Navigating the World Within a Circle: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Tools on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World Within a Circle: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Tools on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World Within a Circle: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Tools on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World Within a Circle: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Tools on Maps
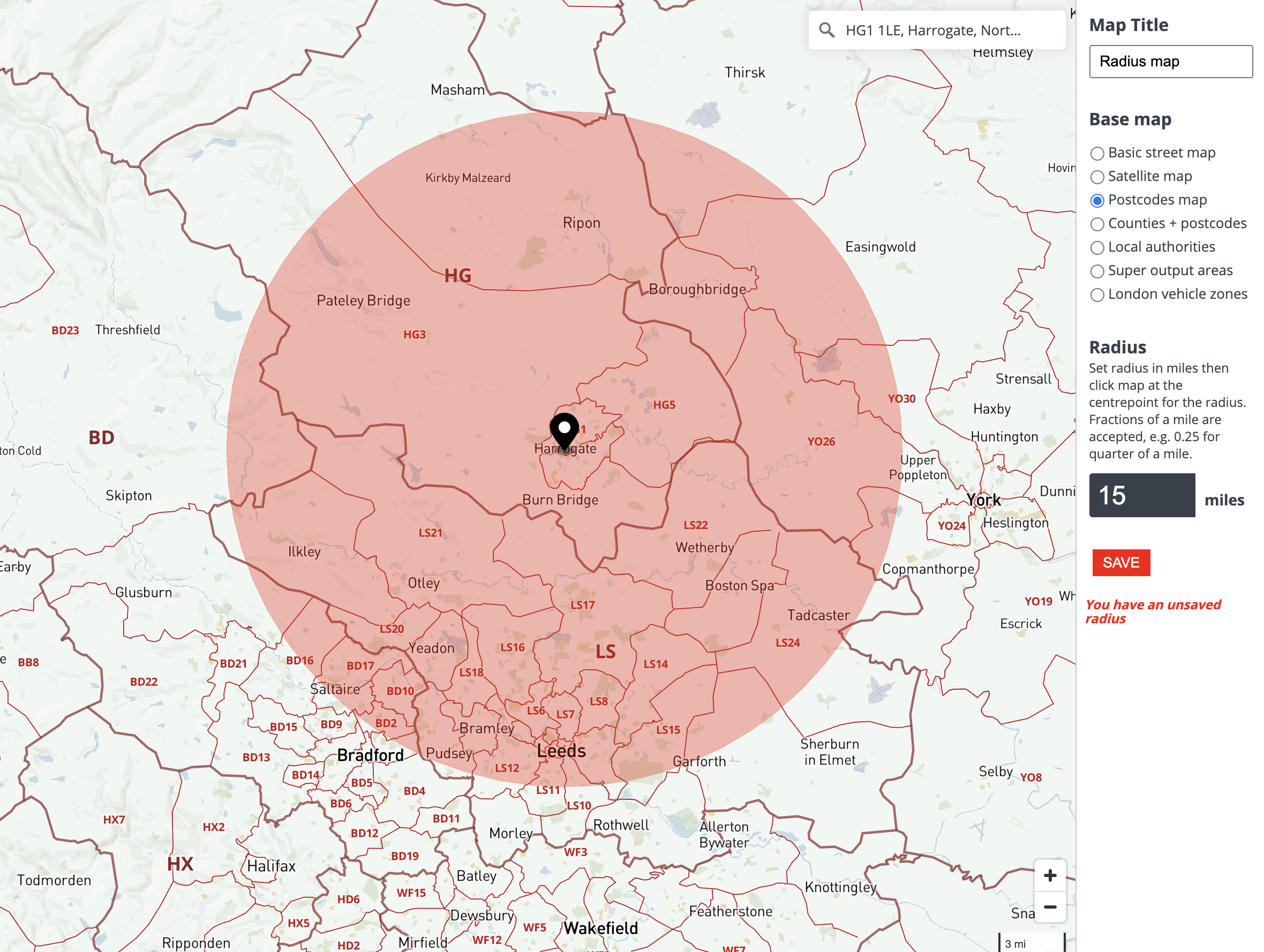
In the realm of digital cartography, the ability to visualize and analyze geographic data within defined areas is paramount. Radius tools, often referred to as "circle tools," empower users to delineate specific zones on maps, enabling them to explore and understand spatial relationships in a focused manner. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted nature of radius tools, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and applications across various fields.
