The Importance of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Importance of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Importance of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Importance of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration
Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our world, serve a vital purpose in navigating, understanding, and analyzing our planet. While a multitude of map types exist, from simple sketches to complex digital models, a fundamental principle underpins their effectiveness: scale. The concept of scale in cartography is not merely a technical detail; it is the very foundation upon which accurate and meaningful spatial information is conveyed.
Understanding Scale: A Foundation for Spatial Accuracy
Scale in cartography refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is expressed in various ways, including:
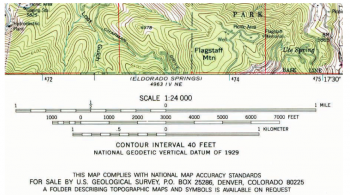
- Representative Fraction (RF): This method uses a fraction, such as 1:100,000, indicating that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
- Verbal Scale: This method uses words to describe the relationship, such as "one inch to one mile," signifying that one inch on the map represents one mile on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: This method employs a line segment divided into units, usually kilometers or miles, corresponding to specific distances on the ground.
Why Scale Matters: Unveiling the Importance of Accurate Representation
The significance of scale in mapmaking stems from its ability to accurately represent spatial relationships and distances. Without a defined scale, maps would be mere abstract depictions, devoid of the crucial information needed for navigation, measurement, and analysis. Consider the following key benefits of using scale in cartography:
1. Accurate Measurement and Distance Calculation:
Scale allows for precise measurement of distances and areas on maps. This is essential for various applications, including:
- Navigation: Sailors, pilots, and travelers rely on scaled maps to determine distances, calculate travel time, and plot accurate courses.
- Land Surveying and Planning: Architects, engineers, and urban planners utilize scaled maps to measure land parcels, design buildings, and plan infrastructure projects.
- Resource Management: Environmental scientists and resource managers rely on scaled maps to assess land use, monitor resource depletion, and plan conservation efforts.
2. Spatial Relationships and Proportions:
Scale ensures that the relative sizes and positions of geographical features are accurately represented on maps. This is critical for:
- Understanding Geographic Context: Maps with consistent scales allow for a clear understanding of the spatial relationships between different locations, such as the proximity of cities, the size of mountains, or the extent of forests.
- Analyzing Spatial Patterns: Researchers and analysts utilize scaled maps to identify spatial patterns, such as population density, disease distribution, or environmental hazards.
- Visualizing Geographic Data: Scaled maps effectively communicate complex spatial information through visual representations, aiding in understanding and interpretation.
3. Consistency and Comparability:
Using a consistent scale across different maps allows for easy comparison and integration of data. This is particularly important for:
- Multi-Map Analysis: Researchers and analysts often combine data from multiple maps to conduct comprehensive studies, and consistent scales facilitate accurate data integration and analysis.
- Data Visualization and Interpretation: Consistent scales ensure that visual representations of data are accurate and meaningful, avoiding distortions or misinterpretations.
4. Adaptability and Flexibility:
Scale is a flexible tool that allows cartographers to adjust the level of detail and information presented on maps. This is achieved by selecting appropriate scales for specific purposes:
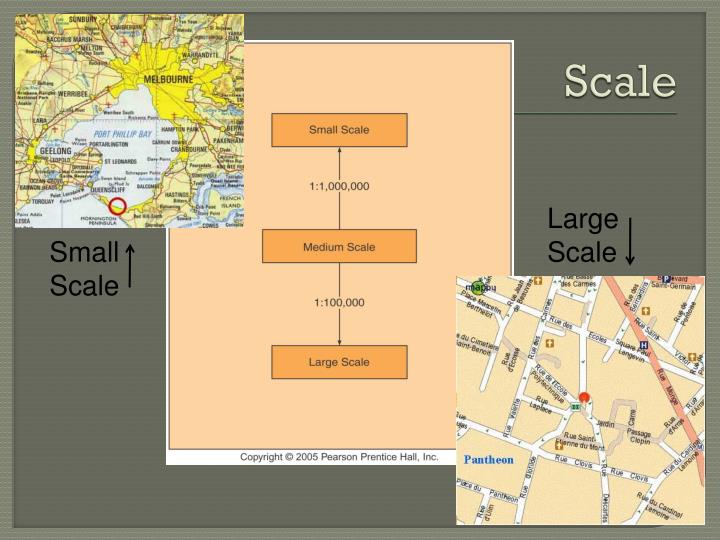
- Large-Scale Maps: These maps, with scales of 1:10,000 or larger, provide detailed information about small areas, ideal for urban planning, engineering projects, and local navigation.
- Medium-Scale Maps: These maps, with scales ranging from 1:10,000 to 1:100,000, offer a balance between detail and coverage, suitable for regional planning, resource management, and tourism.
- Small-Scale Maps: These maps, with scales smaller than 1:100,000, provide a broad overview of large areas, ideal for global studies, geological mapping, and international navigation.
FAQs on Scale in Cartography
1. What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A large-scale map depicts a small area in detail, while a small-scale map shows a large area with less detail. The scale determines the level of detail and the extent of coverage.
2. How does scale affect the accuracy of a map?
Scale directly influences the accuracy of a map. A larger scale allows for greater detail and precision in representing features, while a smaller scale sacrifices detail for broader coverage.
3. Can a map have multiple scales?
While a map typically uses a single scale, some maps may incorporate multiple scales for different sections or features. This allows for presenting a balanced view of both detailed information and broader context.
4. What are the limitations of scale in cartography?
Scale has limitations in representing complex three-dimensional features on a two-dimensional surface. Some distortion is inevitable, particularly at smaller scales.
5. How has technology impacted the use of scale in cartography?
Technological advancements have revolutionized mapmaking, allowing for more accurate and flexible use of scale. Digital mapping software and geographic information systems (GIS) offer advanced tools for manipulating scale, creating interactive maps, and analyzing spatial data.
Tips for Understanding and Using Scale in Cartography
- Pay attention to the scale of a map before using it. Understanding the scale is crucial for interpreting the information presented.
- Compare scales of different maps to assess their relative detail and coverage. This helps in selecting the most appropriate map for a specific purpose.
- Use tools like rulers and compasses to measure distances and areas accurately on scaled maps. These tools aid in precise calculations and analysis.
- Explore different map scales to understand the trade-off between detail and coverage. This allows for a comprehensive perspective on the subject matter.
- Consider the intended audience and purpose when choosing a map scale. Different scales cater to specific needs and levels of detail.
Conclusion
Scale is an indispensable element in cartography, ensuring the accurate representation of spatial information and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation. Its importance extends across various disciplines, from navigation and planning to resource management and scientific research. Understanding and utilizing scale effectively empowers us to navigate our world, analyze spatial patterns, and make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable geographic data. As technology continues to evolve, the role of scale in cartography will remain crucial, fostering a deeper understanding of our planet and its complexities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Importance of Scale in Cartography: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
