The Essential Tool of Cartography: Understanding Map Scales
Related Articles: The Essential Tool of Cartography: Understanding Map Scales
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Essential Tool of Cartography: Understanding Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Tool of Cartography: Understanding Map Scales

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our world, are powerful tools for navigation, planning, and understanding spatial relationships. However, their effectiveness hinges on a crucial element: the map scale. A map scale serves as the bridge between the vastness of reality and the compressed dimensions of a map, enabling us to accurately interpret distances, sizes, and proportions.
Defining the Map Scale
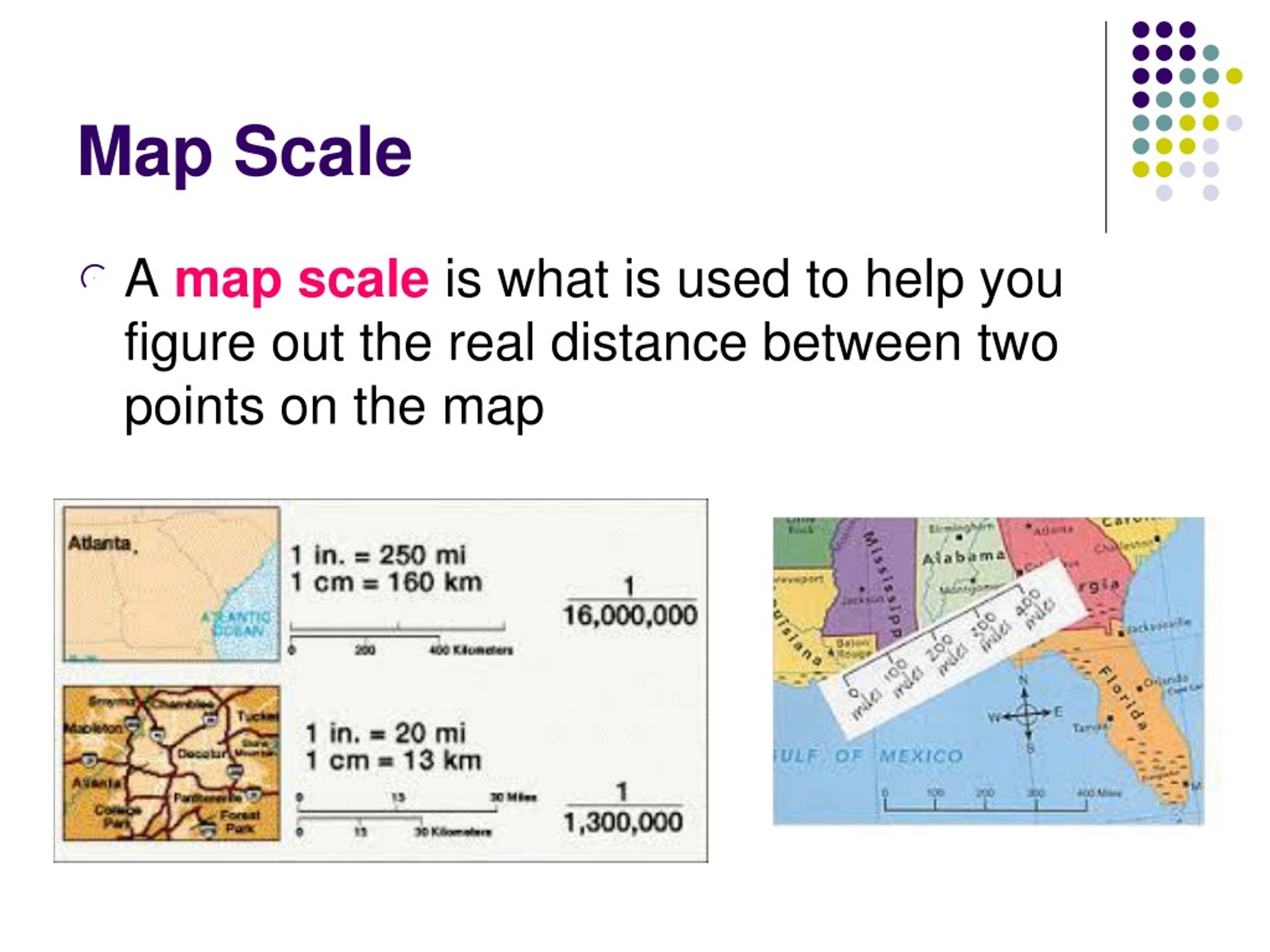
A map scale is a ratio that expresses the relationship between a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially provides a conversion factor, allowing us to translate map measurements into real-world distances. This crucial aspect of cartography ensures that maps accurately depict the relative sizes and positions of features, making them reliable sources of information.
