The Power of IMAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Email Management
Related Articles: The Power of IMAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Email Management
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of IMAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Email Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of IMAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Email Management

The internet has revolutionized communication, and email remains a cornerstone of this digital landscape. However, managing email effectively can be a daunting task, especially for individuals and businesses with high volumes of correspondence. This is where the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) emerges as a powerful tool, enabling seamless and efficient email management across multiple devices.
Understanding IMAP
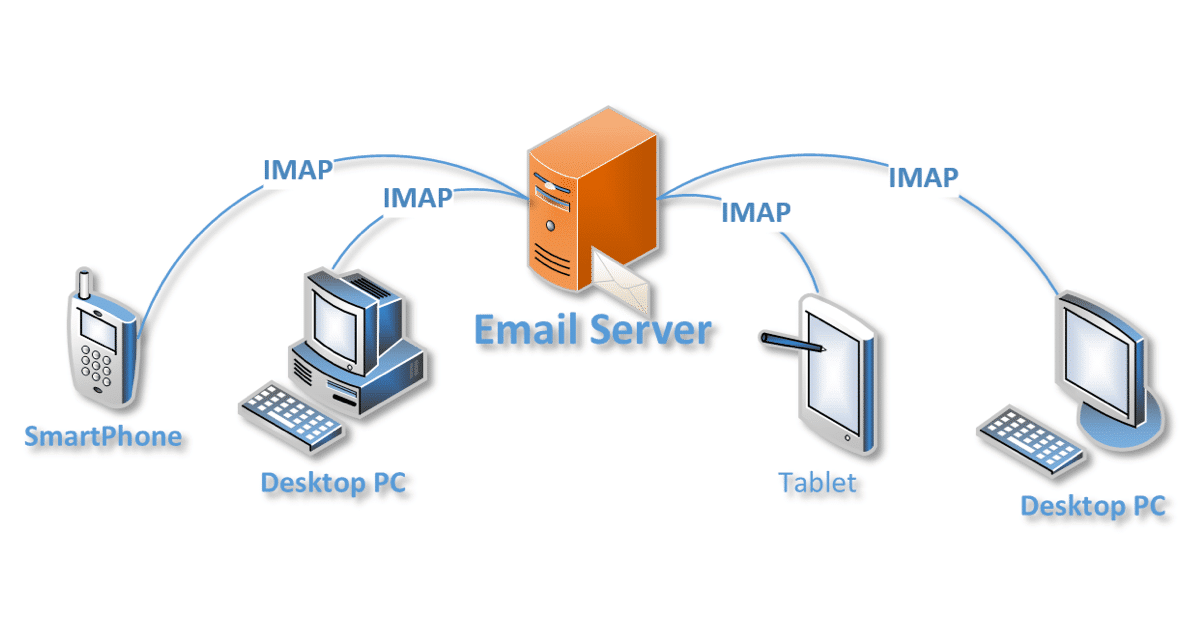
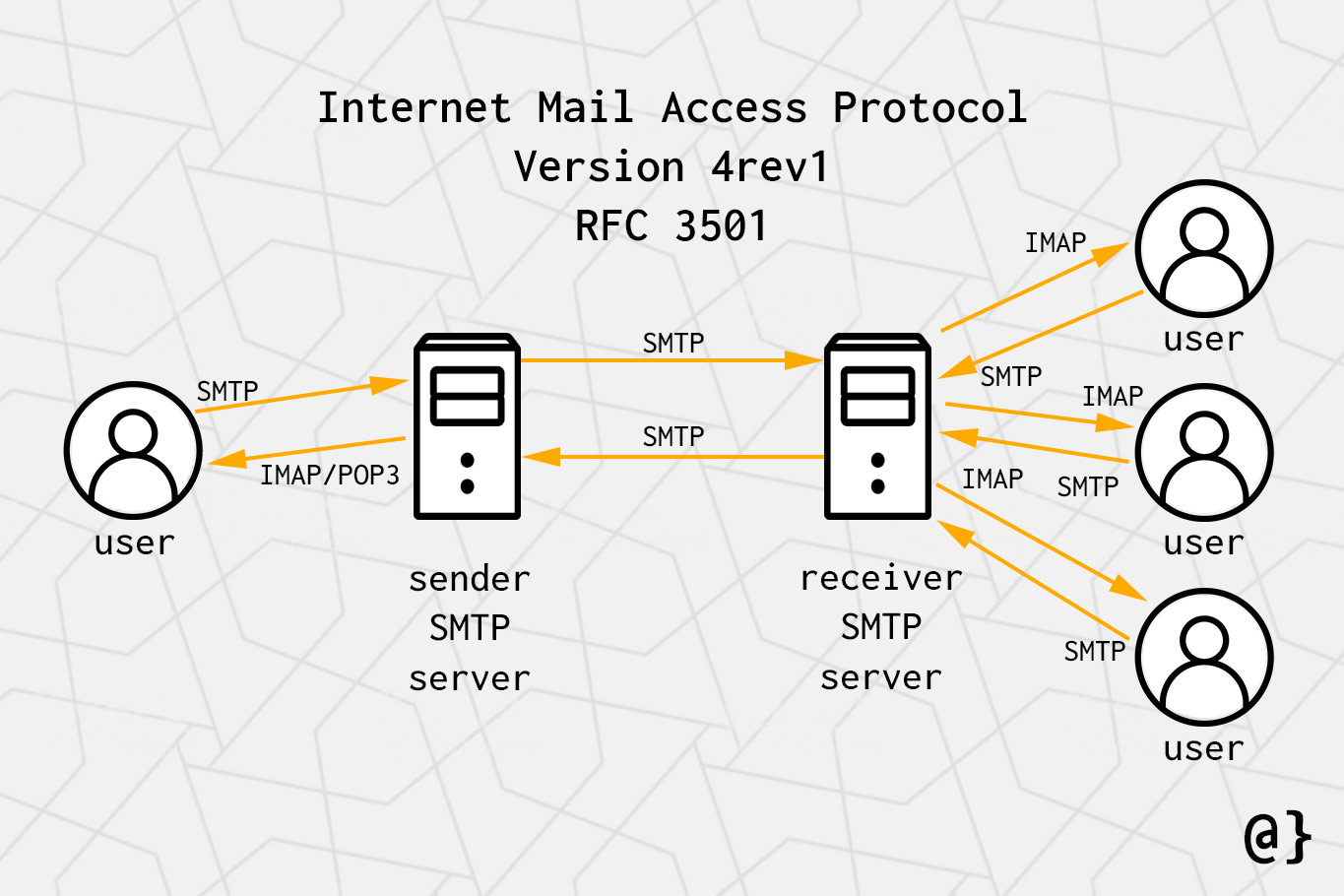
IMAP is a protocol that allows users to access and manage their emails on a server, rather than directly on their device. This means that all emails are stored on the server, and users can access them from any device with an internet connection. Unlike the older POP3 protocol, which downloads emails to the device and deletes them from the server, IMAP keeps emails synchronized across all devices, ensuring a consistent experience.
Benefits of IMAP
IMAP offers several key advantages for email management:
- Centralized Storage: Emails are stored on the server, eliminating the need for local storage and freeing up device space.
- Synchronization: Changes made to emails on one device are reflected on all other devices, ensuring a consistent inbox across platforms.
- Offline Access: Some IMAP clients allow for offline access to emails, providing flexibility even without an internet connection.
- Multiple Device Support: IMAP enables seamless email management across various devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Enhanced Collaboration: IMAP facilitates collaborative email management, allowing multiple users to access and manage shared inboxes.
Working with IMAP
To utilize IMAP, users need an email client that supports the protocol. Popular email clients like Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and Gmail all support IMAP.
The setup process typically involves configuring the client with the server address, port number, and login credentials provided by the email service provider.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Features
IMAP offers advanced features that further enhance email management:
- Folders: IMAP allows users to create and manage folders on the server, providing a structured approach to organizing emails.
- Search Functionality: IMAP supports powerful search capabilities, enabling users to quickly locate specific emails within their inbox.
- Flags and Labels: IMAP allows users to assign flags and labels to emails, facilitating organization and prioritization.
- Message Rules: IMAP supports message rules that automatically filter and manage emails based on predefined criteria.
