The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale
Related Articles: The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale

A map, at its core, is a visual representation of the world, a miniature reflection of reality. But to accurately convey the vastness of the earth, a crucial element comes into play: scale. Scale, in cartography, is the mathematical relationship between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It is the bridge between the miniature world of the map and the expansive reality it represents, allowing us to comprehend the size, distance, and proportions of geographic features.
The Language of Scale
Scale is often expressed in three primary forms:
- Verbal Scale: This is the simplest and most direct way to express scale. It uses a statement like "1 cm represents 10 km" or "1 inch equals 10 miles." This form clearly conveys the relationship between map distance and real-world distance, making it easy to understand.
- Representative Fraction (RF): This form uses a ratio to express the scale, typically written as 1:100,000 or 1/100,000. This indicates that one unit on the map corresponds to 100,000 units on the ground. The advantage of RF is its universality – it remains consistent regardless of the unit of measurement used.
- Graphic Scale: This is a visual representation of scale, typically depicted as a bar with marked divisions representing specific distances on the ground. This allows for quick and easy measurement directly from the map, eliminating the need for calculations.
The Importance of Scale
Scale plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and accuracy of a map. It determines the level of detail that can be displayed and the intended purpose of the map. A large-scale map, with a smaller representative fraction, shows a smaller area in greater detail. This is ideal for representing urban areas, geological formations, or specific features requiring precise measurements. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger representative fraction, covers a larger area but with less detail. This is suitable for showing global patterns, regional landscapes, or the distribution of natural resources.
Scale and Map Interpretation
Understanding scale is essential for interpreting a map accurately. Without it, we cannot determine the true size of features, the distance between locations, or the relative importance of different elements. A map without scale is like a photograph without a focal length – it lacks context and can be misleading.
Choosing the Right Scale
The choice of scale depends heavily on the intended purpose of the map. A detailed map of a city would require a large-scale representation to capture the intricate network of streets and buildings. A map depicting global trade routes, however, would need a small scale to encompass the vast distances involved.
Scale and Technology
The advent of digital mapping technologies has further emphasized the importance of scale. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) utilize precise scale information to accurately represent data and perform spatial analysis. This allows for the creation of highly detailed and interactive maps, providing users with a comprehensive understanding of geographic phenomena.
FAQs about Scale
1. What is the difference between large-scale and small-scale maps?
Large-scale maps have a smaller representative fraction, showing a smaller area in greater detail. Small-scale maps have a larger representative fraction, covering a larger area with less detail.
2. How can I determine the scale of a map?
Look for the scale information, which is typically displayed in the map legend, margin, or title. It may be expressed verbally, as a representative fraction, or graphically.
3. Why is scale important for measuring distances on a map?
Scale provides the conversion factor between map distance and real-world distance. By applying the scale, you can accurately determine the distance between two points on the ground.
4. Can scale be changed on a map?
Yes, but only digitally. Using GIS software, you can adjust the scale of a map to zoom in or out, revealing different levels of detail.
5. What are some examples of how scale is used in everyday life?
Scale is used in various applications, including navigation apps, weather maps, urban planning, and even video games. It helps us understand the size and distance of objects and locations in the real world.
Tips for Working with Scale
- Always check the scale: Before using a map, ensure you understand the scale and how it is represented.
- Use the appropriate scale: Choose a map with a scale suitable for your intended purpose.
- Understand the limitations of scale: Be aware that scale can affect the accuracy and detail of a map.
- Use tools to measure distance: Employ a ruler or online tools to accurately measure distances on a map using the provided scale.
Conclusion
Scale is the invisible language that binds maps to reality. It is the key to unlocking the information encoded within a map, allowing us to comprehend the size, distance, and proportions of the world around us. By understanding scale, we can navigate our surroundings, make informed decisions, and appreciate the intricate beauty of our planet. As technology advances, the importance of scale will only continue to grow, shaping our understanding of the world and empowering us to explore it with greater accuracy and insight.

