Navigating the World: Understanding Map Scale and Its Digital Applications
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Map Scale and Its Digital Applications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Map Scale and Its Digital Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Map Scale and Its Digital Applications
Maps, the silent guides of exploration, have long been instrumental in our understanding of the world. From ancient hand-drawn charts to intricate digital representations, maps provide a visual framework for navigating physical and conceptual landscapes. A crucial element in mapmaking is scale, which defines the relationship between distances on a map and their corresponding distances in reality.
Defining Map Scale:
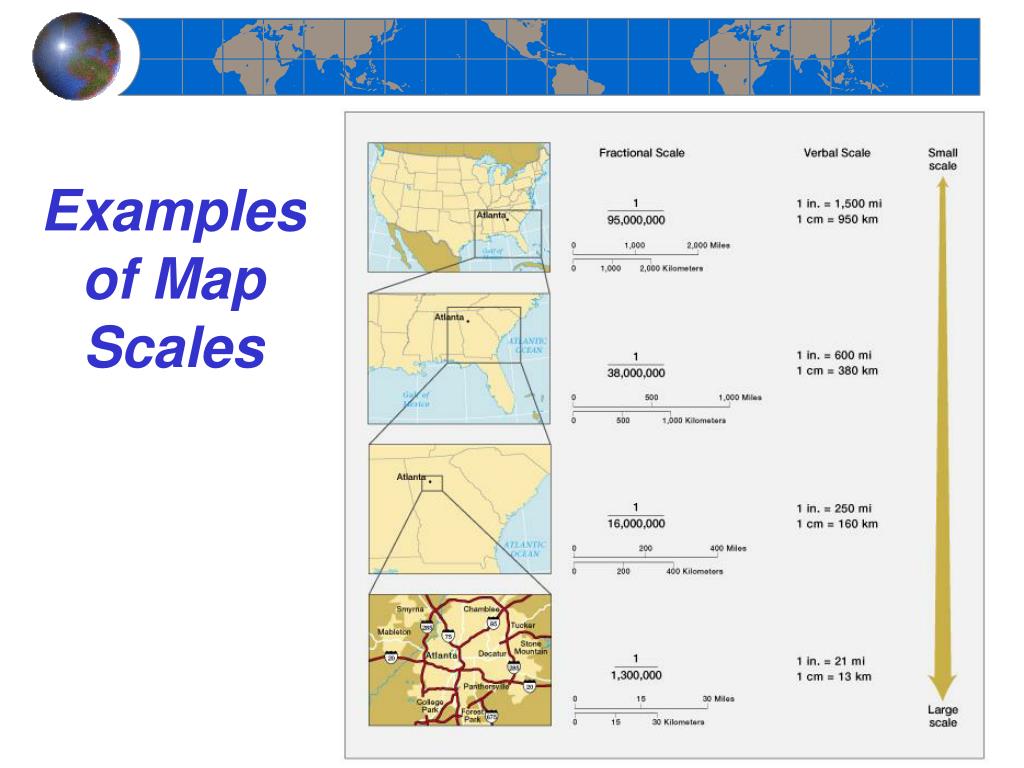
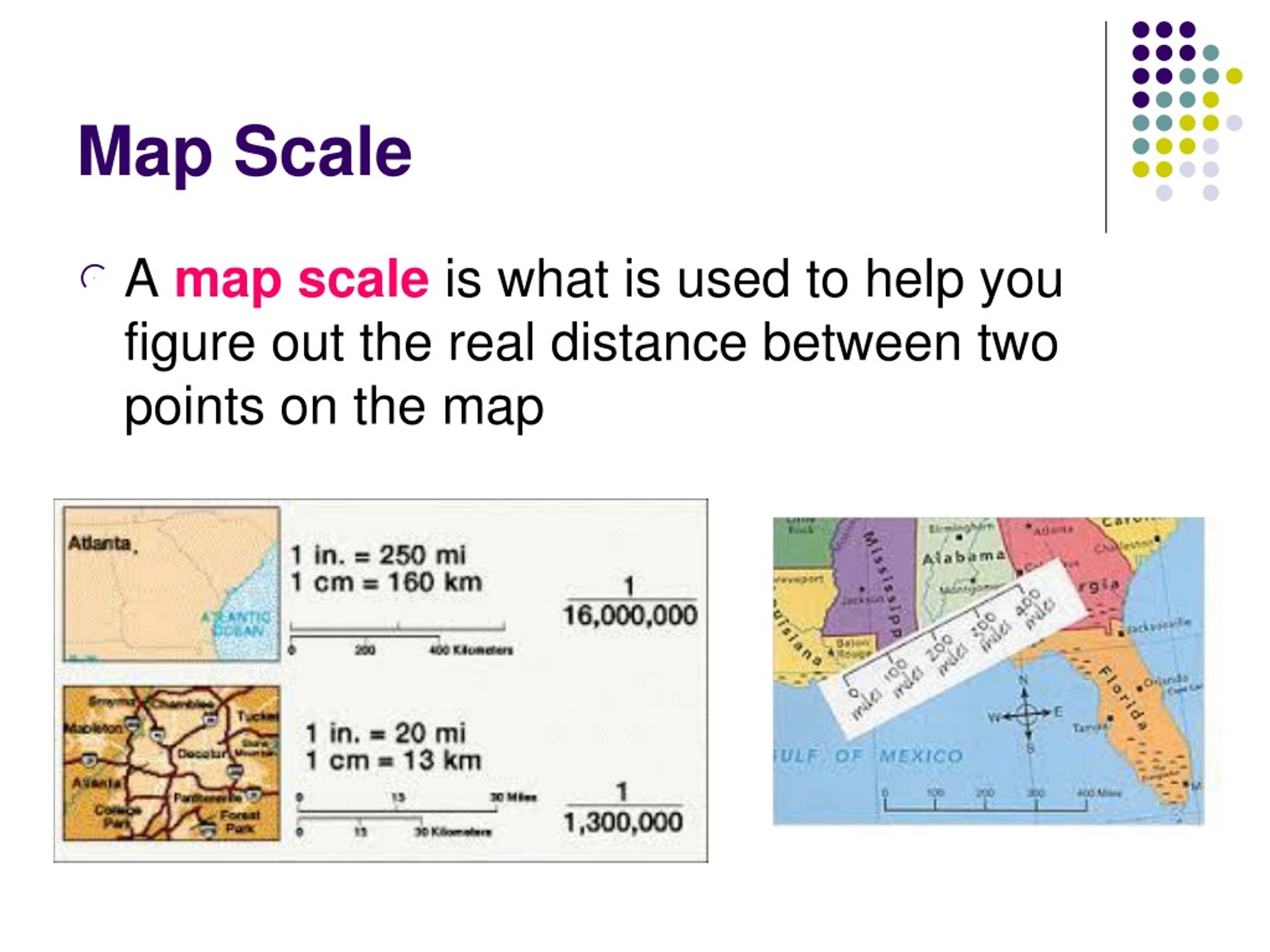
Map scale refers to the ratio that expresses the relationship between a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is typically presented in one of three ways:
- Verbal Scale: This method expresses the scale using words, such as "1 inch to 1 mile" or "1 centimeter to 10 kilometers."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This method uses a fraction, such as 1:100,000, where the numerator represents one unit on the map and the denominator represents the same unit on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: This method employs a line divided into segments representing specific distances on the ground. The line is typically labeled with corresponding units.
The Importance of Map Scale:
Understanding map scale is fundamental to interpreting and utilizing maps effectively. It allows users to:
- Accurately estimate distances: By understanding the scale, users can calculate actual distances between points on a map. This is crucial for planning routes, determining travel time, and understanding the spatial relationships between objects.
- Comprehend the relative size of features: Map scale allows for the visual representation of features at different sizes. This is essential for understanding the relative importance and prominence of various elements on the map, such as cities, rivers, or mountains.
- Analyze spatial relationships: By understanding the scale, users can analyze the spatial relationships between different features on the map. This is crucial for understanding patterns, trends, and geographic connections.
- Develop a sense of place: Scale helps users develop a visual understanding of the world and the relative size and location of different places. This is essential for forming a mental map and navigating unfamiliar environments.
Digital Applications of Map Scale:
The advent of digital mapping technologies has significantly enhanced the use and accessibility of map scale. Digital mapping platforms, such as Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and ArcGIS, leverage map scale to provide users with a range of interactive features, including:
- Dynamic Zoom: Users can easily adjust the map scale by zooming in or out, allowing for a detailed examination of specific areas or a broader overview of a region.
