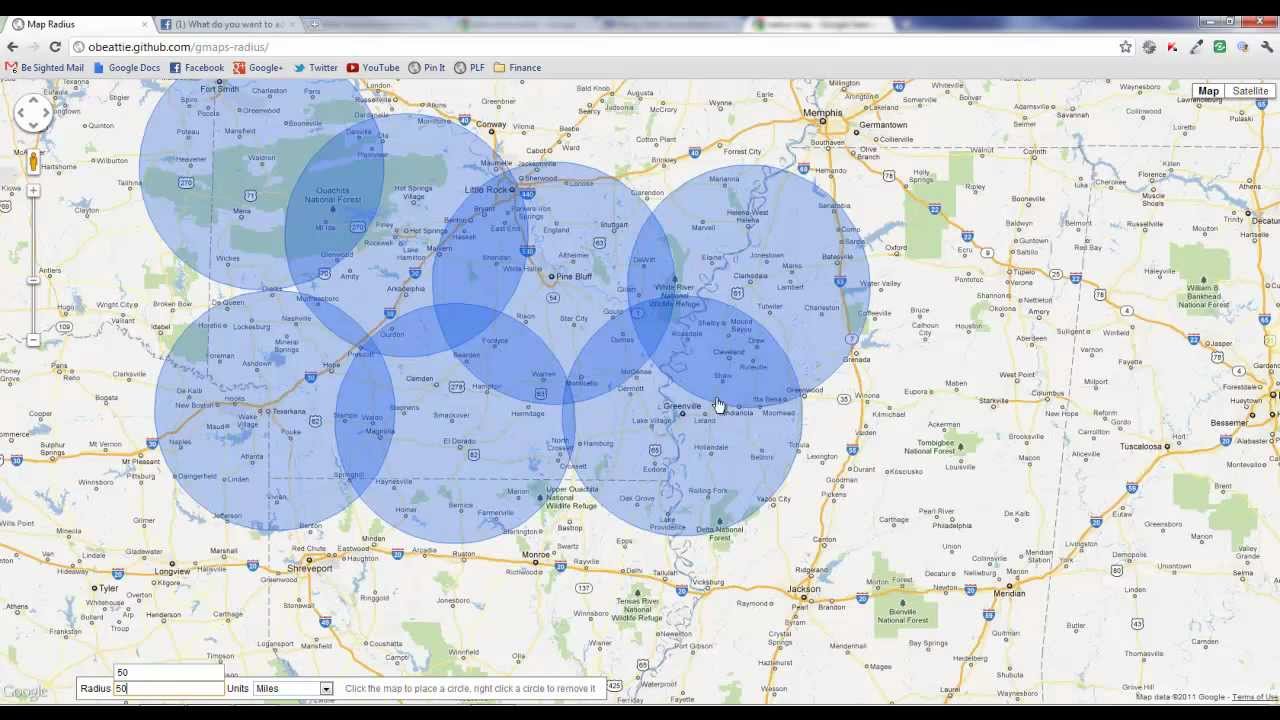
At its core, a radius map is a visual representation of a defined area surrounding a central point. This area, known as the radius, can be adjusted by the user to encompass a specific distance. The map itself can be customized to display various data layers, including demographic information, business locations, traffic patterns, or even environmental data.
Key Features of Interactive Radius Maps
Interactive radius maps offer a wealth of features that enhance their utility and make them highly versatile:
- Dynamic Radius Adjustment: Users can easily adjust the radius to explore different distances from the central point. This allows for flexible analysis and the identification of potential opportunities or challenges within varying geographic scopes.
- Data Overlays: Multiple data layers can be added to the map, providing rich contextual information. Users can visualize demographic trends alongside business locations, traffic patterns alongside environmental data, or any combination relevant to their needs.
- Data Filtering and Sorting: Users can filter and sort data displayed on the map, focusing on specific criteria. This allows for targeted analysis and the identification of key insights within the radius.
- Measurement Tools: Interactive radius maps often include measurement tools, allowing users to calculate distances, areas, and volumes within the radius. This functionality is essential for accurate planning and decision-making.
- Location Search: Users can search for specific locations within the map, pinpointing their exact position and exploring the surrounding area. This feature facilitates easy navigation and exploration.
- Visualization Options: Interactive radius maps offer various visualization options, including markers, heatmaps, polygons, and more. This flexibility allows users to choose the most effective way to represent their data visually.
- Data Export and Sharing: Many radius map tools allow users to export their data or share their map visualizations with others. This facilitates collaboration and the dissemination of findings.
