The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps
Related Articles: The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Concept of Scale
- 3.2 The Importance of Scale Bars
- 3.3 Types of Scale Bars
- 3.4 Using Scale Bars Effectively
- 3.5 FAQs about Scale Bars
- 3.6 Tips for Using Scale Bars
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps

Maps, as visual representations of geographical information, rely on various elements to convey accurate and meaningful data. One such crucial element is the scale bar, a visual representation of the relationship between distances on the map and their corresponding distances in the real world. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of scale bars, their significance, and their application in map interpretation.
Understanding the Concept of Scale
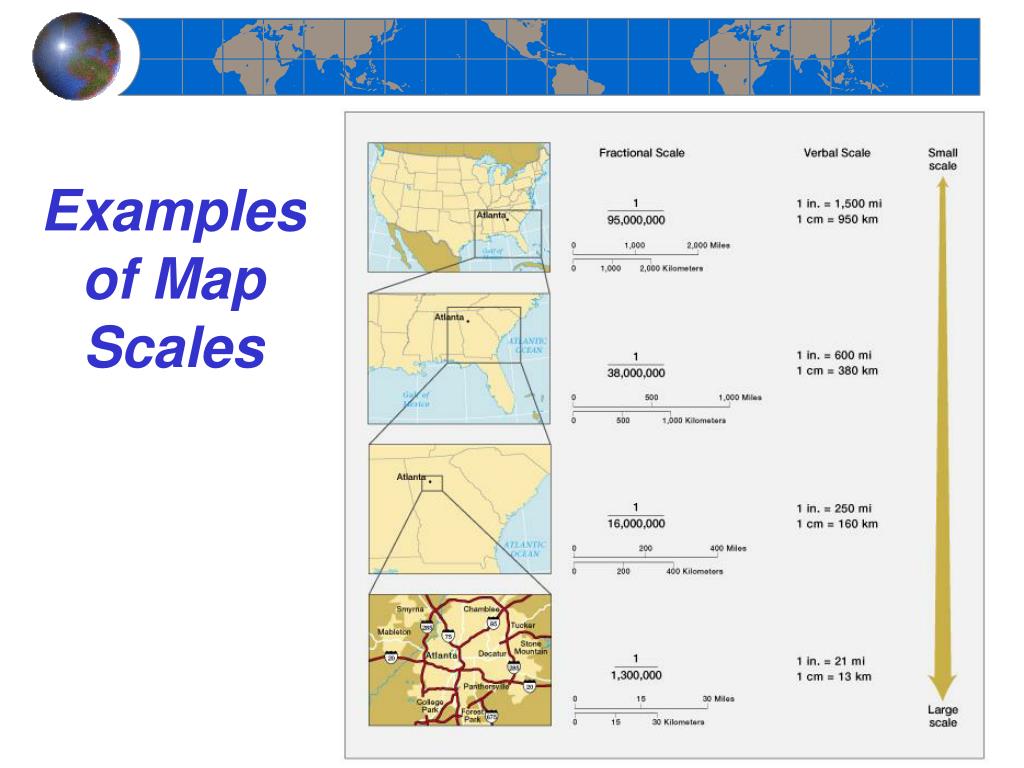
Scale, in the context of maps, refers to the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is typically expressed in a variety of ways, including:
- Verbal Scale: This method expresses the scale as a written statement, such as "1 centimeter on the map equals 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This method uses a ratio to represent the scale, such as 1:100,000. This means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
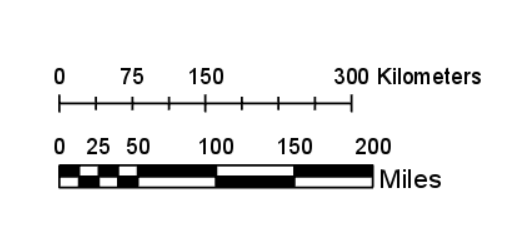
- Graphical Scale: This method uses a visual representation of the scale, typically a line divided into segments with corresponding distances labeled.
While all three methods convey the same information, graphical scales, commonly known as scale bars, are particularly beneficial due to their visual clarity and ease of use.
The Importance of Scale Bars
Scale bars play a crucial role in map interpretation by facilitating:
- Accurate Distance Measurement: By using the scale bar, users can directly measure distances on the map and convert them to real-world distances. This is essential for tasks such as planning travel routes, calculating distances between locations, and understanding the spatial extent of features.
- Relative Size Comparison: Scale bars enable users to compare the relative sizes of different features on the map. This is particularly useful for understanding the scale of geographical phenomena, such as the size of cities, the length of rivers, or the area of forests.