- Measurement Tools: Digital maps often include tools that allow users to measure distances, areas, and perimeters directly on the map. These tools rely on the underlying map scale to provide accurate measurements.
- Scale-dependent Rendering: Digital maps adjust the level of detail displayed based on the current map scale. At smaller scales, only major features are visible, while zooming in reveals increasingly detailed information.
- Data Visualization: Map scale plays a crucial role in data visualization. By adjusting the scale, users can analyze spatial patterns and trends, identifying clusters, outliers, and relationships between data points.
Challenges in Map Scale Interpretation:
While map scale is essential for understanding maps, interpreting it accurately can be challenging. Several factors can influence the perceived scale of a map, including:
- Projection Distortion: Map projections, which transform the Earth’s curved surface into a flat representation, can introduce distortions in distances and shapes. This can affect the accuracy of scale measurements.
- Map Size and Resolution: The size and resolution of a map can influence the perceived scale. A small-scale map printed on a large format may appear to have a larger scale than a large-scale map printed on a small format.
- User Experience and Perspective: The user’s experience, familiarity with the area, and individual perspective can influence how they perceive map scale.
Addressing Challenges:
To mitigate these challenges, it is crucial to:
- Understand the map projection: Familiarize oneself with the projection used for a particular map to understand the potential distortions it introduces.
- Check the scale bar: Always refer to the graphic scale bar on a map to accurately determine distances.
- Use multiple sources: Compare map scales from different sources to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Conclusion:
Map scale is an essential element in mapmaking and map interpretation. It provides a fundamental framework for understanding distances, relative sizes, and spatial relationships. As digital mapping technologies continue to evolve, map scale will remain crucial for providing accurate and informative representations of the world. By understanding the principles of map scale, users can navigate the world with greater precision and insight.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map represents a smaller area with greater detail. It has a larger denominator in the representative fraction (e.g., 1:10,000). A small-scale map represents a larger area with less detail. It has a smaller denominator in the representative fraction (e.g., 1:1,000,000).
Q2: How can I calculate the actual distance between two points on a map?
A: Measure the distance between the two points on the map using a ruler or a measuring tool. Then, use the map’s scale to convert the measured distance into the actual distance on the ground. For example, if the distance on the map is 2 inches and the scale is 1 inch to 1 mile, then the actual distance is 2 miles.
Q3: Why is map scale important for navigation?
A: Map scale allows for accurate distance estimation, which is crucial for planning routes, determining travel time, and navigating unfamiliar environments. Understanding the scale helps users to avoid getting lost and to make informed decisions about their travel plans.
Q4: How does map scale affect data visualization?
A: Map scale influences the level of detail displayed and the spatial relationships between data points. Adjusting the scale allows users to analyze spatial patterns, identify clusters, and understand the distribution of data across different areas.
Q5: What are some examples of map scale in everyday life?
A: Map scale is used in various everyday applications, including:
- Road maps: Road maps typically use a small scale to show a large area, allowing users to plan long journeys.
- City maps: City maps often use a larger scale to show detailed information about streets, buildings, and landmarks.
- Navigation apps: Navigation apps use dynamic map scales that adjust based on the user’s location and zoom level.
- Satellite imagery: Satellite images typically use a very small scale to capture a broad view of the Earth’s surface.
Tips:
- Always refer to the map’s scale bar: The scale bar provides a visual representation of the map scale, allowing for accurate distance estimation.
- Use online mapping tools: Online mapping platforms often include measurement tools and dynamic zoom capabilities, making it easier to interpret map scale.
- Understand the limitations of map projections: Be aware of the potential distortions introduced by map projections and how they can affect scale measurements.
- Compare scales from different sources: When using multiple maps or sources, ensure that the scales are consistent to avoid confusion.
- Practice interpreting map scale: Regularly use maps and practice interpreting map scale to improve your understanding and skills.
Conclusion:
Map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography that plays a vital role in our understanding of the world. By understanding the principles of map scale and its applications, users can navigate the world with greater accuracy, insight, and confidence. As digital mapping technologies continue to evolve, map scale will remain a crucial component in providing informative and interactive representations of our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Map Scale and Its Digital Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
