The Art and Science of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Creating Accurate Representations of the World
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Creating Accurate Representations of the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Creating Accurate Representations of the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Creating Accurate Representations of the World

Maps, those seemingly simple representations of our complex world, hold within them a fundamental principle: scale. This principle, often expressed as a ratio, dictates the relationship between distances on a map and their corresponding distances in reality. The ability to accurately represent this relationship is crucial for mapmakers, ensuring that maps are both informative and reliable. This article delves into the intricate world of map scale, exploring its various forms, its importance in cartography, and the tools and techniques used to create accurate representations of our planet.
Understanding the Concept of Map Scale
Map scale is the ratio that defines the relationship between a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio can be expressed in three primary ways:
1. Verbal Scale: This method expresses scale using words, typically stating the distance on the map that represents a specific distance on the ground. For example, "1 inch equals 1 mile" indicates that every inch measured on the map corresponds to one mile in reality.
2. Representative Fraction (RF): This method utilizes a fraction to express the scale, with the numerator representing the map distance and the denominator representing the corresponding ground distance. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 signifies that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
3. Graphic Scale: This method presents a visual representation of the scale using a graduated line, often labeled with specific distances. Users can directly measure distances on the map and compare them to the graphic scale to determine the corresponding ground distance.
The Importance of Map Scale in Cartography
The accuracy and usefulness of any map hinge upon the proper application of scale. A map’s scale dictates its level of detail and the extent of the area it can represent. Larger scales, such as 1:10,000, depict smaller areas with greater detail, making them suitable for urban planning or surveying. Smaller scales, such as 1:1,000,000, cover vast regions but offer less detail, proving useful for regional planning or global mapping.
Creating Accurate Map Scales: Tools and Techniques
The process of creating accurate map scales involves a combination of technology and meticulous attention to detail. Here are some key elements involved:
1. Geographic Coordinate Systems: These systems, such as the widely used Geographic Coordinate System (GCS) or Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) system, provide a framework for defining locations on Earth using latitude and longitude.
2. Projections: Maps are two-dimensional representations of a three-dimensional sphere, necessitating the use of projections to translate geographic coordinates onto a flat surface. Different projections distort distances and shapes in various ways, influencing the accuracy of the map scale.
3. Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides powerful tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing geographic data. These systems allow users to manipulate data, create maps, and define accurate scales for their representations.
4. Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): DEMs represent the terrain’s elevation data, providing crucial information for creating accurate topographic maps and ensuring the correct representation of distances and slopes.
5. Map Scale Adjustment: The process of adjusting map scale involves manipulating the size of map elements to ensure they accurately represent the corresponding ground distances. This adjustment is crucial for maintaining consistency and accuracy across different map scales.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Scale
1. What are the different types of map scales?
The three primary types of map scales are verbal, representative fraction (RF), and graphic. Each method offers a different way to express the relationship between map distances and ground distances.
2. How do I choose the appropriate map scale for my needs?
The ideal map scale depends on the intended purpose of the map. For detailed local maps, larger scales are preferred, while for regional or global maps, smaller scales are more appropriate.
3. Can map scales be changed after a map is created?
While changing the scale after creation is possible, it can introduce inaccuracies and distortions. It is generally advisable to establish the desired scale before creating the map to ensure accuracy.
4. What are the potential consequences of using an inaccurate map scale?
Inaccurate map scales can lead to misinterpretations of distances, areas, and shapes, potentially causing errors in navigation, planning, and decision-making.
5. How can I ensure the accuracy of map scales?
Using reliable data sources, employing appropriate projections, and utilizing accurate measurement tools are crucial for ensuring the accuracy of map scales.
Tips for Creating Accurate Map Scales:
1. Define the Purpose and Scope: Clearly define the intended use of the map and the area it will cover to determine the appropriate scale.
2. Choose the Right Projection: Select a projection that minimizes distortion for the specific area being mapped.
3. Utilize Reliable Data Sources: Ensure the accuracy of the data used to create the map by relying on reputable sources.
4. Employ Accurate Measurement Tools: Utilize precise tools for measuring distances and areas on the map to maintain accuracy.
5. Review and Validate: Thoroughly review the map for any inconsistencies or errors related to the scale.
Conclusion: The Significance of Map Scale in a Data-Driven World
Map scale, a seemingly simple concept, plays a pivotal role in the creation and interpretation of maps. It determines the level of detail, the extent of the area represented, and ultimately, the accuracy and usefulness of the map. In an era increasingly driven by data and information, understanding and mastering map scale remains crucial for accurate spatial analysis, effective planning, and informed decision-making. By appreciating the science behind map scale, we unlock the potential of maps to provide reliable and insightful representations of our complex world.




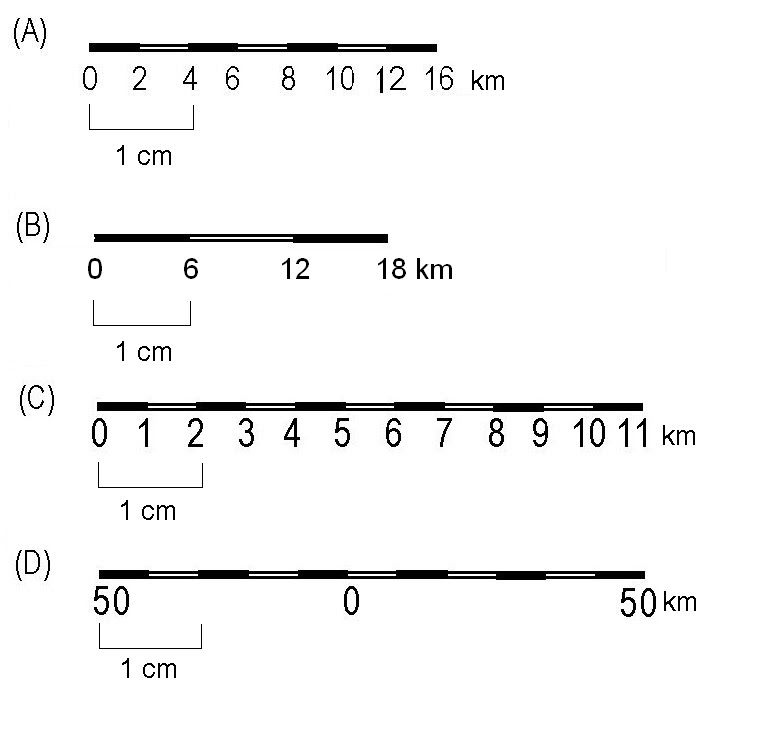
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Map Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Creating Accurate Representations of the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