Types of Map Scales
Map scales are typically presented in three primary forms:
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method expresses the scale as a written statement, such as "1 inch equals 1 mile" or "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers." While intuitive, this form can be cumbersome for precise calculations.
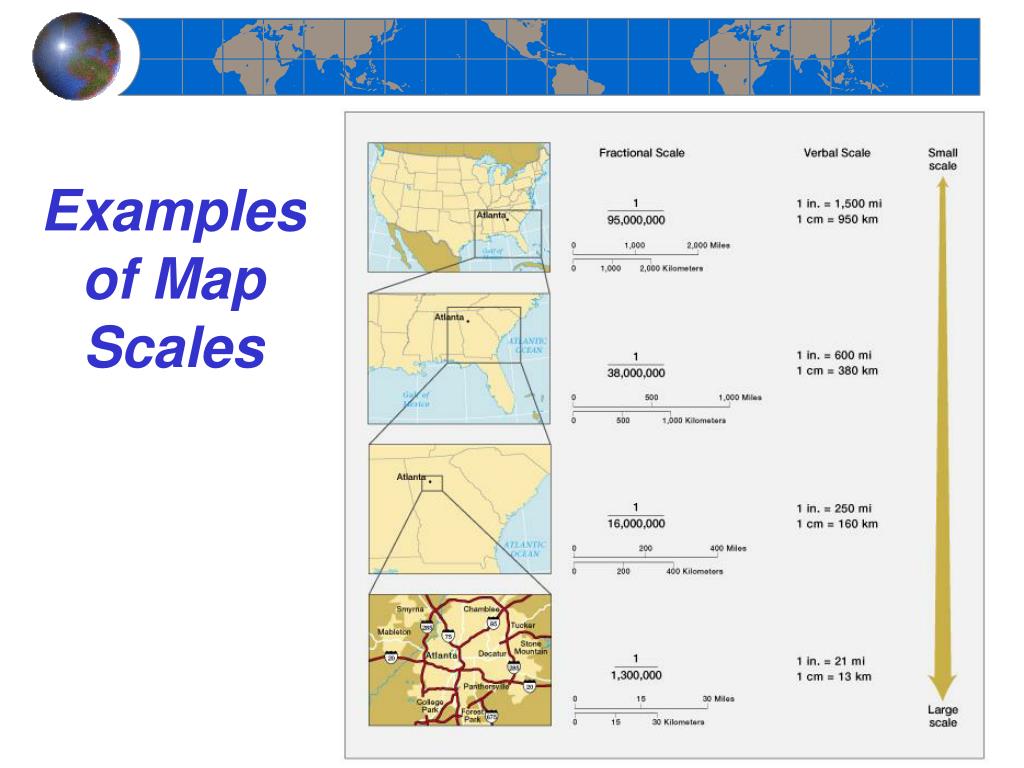
- Representative Fraction (RF): This numerical representation expresses the scale as a fraction, with the numerator representing the map distance and the denominator representing the corresponding ground distance. For example, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground. This format is highly precise and commonly used in cartography.
- Graphic Scale: This visual representation of the scale employs a line divided into segments that correspond to specific distances on the ground. This method allows for quick estimations of distances directly on the map, making it particularly useful for field work and navigation.
The Importance of Map Scales
Understanding map scales is crucial for various reasons:
- Accurate Distance Measurement: Maps are used for planning journeys, calculating travel times, and determining distances between locations. The map scale allows us to convert map measurements into real-world distances, ensuring accurate calculations and informed decision-making.
- Spatial Relationship Interpretation: Map scales enable us to visualize the relative sizes and proportions of geographical features. This helps us comprehend the spatial relationships between objects, such as the relative size of cities, the length of rivers, or the area covered by forests.
