The Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Funding: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Funding: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Funding: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Funding: A Comprehensive Overview

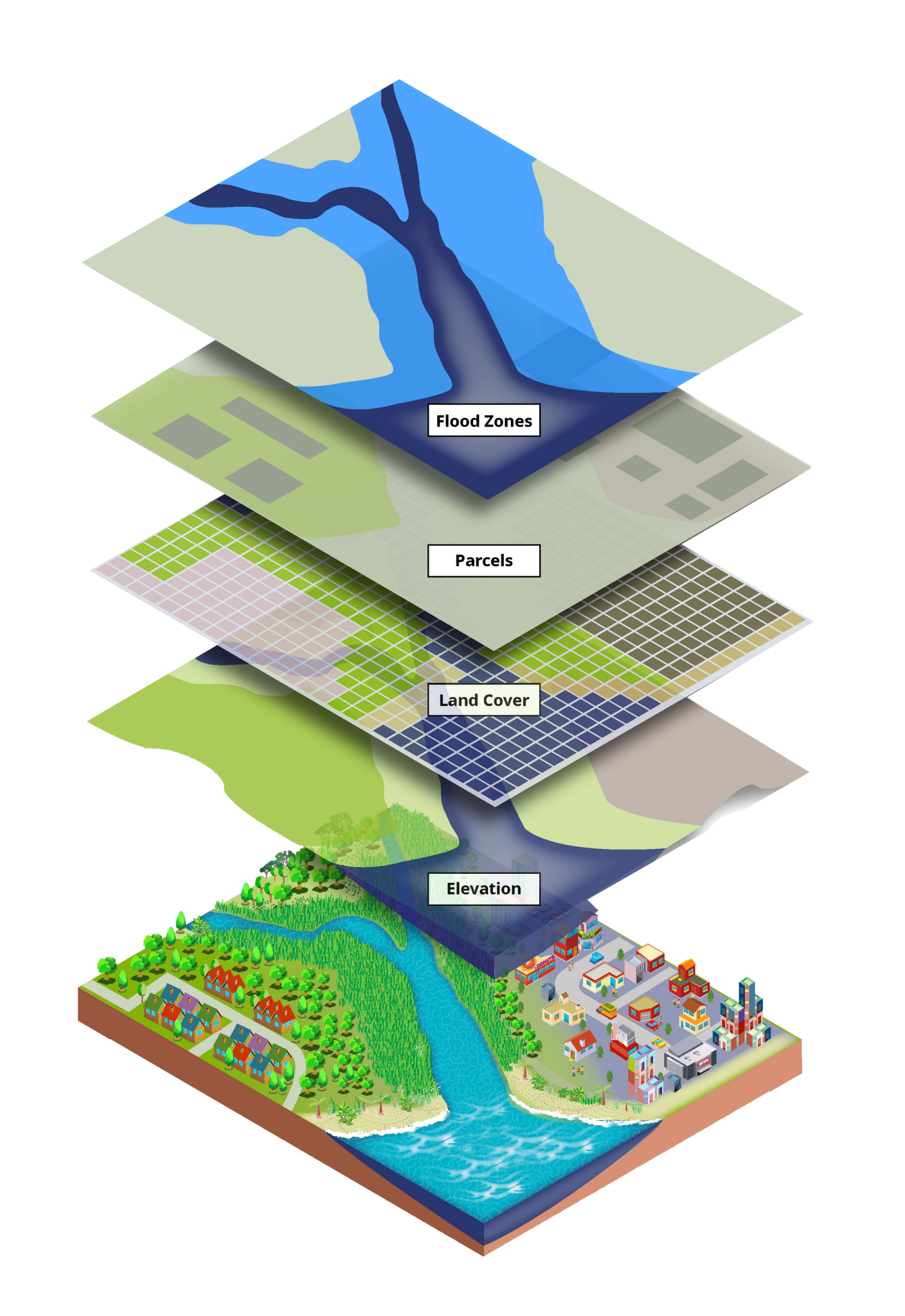
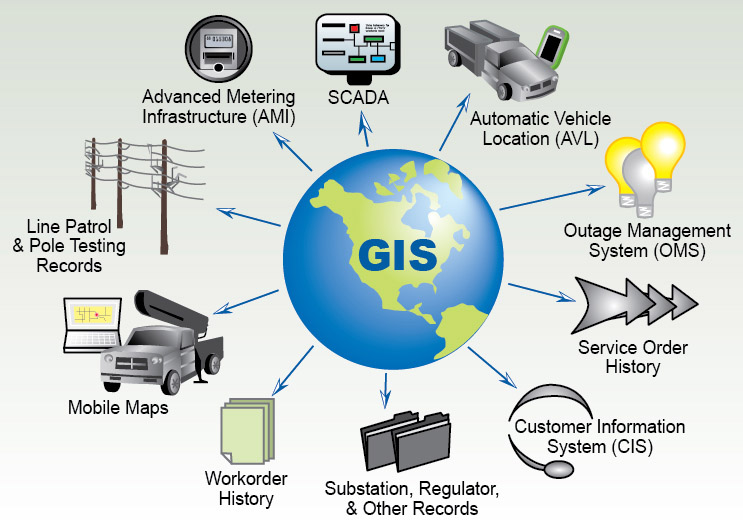
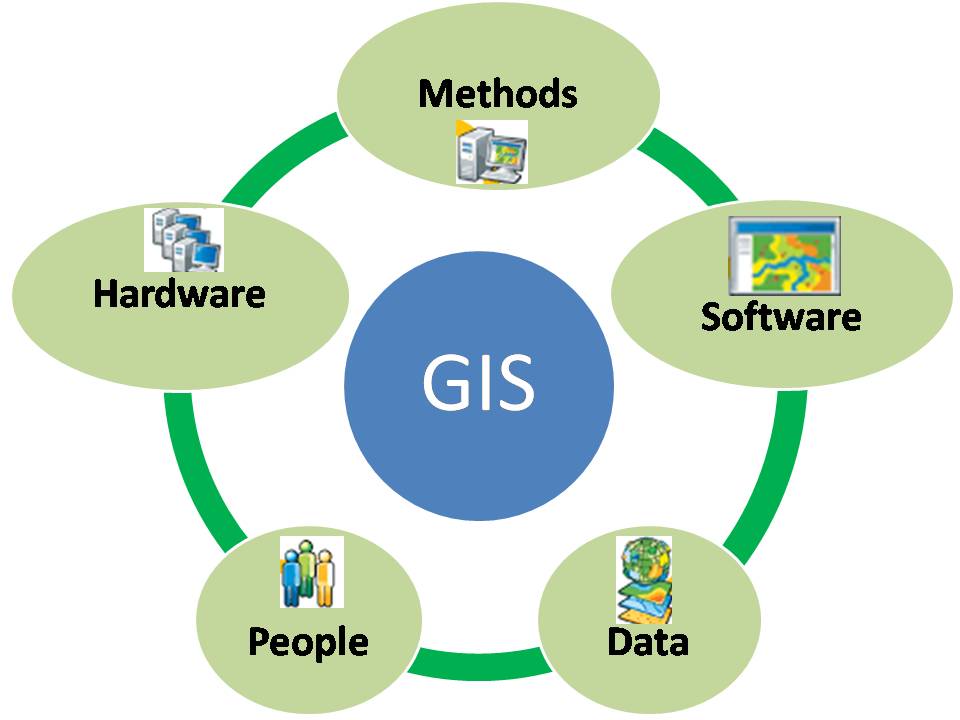
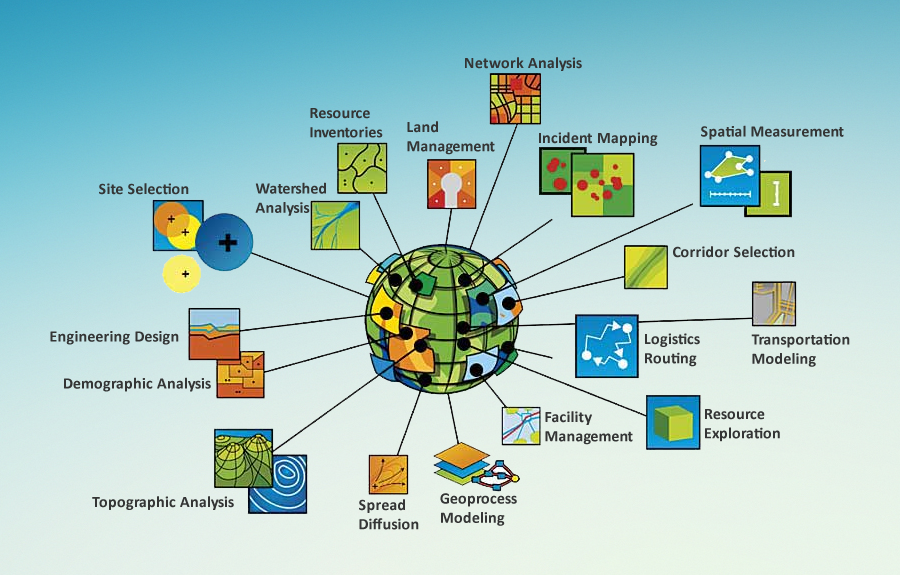
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools that transform data into actionable insights by visually representing and analyzing spatial information. GIS funding, therefore, plays a crucial role in enabling organizations, governments, and individuals to leverage these capabilities for a wide range of applications.
This article explores the multifaceted world of GIS funding, examining its various forms, beneficiaries, and the profound impact it has on diverse sectors. We will delve into the funding landscape, explore the benefits of investing in GIS, and highlight key considerations for securing and effectively utilizing these resources.
Understanding the Landscape: Sources and Mechanisms of GIS Funding
GIS funding originates from various sources, each with its own unique purpose and criteria. A comprehensive understanding of these funding sources is essential for navigating the landscape and securing the necessary resources for GIS initiatives:
-