Understanding the Essence of Radius Tools
At its core, a radius tool allows users to draw circles of varying sizes on a map, centered around a designated point. This seemingly simple action unlocks a wealth of possibilities, transforming a map from a static representation into an interactive platform for spatial analysis. The tool’s versatility stems from its ability to:
- Define a specific area: By drawing a circle around a point of interest, users can isolate a particular region, effectively filtering out extraneous data and focusing attention on a defined zone.
- Measure distance: The radius of the circle represents a specific distance from the center point, allowing users to assess the proximity of other locations or features.
- Visualize spatial relationships: The tool enables users to understand how features are distributed within a defined area, revealing patterns, clusters, and relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Applications Across Disciplines
The impact of radius tools extends beyond the realm of simple distance measurement, finding practical applications in a diverse array of fields:
- Real Estate: Brokers and agents can leverage radius tools to identify properties within a specific distance from desired amenities, schools, or transportation hubs. This facilitates targeted property searches and enhances client communication.
- Retail and Business: Marketing teams can utilize radius tools to analyze customer demographics within a defined radius of their stores or businesses, enabling targeted advertising campaigns and strategic location planning.
- Emergency Response: Emergency responders can utilize radius tools to delineate areas affected by natural disasters or incidents, facilitating efficient resource allocation and communication.
- Urban Planning: Planners can employ radius tools to assess the impact of proposed developments on surrounding areas, analyzing factors like traffic flow, noise pollution, and proximity to existing infrastructure.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers can use radius tools to define areas of interest for environmental monitoring, wildlife tracking, or pollution analysis.
- Logistics and Transportation: Radius tools aid in optimizing delivery routes, identifying potential hazards within specific areas, and planning efficient transportation networks.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics can utilize radius tools to identify patient populations within specific service areas, enabling targeted outreach programs and resource allocation.
Features and Functionality
Radius tools come equipped with a range of features that enhance their usability and analytical capabilities:
- Adjustable Radius: Users can easily adjust the radius of the circle, allowing for precise control over the size of the defined area.
- Multiple Circles: Many tools allow for the creation of multiple circles simultaneously, enabling comparisons between different areas or the analysis of multiple points of interest.
- Geocoding: The ability to search for specific addresses or locations and automatically center the circle on them streamlines the process of defining areas of interest.
- Data Overlay: Radius tools often integrate with data layers, allowing users to visualize data points, features, or demographics within the defined area, providing valuable insights into spatial relationships.
- Measurement Tools: Some tools offer integrated distance and area measurement capabilities, providing precise information about the defined zone.
- Export and Sharing: The ability to export results as images, reports, or data files facilitates communication and collaboration.
Benefits of Utilizing Radius Tools
The implementation of radius tools in various fields yields numerous benefits, enhancing decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering a deeper understanding of spatial relationships:
- Targeted Analysis: By focusing on specific areas, users can gain deeper insights into localized patterns, trends, and relationships that might go unnoticed in broader geographic contexts.
- Improved Efficiency: Radius tools streamline the process of identifying relevant information and data, saving time and effort compared to manual analysis methods.
- Enhanced Communication: The ability to visualize data within defined areas facilitates clear communication of complex spatial information to stakeholders, promoting informed decision-making.
- Data-Driven Insights: Radius tools enable users to analyze data in a spatial context, leading to data-driven insights that inform strategic planning and decision-making.
- Increased Accuracy: Precise measurement tools within radius tools ensure accurate analysis and reporting, minimizing errors and promoting reliable results.