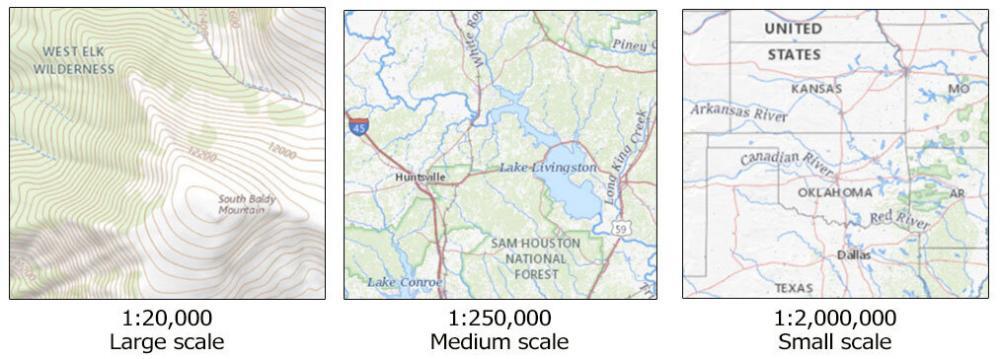
- Map Analysis and Comparison: Different maps may use different scales, making it essential to understand the scale used to compare and analyze information effectively. For instance, a small-scale map might show the overall geographic context of a region, while a large-scale map might provide detailed information about a specific city.
- Data Visualization and Interpretation: The map scale plays a critical role in data visualization. By choosing the appropriate scale, cartographers can effectively communicate complex data patterns, trends, and relationships within a geographical context.
Factors Influencing Map Scale Selection
The choice of map scale depends on several factors:
- Purpose of the Map: The intended use of the map dictates the level of detail required. Maps for navigation typically use larger scales to show specific roads and landmarks, while maps for regional analysis may use smaller scales to depict broader geographical patterns.
- Area Covered: The size of the area being mapped influences the scale selection. Smaller areas require larger scales to capture detail, while larger areas necessitate smaller scales to maintain a manageable map size.
- Available Data: The availability and resolution of data influence the level of detail that can be represented on a map. High-resolution data allows for larger scales with greater detail, while low-resolution data restricts the scale to a broader overview.
- Map Format: The format of the map, such as a printed map or a digital map, also affects scale selection. Digital maps can accommodate larger scales and more detail due to their ability to zoom in and out.
Applications of Map Scales
Map scales are fundamental tools in various disciplines and applications:
- Navigation: Map scales are essential for accurate navigation, enabling travelers to determine distances, plan routes, and locate specific destinations.
- Urban Planning: Planners use map scales to analyze urban landscapes, assess population density, identify infrastructure needs, and plan for future growth.
- Environmental Studies: Map scales are crucial for studying environmental issues, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change, allowing researchers to analyze spatial patterns and trends.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software relies heavily on map scales for data analysis, visualization, and spatial modeling.
- Military Operations: Military strategists use map scales to plan maneuvers, assess terrain, and coordinate troop movements.
FAQs about Map Scales
Q: What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A: A large-scale map shows a smaller area with more detail, while a small-scale map shows a larger area with less detail. The scale is inversely proportional to the area covered: larger scales cover smaller areas, and smaller scales cover larger areas.
Q: How do I determine the scale of a map?
A: The map scale is typically indicated on the map itself. Look for a verbal scale, a representative fraction, or a graphic scale.
Q: How can I use a map scale to measure distances?
A: Measure the distance on the map using a ruler or a measuring tool. Then, use the map scale to convert the map measurement into the corresponding ground distance. For example, if the map scale is 1:100,000 and you measure a distance of 5 centimeters on the map, the actual ground distance is 5 centimeters x 100,000 = 500,000 centimeters, or 5 kilometers.
Q: Why is it important to use the correct map scale?
A: Using the wrong map scale can lead to inaccurate measurements, misinterpretations of spatial relationships, and incorrect decisions. It is crucial to use the appropriate scale for the intended purpose of the map.
Tips for Using Map Scales
- Always check the map scale: Ensure you understand the scale used for the map you are using.
- Use the appropriate scale for your needs: Choose a scale that provides the necessary level of detail for your intended purpose.
- Consider the limitations of the scale: Remember that maps are simplifications of reality and may not capture all details, especially at smaller scales.
- Practice using different types of scales: Familiarize yourself with verbal, representative fraction, and graphic scales to interpret them effectively.
Conclusion
The map scale is a fundamental element of cartography, serving as the bridge between the real world and its representation on a map. Understanding and applying map scales is essential for accurate distance measurement, spatial relationship interpretation, data visualization, and informed decision-making in various fields. By comprehending the role and significance of map scales, we unlock the full potential of maps as powerful tools for navigation, planning, and understanding our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Tool of Cartography: Understanding Map Scales. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