Government Funding: Governments at all levels play a significant role in supporting GIS development and implementation. Federal, state, and local agencies allocate funds for projects that address societal needs, such as infrastructure development, disaster management, environmental protection, and public health. These funding opportunities often come with specific guidelines and priorities, requiring careful alignment of project goals with government objectives.
-
Private Sector Investment: Companies across diverse industries are increasingly recognizing the value of GIS in enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing resource allocation, and gaining a competitive edge. Private sector investments in GIS can take various forms, including:
- Direct Funding: Companies may allocate internal funds for GIS projects that directly support their business operations, such as supply chain management, customer segmentation, and market analysis.
- Partnerships: Companies may collaborate with research institutions or technology providers to develop and implement innovative GIS solutions, sharing the costs and benefits.
- Venture Capital: Startups developing cutting-edge GIS technologies may seek funding from venture capitalists, who invest in promising companies with high growth potential.
-
Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations, particularly those focused on environmental conservation, social justice, and community development, often rely on grants and donations to support their GIS initiatives. These organizations utilize GIS for projects such as mapping vulnerable communities, tracking deforestation, and analyzing social equity indicators.
-
International Funding: International organizations and development banks provide funding for GIS projects in developing countries, focusing on areas like sustainable agriculture, disaster preparedness, and climate change mitigation. These initiatives often involve capacity building and technology transfer, empowering local communities to utilize GIS for their own development.
Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of GIS Funding
GIS funding enables organizations and communities to realize the transformative power of spatial information, fostering innovation and progress across diverse sectors:
-
Improved Decision-Making: GIS provides a powerful platform for visualizing complex data, revealing spatial patterns and relationships that might otherwise remain hidden. This enhanced understanding empowers decision-makers in various fields, from urban planning to healthcare, to make more informed and data-driven choices.
-
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: GIS streamlines workflows and optimizes resource allocation by providing real-time information about locations, assets, and operations. This leads to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity across industries, from transportation and logistics to agriculture and mining.
-
Enhanced Public Safety and Disaster Management: GIS plays a critical role in emergency response and disaster management by providing critical information on affected areas, evacuation routes, and resource allocation. This enables swift and effective responses, minimizing damage and saving lives.
