The Challenge of Representing the Earth: Understanding Accurate Scale in World Maps
Related Articles: The Challenge of Representing the Earth: Understanding Accurate Scale in World Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Challenge of Representing the Earth: Understanding Accurate Scale in World Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Challenge of Representing the Earth: Understanding Accurate Scale in World Maps
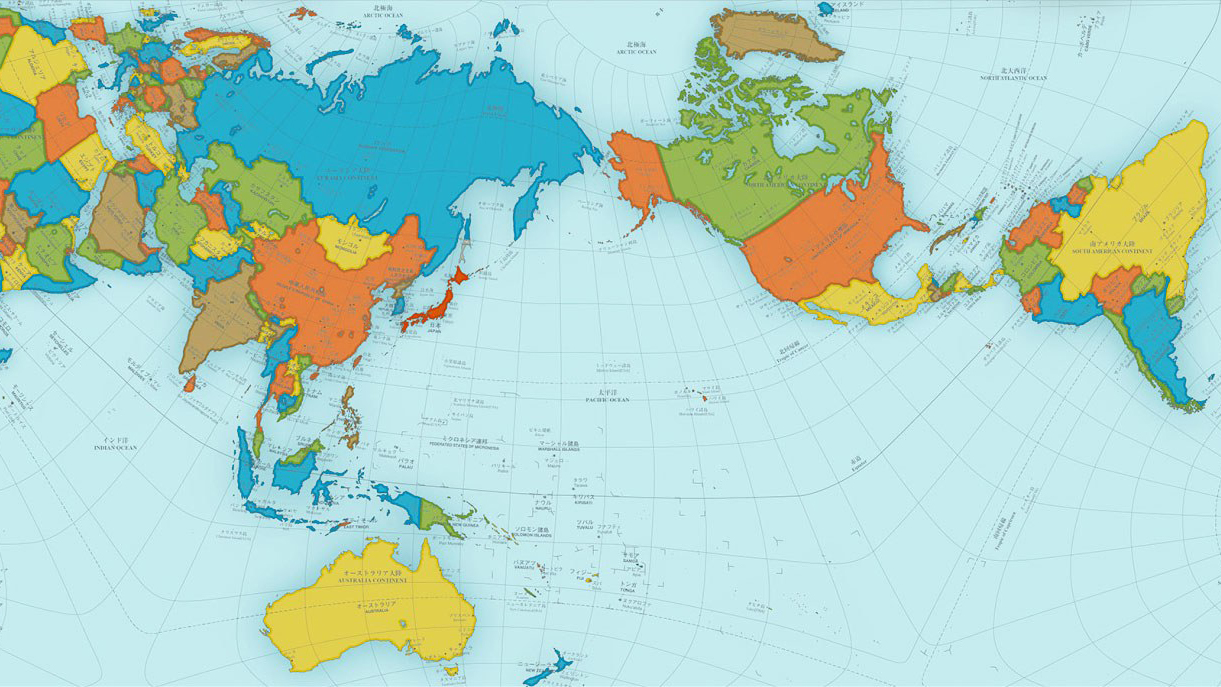
The world map, a ubiquitous tool for understanding our planet, presents a significant challenge: accurately representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane. This challenge necessitates the use of projections, mathematical transformations that distort certain aspects of the globe to fit it onto a two-dimensional surface. While these projections are essential for creating maps, they inevitably introduce inaccuracies, particularly in terms of scale.
Scale, a Fundamental Concept in Cartography
Scale refers to the ratio between distances on a map and corresponding distances on the Earth’s surface. A map’s scale determines how much it shrinks or expands the real world. Accurate scale is crucial for various applications, including:
- Navigation: Accurate scale ensures that distances and bearings on a map correspond to actual distances and directions on the ground, facilitating safe and efficient navigation.
- Geographic Analysis: Accurate scale allows for precise measurements of distances, areas, and proportions, enabling accurate geographic analysis and comparisons.
- Spatial Planning: Accurate scale is essential for planning infrastructure projects, urban development, and resource management, ensuring that proposed solutions fit within the real-world context.
- Education: Maps with accurate scale provide a more realistic representation of the Earth, facilitating a deeper understanding of geographic concepts and relationships.
The Inevitable Distortions of Projections
Projections, while necessary, introduce distortions that affect scale accuracy. These distortions vary depending on the type of projection used. Some common projections and their inherent distortions include:
- Mercator Projection: This projection, widely used for world maps, preserves angles but distorts areas, making high-latitude regions appear larger than they are in reality.
- Robinson Projection: This projection attempts to minimize distortions by compromising on both angles and areas. While it provides a balanced representation, it does not maintain accurate scale for any specific location.
- Equirectangular Projection: This projection preserves distances along the equator but stretches areas further away from it, causing distortions in both shape and size.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Projection
The choice of projection directly impacts the accuracy of scale on a map. For specific applications, choosing the most appropriate projection is crucial. For instance:
- Navigation: A projection that preserves angles, such as the Mercator projection, is suitable for navigation, as it accurately represents directions.
- Area Analysis: Projections that minimize area distortions, such as the Robinson projection, are preferable for comparing the sizes of different regions.
- Local Mapping: For small-scale maps of specific areas, projections that maintain accurate scale for the region in question are the most suitable.
Beyond the Traditional World Map
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of alternative methods for representing the Earth on a flat surface. These methods, such as the use of interactive globes and 3D maps, offer more accurate representations of the globe, overcoming the limitations of traditional projections.
FAQs about Accurate Scale on World Maps
Q: Why is it impossible to create a perfectly accurate world map?
A: The Earth is a sphere, while maps are flat surfaces. Any attempt to represent a curved surface on a flat one will inevitably involve distortions, impacting scale accuracy.
Q: What is the most accurate projection for a world map?
A: There is no single "most accurate" projection. The best projection depends on the specific application and the type of distortion that is most important to minimize.
Q: Can I use a world map for measuring distances accurately?
A: World maps, due to their inherent distortions, are not suitable for precise distance measurements. For accurate measurements, specialized maps with specific projections and scales are required.
Q: How can I understand the scale of a world map?
A: The scale of a map is typically indicated in the map’s legend or margin. This scale can be expressed in various ways, such as a verbal scale (e.g., "1 inch equals 100 miles"), a representative fraction (e.g., 1:100,000), or a graphic scale (a visual representation of the scale).
Tips for Understanding and Using World Maps with Accurate Scale
- Be Aware of Distortions: Recognize that all world maps involve distortions. Understand the limitations of the projection used and how it affects scale accuracy.
- Consult the Map Legend: Always check the map legend to understand the scale and the projection used. This information will help you interpret the map accurately.
- Use Specialized Maps: For specific applications requiring accurate measurements, consult specialized maps with appropriate scales and projections.
- Embrace Interactive Tools: Utilize interactive globes and 3D maps, which offer more accurate representations of the Earth and allow for flexible exploration.
Conclusion
Understanding accurate scale in world maps is crucial for navigating, analyzing, and interpreting our planet. While the challenge of representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane remains, advancements in cartography and technology continue to provide increasingly accurate and informative representations of our world. By understanding the limitations of projections and choosing appropriate tools, we can leverage the power of maps to explore, analyze, and understand our planet more effectively.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Challenge of Representing the Earth: Understanding Accurate Scale in World Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