- Understanding Map Distortion: Maps are projections of the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, which inevitably introduces some degree of distortion. Scale bars help users understand the extent of distortion in different parts of the map. For example, a map with a constant scale bar may have different levels of distortion at different latitudes.
- Map Consistency: Scale bars ensure consistency in the representation of distances across the entire map. This is especially important for maps that cover large areas, as different parts of the map may have different levels of detail.
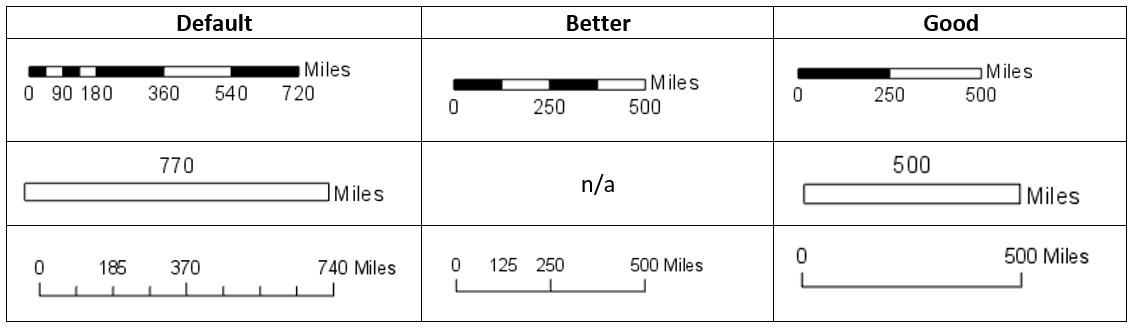
Types of Scale Bars
Scale bars can be classified into different types based on their construction and application:
- Linear Scale Bar: This is the most common type of scale bar, consisting of a straight line divided into segments with corresponding distances labeled. These segments can be in any unit of measurement, such as kilometers, miles, or meters.
- Bar Scale: Similar to the linear scale bar, this type uses a line divided into segments but includes a specific bar length representing a specific distance. This allows for easy visual estimation of distances.
- Ratio Scale Bar: This type of scale bar displays a ratio of map distance to ground distance, such as 1:100,000. While less intuitive than linear or bar scales, it is often used for maps with complex projections or varying scales.
- Variable Scale Bar: This type of scale bar is used for maps with varying scales, such as those covering large geographical areas. It typically consists of multiple segments, each representing a different scale.
Using Scale Bars Effectively
To effectively use a scale bar, users should follow these steps:
- Identify the Scale Bar: Locate the scale bar on the map. It is typically placed in a clear and prominent location, often in the map’s margin or legend.
- Determine the Units: Identify the units of measurement used in the scale bar, such as kilometers, miles, or meters.
- Measure the Distance: Use a ruler or other measuring tool to measure the distance between two points on the map.
- Convert to Real-World Distance: Use the scale bar to convert the measured map distance into the corresponding real-world distance.
FAQs about Scale Bars
1. What is the difference between a scale bar and a scale ratio?
A scale bar is a visual representation of the scale, while a scale ratio is a numerical expression of the scale. Both convey the same information but in different formats.
2. Why are scale bars important for map interpretation?
Scale bars allow users to accurately measure distances on the map and understand the relative sizes of features. They also help users understand map distortion and ensure consistency in distance representation.
3. Can a map have multiple scale bars?
Yes, maps can have multiple scale bars, especially those covering large areas or those with varying scales. Each scale bar represents a specific scale for a particular part of the map.
4. How do I determine the accuracy of a scale bar?
The accuracy of a scale bar depends on the accuracy of the map itself. Maps with higher levels of detail and accuracy typically have more accurate scale bars.
5. What are some common errors made when using scale bars?
Common errors include misinterpreting the units of measurement, using the wrong scale bar for a particular part of the map, and not accounting for map distortion.
Tips for Using Scale Bars
- Always check the units of measurement: Ensure you are using the correct units when measuring distances.
- Use a ruler or other measuring tool: For accurate measurements, use a ruler or other measuring tool.
- Pay attention to map distortion: Understand that maps are projections and may have distortion, especially at higher latitudes.
- Consult the map legend: The map legend may provide additional information about the scale bar and its application.
Conclusion
Scale bars are essential elements of maps, providing a visual representation of the relationship between map distances and real-world distances. By understanding the concept of scale, the importance of scale bars, and how to use them effectively, users can gain a deeper understanding of map information and make informed decisions based on the data presented. The ability to accurately measure distances, compare relative sizes, and understand map distortion are crucial skills for anyone interpreting maps, whether for personal exploration, professional analysis, or research purposes.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Guide to Understanding Scale Bars on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!