FAQs Regarding Radius Tools
Q: What are the limitations of radius tools?
A: While radius tools offer significant advantages, they are not without limitations. One notable limitation is the assumption of a circular shape, which may not always accurately represent real-world scenarios. Additionally, the reliance on geographic data accuracy can influence the reliability of results.
Q: How do I choose the right radius tool for my needs?
A: The choice of radius tool depends on specific requirements and functionalities. Factors to consider include the platform (web-based, desktop, or mobile), data integration capabilities, measurement tools, and the level of customization offered.
Q: What are some best practices for using radius tools effectively?
A: To maximize the benefits of radius tools, users should:
- Clearly define the purpose of the analysis: Establish specific research questions or objectives to guide the selection of points of interest and the appropriate radius size.
- Ensure data accuracy: Utilize reliable data sources and verify the accuracy of geographic information.
- Consider the scale of analysis: Select the appropriate radius size based on the scale of the study area and the desired level of detail.
- Explore different radius sizes: Experiment with varying radii to uncover potential patterns and insights that might not be apparent at a single scale.
- Interpret results carefully: Consider the limitations of the tool and the potential biases in data when drawing conclusions from the analysis.
Tips for Effective Radius Tool Implementation
- Integrate with other mapping tools: Combine radius tools with other functionalities like data visualization, layer management, and analysis tools to enhance the depth of analysis.
- Utilize real-world data: Incorporate data from various sources, such as demographic information, crime statistics, or environmental data, to enrich the analysis and gain comprehensive insights.
- Collaborate with experts: Engage with experts in relevant fields to interpret results, validate findings, and ensure the effective application of radius tools within specific contexts.
- Stay informed about advancements: Keep abreast of emerging tools and technologies that enhance radius tool functionalities and expand their applications.
Conclusion
Radius tools have emerged as indispensable instruments in the realm of digital cartography, empowering users to analyze geographic data within defined areas, fostering a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, and driving informed decision-making. By leveraging the versatility and analytical capabilities of these tools, individuals and organizations across diverse fields can unlock valuable insights, optimize resource allocation, and make informed choices that shape the world around us. As technology continues to evolve, the role of radius tools in spatial analysis is poised to expand, further enhancing our ability to navigate and understand the complex world we inhabit.


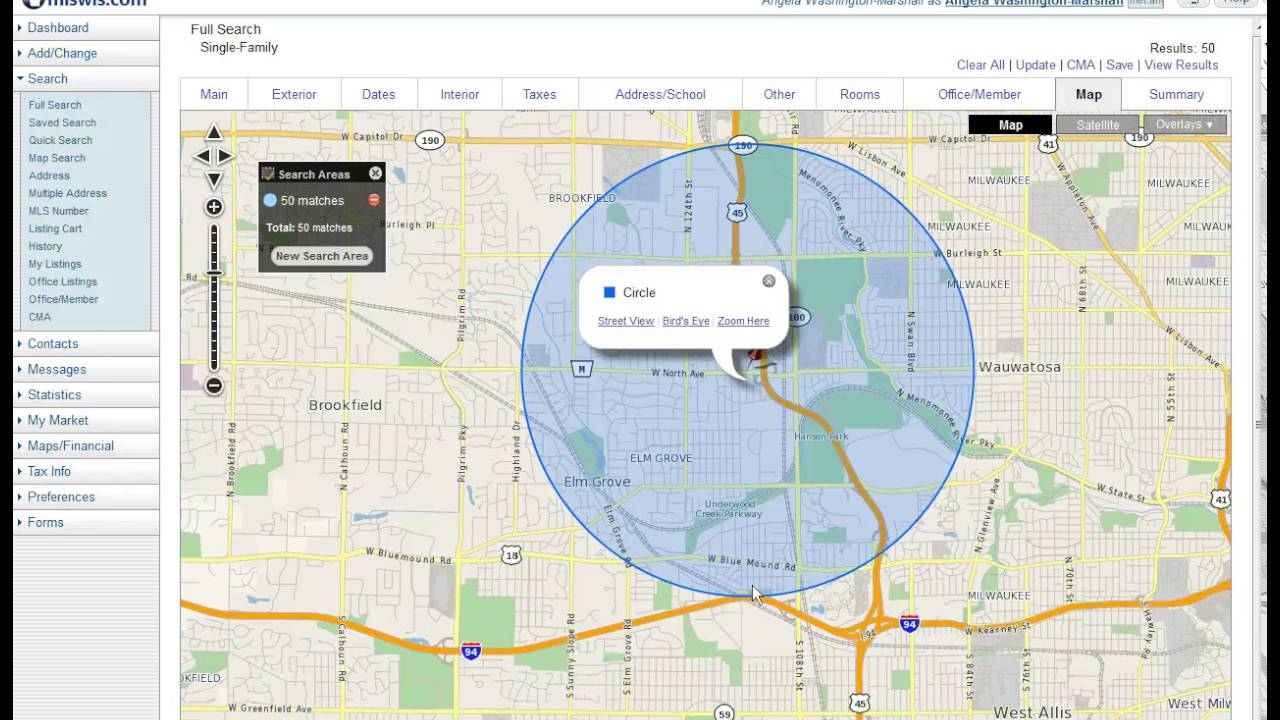


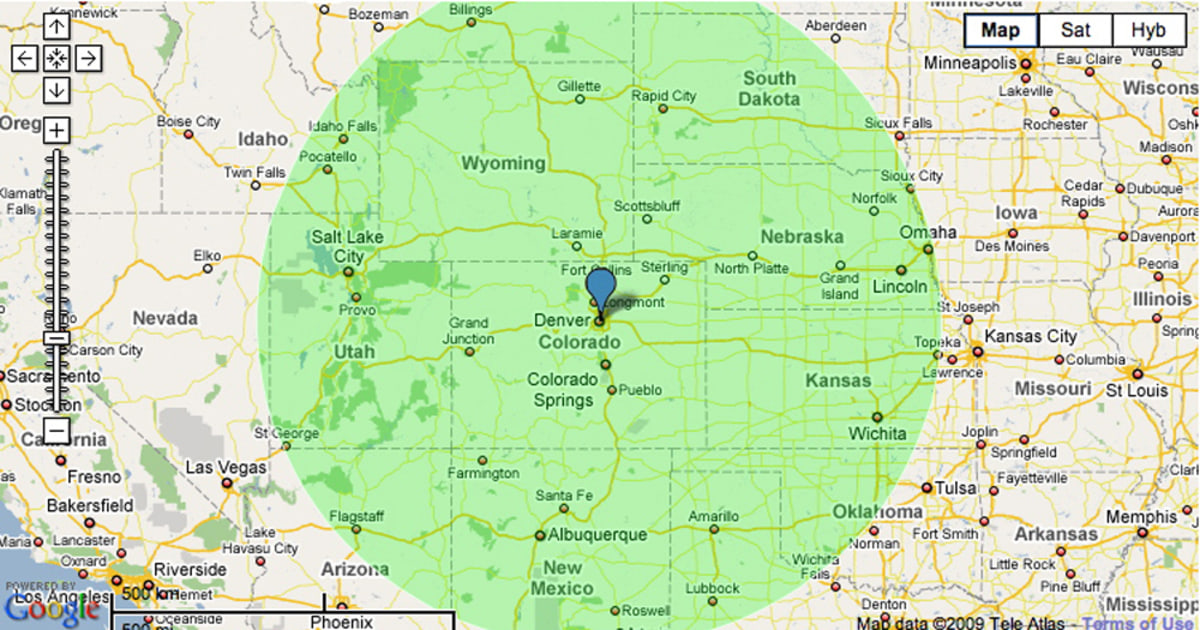
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World Within a Circle: A Comprehensive Guide to Radius Tools on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
