The Crucial Role of Map Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of Map Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of Map Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of Map Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration

Maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, and their accuracy and effectiveness hinge upon a fundamental concept: scale. Map scale, a crucial aspect of cartography, determines the relationship between distances on a map and the corresponding distances on the ground. It allows cartographers to translate vast landscapes onto manageable surfaces, facilitating navigation, analysis, and understanding of geographic information.
Understanding Map Scale: A Foundation of Cartography
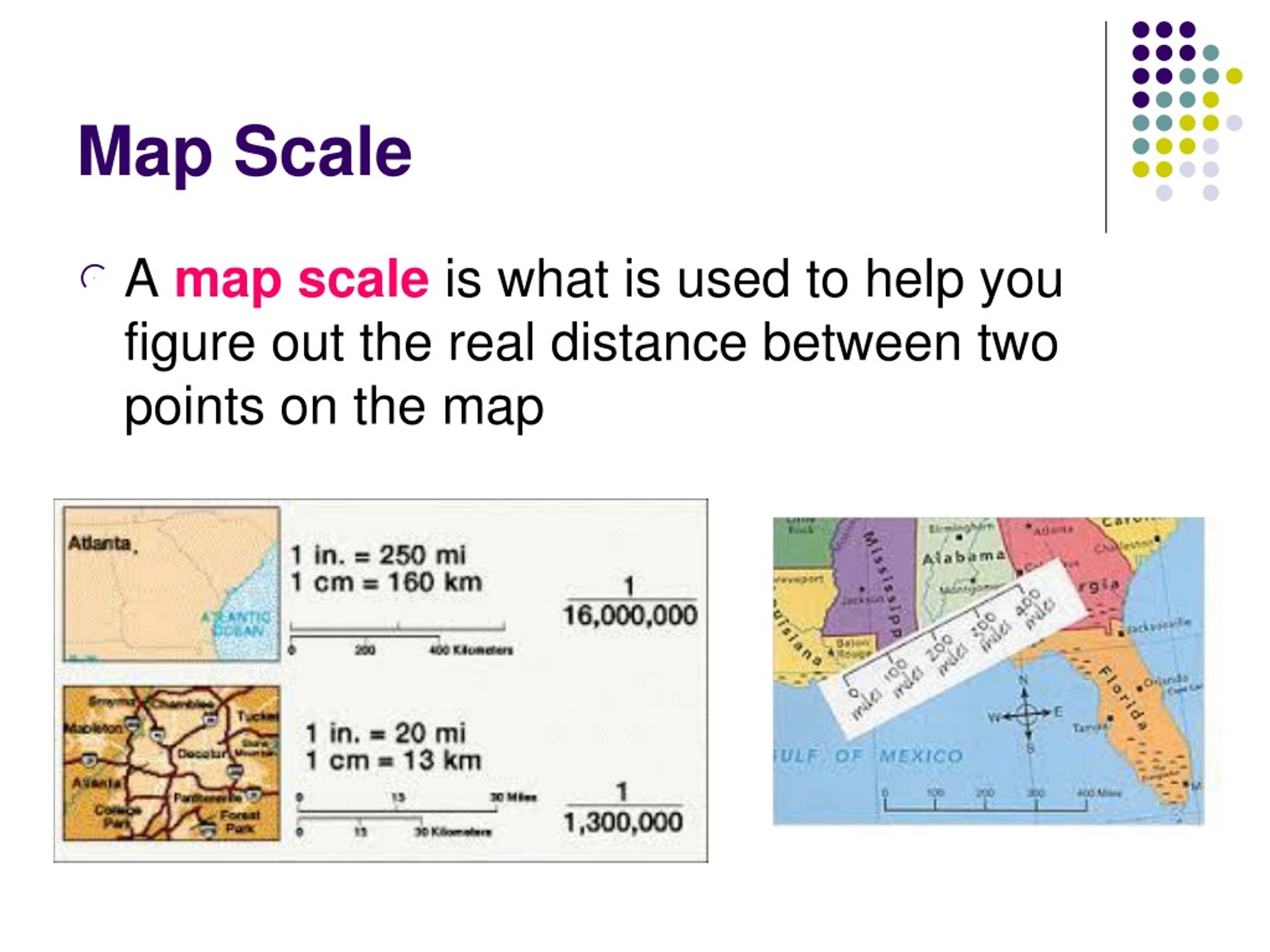
Map scale expresses the ratio between the distance on a map and the equivalent distance in reality. This ratio can be presented in various formats, each offering a unique perspective:
- Verbal Scale: A simple statement describing the relationship, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground." This format is intuitive and easy to understand.