-
Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection: GIS empowers organizations and communities to monitor environmental changes, track resource usage, and assess the impact of human activities. This facilitates informed decision-making for sustainable development, conservation efforts, and mitigation of environmental hazards.
-
Social Equity and Community Empowerment: GIS tools can be used to map social vulnerabilities, identify disparities, and measure the impact of social programs. This empowers communities to advocate for better access to resources, services, and opportunities, fostering social justice and equity.
Navigating the Funding Process: Key Considerations for Success
Securing and effectively utilizing GIS funding requires a strategic approach, encompassing careful planning, compelling proposals, and robust implementation:
-
Identify Clear Objectives: Define specific and measurable goals for the GIS project, outlining the intended outcomes and benefits. This clarity will guide the funding application process and ensure alignment with the priorities of potential funders.
-
Develop a Compelling Proposal: Craft a well-structured and persuasive proposal that highlights the project’s potential impact, feasibility, and sustainability. Emphasize the project’s relevance to the funder’s priorities and demonstrate a clear understanding of the funding requirements.
-
Demonstrate Project Viability: Provide evidence of the project’s feasibility and sustainability, including detailed budgets, timelines, and resource allocation plans. Showcase the expertise and experience of the project team, demonstrating their capacity to successfully execute the project.
-
Establish Strong Partnerships: Collaborate with relevant stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector organizations, and community groups, to leverage their expertise and resources. These partnerships can enhance the project’s impact, broaden its reach, and increase its chances of securing funding.
-
Ensure Effective Implementation and Monitoring: Develop a robust implementation plan that outlines clear milestones, performance indicators, and monitoring mechanisms. Regularly track project progress, adjust strategies as needed, and ensure accountability for achieving the intended outcomes.
FAQs about GIS Funding
Q: What are the common funding cycles for GIS projects?
A: Funding cycles vary depending on the source and type of project. Government grants often have specific application deadlines and funding periods. Private sector investments may be more flexible, but require careful due diligence and negotiation. Non-profit organizations may rely on annual fundraising campaigns or specific grant opportunities.
Q: What are the typical requirements for GIS funding applications?
A: Funding applications typically require detailed project descriptions, budgets, timelines, team qualifications, and letters of support. Specific requirements may vary depending on the funder and the project’s scope.
Q: How can I find potential funding sources for my GIS project?
A: There are several resources for identifying potential funding sources, including:
- Government Websites: Federal, state, and local agencies often have dedicated websites outlining funding opportunities and application procedures.
- Grant Databases: Online databases like Grants.gov and Foundation Center provide comprehensive listings of grant opportunities from various organizations.
- Industry Associations: Professional organizations in the GIS field often offer funding information and networking opportunities.
- Networking and Collaboration: Attending conferences, workshops, and events provides opportunities to connect with potential funders and learn about emerging funding trends.
Q: What are some common challenges associated with GIS funding?
A: Securing GIS funding can be challenging due to:
- Competition: A high volume of applications often exists for limited funding resources.
- Specific Requirements: Funder priorities and application guidelines may be complex and demanding.
- Sustainability: Sustaining funding over the long term can be challenging, requiring ongoing efforts to demonstrate project impact and secure renewed support.
Tips for Successful GIS Funding
- Focus on Impact: Highlight the project’s potential to solve real-world problems, improve decision-making, and enhance societal well-being.
- Tailor Proposals: Customize proposals to align with the specific priorities and interests of each potential funder.
- Showcase Expertise: Demonstrate the project team’s technical skills, experience, and commitment to successful implementation.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the project planning and funding application process to build support and strengthen partnerships.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly track project progress, assess outcomes, and share findings with funders to demonstrate the project’s value and justify continued support.
Conclusion: The Future of GIS Funding and its Impact
GIS funding is a critical driver of innovation, progress, and societal well-being. As the field continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of funding opportunities. Organizations and communities must embrace a proactive approach, understanding the funding landscape, developing compelling proposals, and ensuring effective project implementation to maximize the benefits of GIS. The future of GIS funding holds immense potential for transforming our world, empowering us to address complex challenges, and build a more sustainable and equitable future.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Funding: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
