The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale
Related Articles: The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale

Maps are powerful tools that enable us to visualize and comprehend the vastness of our world. However, their effectiveness hinges on one crucial element: scale. Scale, in the context of maps, is the ratio that represents the relationship between distances on a map and their corresponding distances on the Earth’s surface. It essentially allows us to translate the real world onto a manageable, two-dimensional representation.
Understanding the Concept of Scale
Scale is expressed in various ways, each conveying the same fundamental information:
- Verbal Scale: This is the most straightforward approach, stating the relationship directly. For example, "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This uses a ratio to express the relationship, such as "1:100,000." This means one unit of measurement on the map corresponds to 100,000 units of the same measurement on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: This uses a visual bar, often divided into segments, to represent distances. This allows for quick estimations of distances without the need for calculations.
Importance of Scale in Map Interpretation
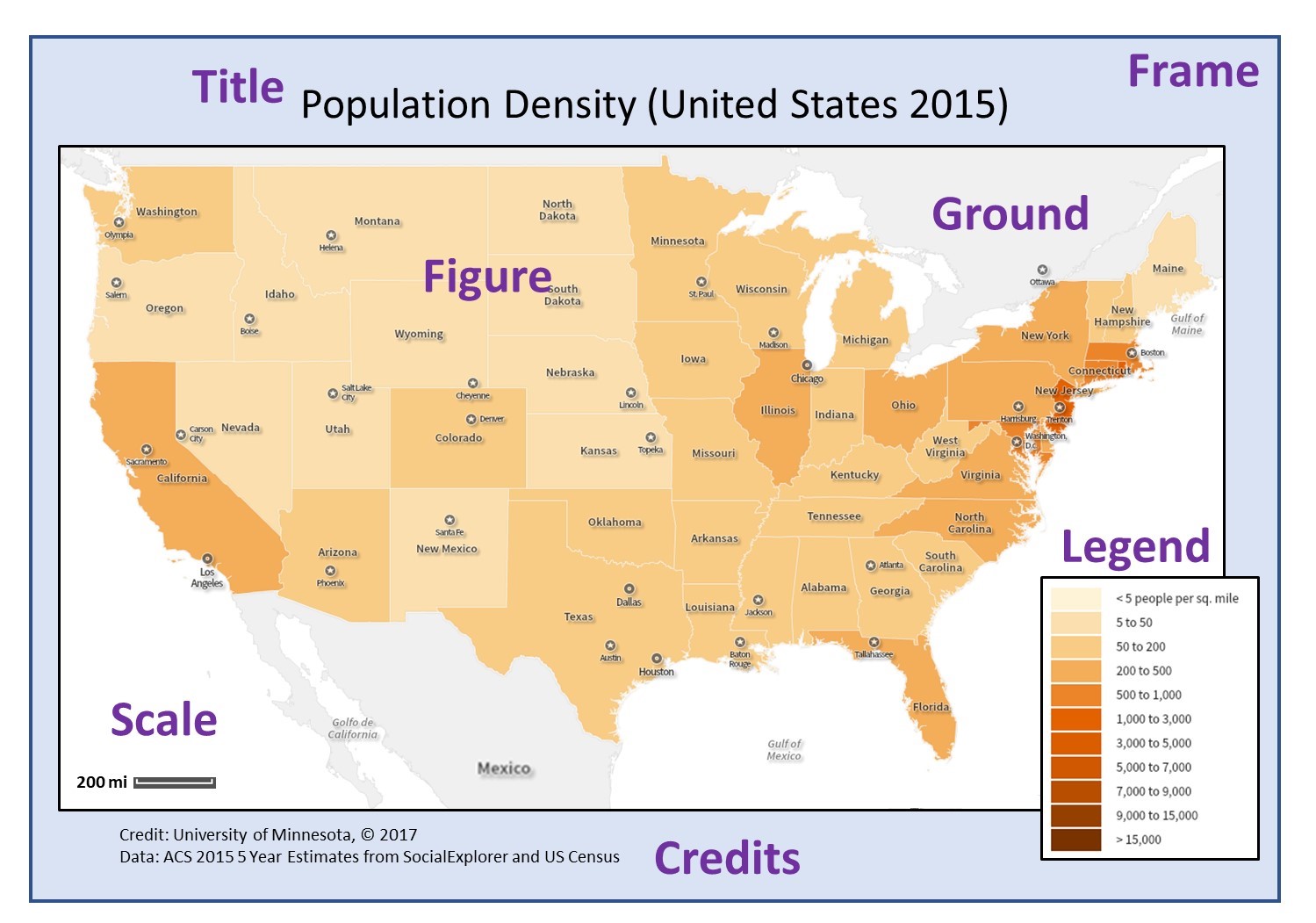
Scale is not merely a technical detail; it is the cornerstone of accurate map interpretation. It dictates the level of detail and the extent of the area represented on a map. A large-scale map, with a smaller representative fraction, shows a smaller area with greater detail, suitable for urban planning or local navigation. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger representative fraction, depicts a vast area with less detail, ideal for regional planning or global analysis.
Benefits of Scale in Map Usage
Scale plays a crucial role in various applications:
- Navigation: Scale allows for accurate estimation of distances and directions, facilitating travel and exploration.
- Planning: Whether for urban development, resource management, or disaster response, scale provides a framework for understanding spatial relationships and making informed decisions.
- Analysis: Scale enables the study of spatial patterns, trends, and relationships between different features, contributing to research and data interpretation.
- Communication: Scale facilitates clear and concise communication of spatial information, enabling effective collaboration and knowledge sharing.
FAQs on Scale in Maps
1. How do I determine the scale of a map?
The scale of a map is typically indicated in the map legend or on the map itself. Look for verbal scales, representative fractions, or graphic scales.
2. What is the difference between large-scale and small-scale maps?
Large-scale maps have a smaller representative fraction, showing a smaller area with greater detail. Small-scale maps have a larger representative fraction, depicting a larger area with less detail.
3. How can I convert between different scale units?
You can convert between different units using simple ratios and conversion factors. For example, to convert from a representative fraction of 1:100,000 to a verbal scale in centimeters, you would divide 100,000 by 100,000 to get 1 centimeter representing 1 kilometer.
4. How does scale affect map accuracy?
Scale directly impacts map accuracy. Larger scales provide more detail and thus greater accuracy for smaller areas. Smaller scales, while covering larger areas, sacrifice detail and may not accurately represent certain features.
5. What are the limitations of scale in map interpretation?
Scale is a compromise between detail and coverage. A map cannot depict everything at all scales. Understanding the limitations of the scale used is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Tips for Using Scale Effectively
- Consider the purpose of the map: Select a scale that best suits your needs, whether for navigation, planning, or analysis.
- Pay attention to the map legend: The legend provides essential information about the scale and other map symbols.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool: This allows for accurate measurement of distances on the map.
- Understand the limitations of scale: Be aware of the level of detail and coverage provided by the chosen scale.
Conclusion
Scale is the unsung hero of map interpretation. It provides the essential framework for understanding the relationship between the map and the real world. By comprehending the nuances of scale, we can unlock the full potential of maps, navigating our world with precision, planning for the future with clarity, and analyzing spatial patterns with insightful understanding. Scale is not just a technical detail; it is the language that allows us to speak the language of maps.

![Map Scales [ Area ] – GeoGebra](https://www.geogebra.org/resource/PwbGM5yT/ijVIMbBQClZkw4Yi/material-PwbGM5yT.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