- Representative Fraction (RF): Expressed as a fraction, RF represents the ratio of map distance to ground distance, for example, 1:100,000. This format highlights the precise numerical relationship.
- Graphic Scale: A visual representation of scale using a line divided into segments representing specific distances on the ground. This format allows for quick estimations without calculations.
The Importance of Scale in Map Creation and Interpretation
The choice of map scale significantly influences the map’s content and intended use. Large-scale maps, with a relatively small ratio, depict smaller areas in greater detail, suitable for urban planning, local navigation, or geological surveys. Conversely, small-scale maps, with a larger ratio, cover vast regions but provide a more generalized representation, ideal for regional analysis, global studies, or long-distance travel.
Factors Influencing Scale Selection
Several factors guide the selection of an appropriate map scale:
- Purpose of the map: The intended use dictates the level of detail required. Maps for navigation demand precise representation of roads and landmarks, while maps for thematic analysis may prioritize specific features like population density or elevation.
- Area to be mapped: The size of the area dictates the level of generalization necessary. Large areas require smaller scales to fit within manageable dimensions, while smaller areas allow for greater detail and larger scales.
- Available data: The accuracy and resolution of the data influence the level of detail that can be accurately depicted. High-resolution data allows for larger scales with more specific features, while lower resolution data restricts the level of detail and necessitates smaller scales.
- Target audience: The intended users of the map influence the complexity and clarity of the representation. Maps for general audiences may employ simplified symbols and clear labeling, while maps for specialized purposes can utilize more technical details.
Applications of Map Scale in Diverse Fields
Map scale plays a vital role in various disciplines:
- Navigation: Maps for navigation rely on accurate scale to guide travelers along specific routes, allowing them to estimate distances and identify landmarks.
- Urban Planning: Large-scale maps are essential for urban planning, enabling detailed representation of streets, buildings, and infrastructure for efficient development and management.
- Environmental Studies: Maps with appropriate scales are crucial for analyzing environmental phenomena, including deforestation, pollution levels, and habitat distribution.
- Geology and Resource Management: Geologists use maps at various scales to study geological formations, identify mineral deposits, and manage resource extraction.
- Military Operations: Military maps utilize precise scales to facilitate tactical planning, deployment of forces, and understanding of terrain features.
Challenges and Considerations in Map Scale
While map scale is a fundamental concept, its application presents challenges:
- Distortion: The process of transferring three-dimensional reality onto a two-dimensional surface inevitably introduces distortion, especially at smaller scales. This distortion can affect the representation of shapes, areas, and distances.
- Generalization: As scale decreases, features are generalized to fit within the reduced space. This simplification can lead to loss of detail and potentially misrepresent the true nature of the landscape.
- Data Availability: The accuracy and resolution of available data can limit the level of detail that can be represented at larger scales. This constraint necessitates careful selection of data sources and appropriate generalization techniques.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Scale
Q: How do I determine the appropriate map scale for my project?
A: The choice of map scale depends on the specific purpose, area to be mapped, available data, and target audience. Consider the level of detail required, the size of the area, and the accuracy of the data to select a scale that best serves your needs.
Q: What are the limitations of using a small-scale map?
A: Small-scale maps offer a broad overview but lack the detail of larger scales. They may not accurately represent local features and can lead to misinterpretations regarding distances and specific locations.
Q: Can I change the scale of an existing map?
A: Changing the scale of a map can introduce distortion and inaccuracies. It is generally recommended to use maps at their original scale for accurate representation.
Q: What are the advantages of using a graphic scale?
A: Graphic scales offer a visual representation of scale, allowing for quick estimations without calculations. They are particularly useful when working with maps that lack a verbal or representative fraction scale.
Tips for Working with Map Scale
- Understand the limitations of scale: Be aware of the inherent distortions and generalizations associated with different scales.
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a scale that balances the need for detail with the overall purpose of the map.
- Use multiple scales: Consider using multiple scales for different aspects of your project, allowing for both broad overview and specific detail.
- Be mindful of data accuracy: Ensure that the data used for map creation is accurate and appropriate for the selected scale.
- Communicate scale clearly: Provide clear and consistent information about the map scale, using both verbal and graphic scales where applicable.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Scale in Cartography
Map scale is a fundamental concept that underpins the creation and interpretation of maps. Understanding its role and implications is crucial for accurate representation of geographic information, facilitating navigation, analysis, and informed decision-making across diverse fields. The selection of appropriate scale, along with careful consideration of its limitations, ensures that maps effectively convey the complexities of the Earth’s surface, providing valuable insights for various applications.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of Map Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