![Map Scales [ Area ] – GeoGebra](https://www.geogebra.org/resource/PwbGM5yT/ijVIMbBQClZkw4Yi/material-PwbGM5yT.png)




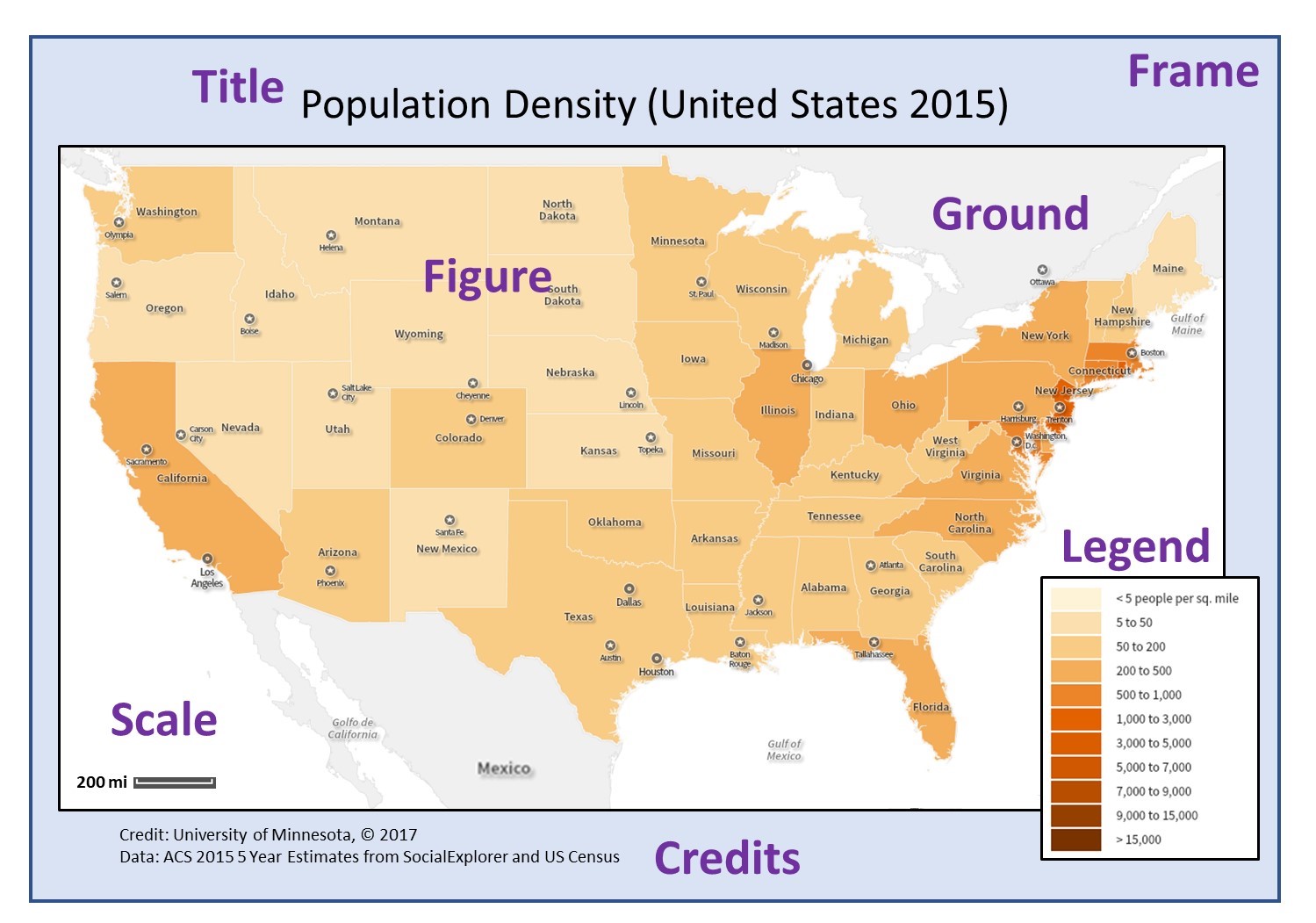
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Language of Maps: Understanding Scale. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