Security Considerations
While IMAP offers numerous benefits, it is important to consider security aspects.
- Secure Connections: Always use IMAP over SSL/TLS to encrypt communication between your client and the server, ensuring data privacy.
- Strong Passwords: Choose strong and unique passwords for your email account to protect against unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for an additional layer of security, requiring a second verification step during login.
IMAP: A Modern Approach to Email Management
IMAP has revolutionized email management by providing a centralized, synchronized, and secure platform for accessing and managing emails. Its flexibility, advanced features, and robust security measures make it an indispensable tool for individuals and businesses alike. By understanding and utilizing IMAP, users can streamline their email workflows, enhance productivity, and maximize the benefits of this essential communication tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between IMAP and POP3?
A: IMAP and POP3 are both email protocols, but they differ in how they handle email retrieval. POP3 downloads emails to the device and deletes them from the server, while IMAP keeps emails synchronized across all devices and stores them on the server.
Q: Is IMAP secure?
A: IMAP itself is not inherently secure, but using IMAP over SSL/TLS encrypts communication between your client and the server, ensuring data privacy.
Q: How do I configure IMAP in my email client?
A: The configuration process varies depending on the email client. Typically, you need to provide the server address, port number, and login credentials. Consult your email client’s documentation or support resources for detailed instructions.
Q: What are some popular IMAP email clients?
A: Popular IMAP email clients include Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and Gmail.
Tips for Effective IMAP Usage
- Organize your inbox: Create folders to categorize emails and maintain a structured inbox.
- Utilize search functionality: Leverage IMAP’s powerful search capabilities to quickly locate specific emails.
- Set up message rules: Automate email management by creating rules that filter and organize emails based on predefined criteria.
- Enable IMAP over SSL/TLS: Ensure secure communication by encrypting data transmission between your client and the server.
- Regularly check for updates: Keep your email client and operating system updated to benefit from the latest security patches and features.
Conclusion
IMAP is a powerful and versatile protocol that has transformed email management by offering a centralized, synchronized, and secure platform for accessing and managing emails. By embracing IMAP, users can streamline their email workflows, enhance productivity, and experience a more efficient and secure communication experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of IMAP: A Comprehensive Guide to Email Management. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