Applications of Interactive Radius Maps
The applications of interactive radius maps are vast and continue to expand. Here are some prominent examples:
Retail and Marketing:
- Store Location Analysis: Retailers can use radius maps to identify ideal locations for new stores, considering factors like population density, competitor proximity, and customer demographics.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Radius maps enable businesses to target specific geographic areas with tailored marketing campaigns, reaching customers within a defined radius of their locations.
- Customer Segmentation: By overlaying demographic data, retailers can segment their customer base based on location and characteristics, allowing for more effective marketing and product development strategies.
Logistics and Transportation:
- Route Optimization: Logistics companies can use radius maps to optimize delivery routes, minimizing travel time and fuel consumption.
- Warehouse Location Analysis: Radius maps help identify optimal warehouse locations based on proximity to suppliers, customers, and transportation infrastructure.
- Traffic Management: By visualizing traffic patterns within a radius, transportation agencies can identify congestion points and implement strategies to improve traffic flow.
Healthcare:
- Patient Outreach: Healthcare providers can use radius maps to target specific geographic areas with outreach programs, ensuring access to healthcare services for underserved populations.
- Hospital Location Analysis: Radius maps help identify optimal hospital locations based on population density, accessibility, and existing healthcare infrastructure.
- Disease Surveillance: Public health officials can use radius maps to monitor disease outbreaks and track the spread of infections within defined areas.
Urban Planning:
- Land Use Planning: Urban planners can use radius maps to analyze land use patterns, identify areas for development, and assess the impact of infrastructure projects.
- Community Engagement: Radius maps facilitate community engagement by allowing residents to visualize proposed developments and provide feedback on their potential impact.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Radius maps can be used to assess the environmental impact of development projects, considering factors like air quality, water pollution, and noise levels.
Beyond Specific Industries:
Interactive radius maps also find applications in fields like:
- Real Estate: Evaluating property values, identifying potential investment opportunities, and understanding market trends within specific geographic areas.
- Education: Analyzing school district boundaries, identifying areas with high student populations, and planning school expansion projects.
- Government: Assessing the impact of policy decisions, identifying areas with high social vulnerability, and planning emergency response efforts.
Benefits of Using Interactive Radius Maps
The benefits of using interactive radius maps are numerous and contribute to their widespread adoption across various industries:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By visualizing spatial data and analyzing trends within defined areas, radius maps provide valuable insights that inform better decision-making.
- Improved Efficiency: Radius maps streamline processes by automating tasks like route optimization, location analysis, and data visualization, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Data-Driven Insights: Radius maps offer a data-driven approach to problem-solving, enabling users to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities that might not be readily apparent.
- Increased Collaboration: Radius maps facilitate collaboration by providing a shared platform for data visualization and analysis, fostering communication and understanding among stakeholders.
- Improved Communication: Radius maps present complex spatial data in an easily understandable format, enhancing communication and engagement with stakeholders.
FAQs about Interactive Radius Maps:
Q: What is the difference between a radius map and a regular map?
A: A regular map simply displays geographic features, while a radius map focuses on a specific area around a central point. Interactive radius maps go further by allowing users to adjust the radius, overlay data, and interact with the map in various ways.
Q: How can I create an interactive radius map?
A: There are various software tools and platforms available for creating interactive radius maps. Some popular options include Google Maps, ArcGIS Online, Mapbox, and Leaflet.
Q: What types of data can be used with radius maps?
A: Radius maps can be used with a wide range of data, including demographic information, business locations, traffic patterns, environmental data, crime statistics, and more.
Q: What are some limitations of radius maps?
A: Radius maps are not without limitations. They rely on accurate data, and the quality of the analysis can be affected by data inaccuracies or biases. Additionally, radius maps may not be suitable for all types of analysis, especially those requiring complex spatial relationships or multi-dimensional data.
Tips for Using Interactive Radius Maps Effectively:
- Define your objectives: Clearly define your goals for using the radius map to ensure you select the appropriate data and tools.
- Choose the right data: Select data relevant to your objectives and ensure its accuracy and reliability.
- Experiment with different radii: Adjust the radius to explore different geographic scopes and identify the most relevant insights.
- Utilize data overlays: Combine multiple data layers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area within the radius.
- Visualize data effectively: Choose the most appropriate visualization options for your data and audience.
- Share your findings: Communicate your results effectively with stakeholders to inform decision-making and promote collaboration.
Conclusion:
Interactive radius maps have become essential tools for navigating and analyzing the world around us. By visualizing spatial data within defined areas, they provide valuable insights that inform decision-making in a wide range of industries and applications. Their dynamic features, data overlay capabilities, and intuitive interface make them powerful tools for exploring, understanding, and acting upon geographic information. As technology continues to advance, interactive radius maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving informed decision-making in the years to come.
![Printable Detailed Interactive World Map With Countries [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Interactive-World-Map-Printable.jpg?6bfec1u00266bfec1)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Radius Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
