The Power of Mapping: Navigating the Complexities of Data with B-Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Mapping: Navigating the Complexities of Data with B-Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Mapping: Navigating the Complexities of Data with B-Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Mapping: Navigating the Complexities of Data with B-Maps
In the realm of data analysis and visualization, navigating complex datasets and extracting meaningful insights is paramount. This is where the concept of "B-maps" comes into play, offering a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting data patterns. While the term "B-map" itself might not be widely recognized, its underlying principles and applications hold significant value across various disciplines.
Understanding B-maps: A Visual Framework for Data Exploration
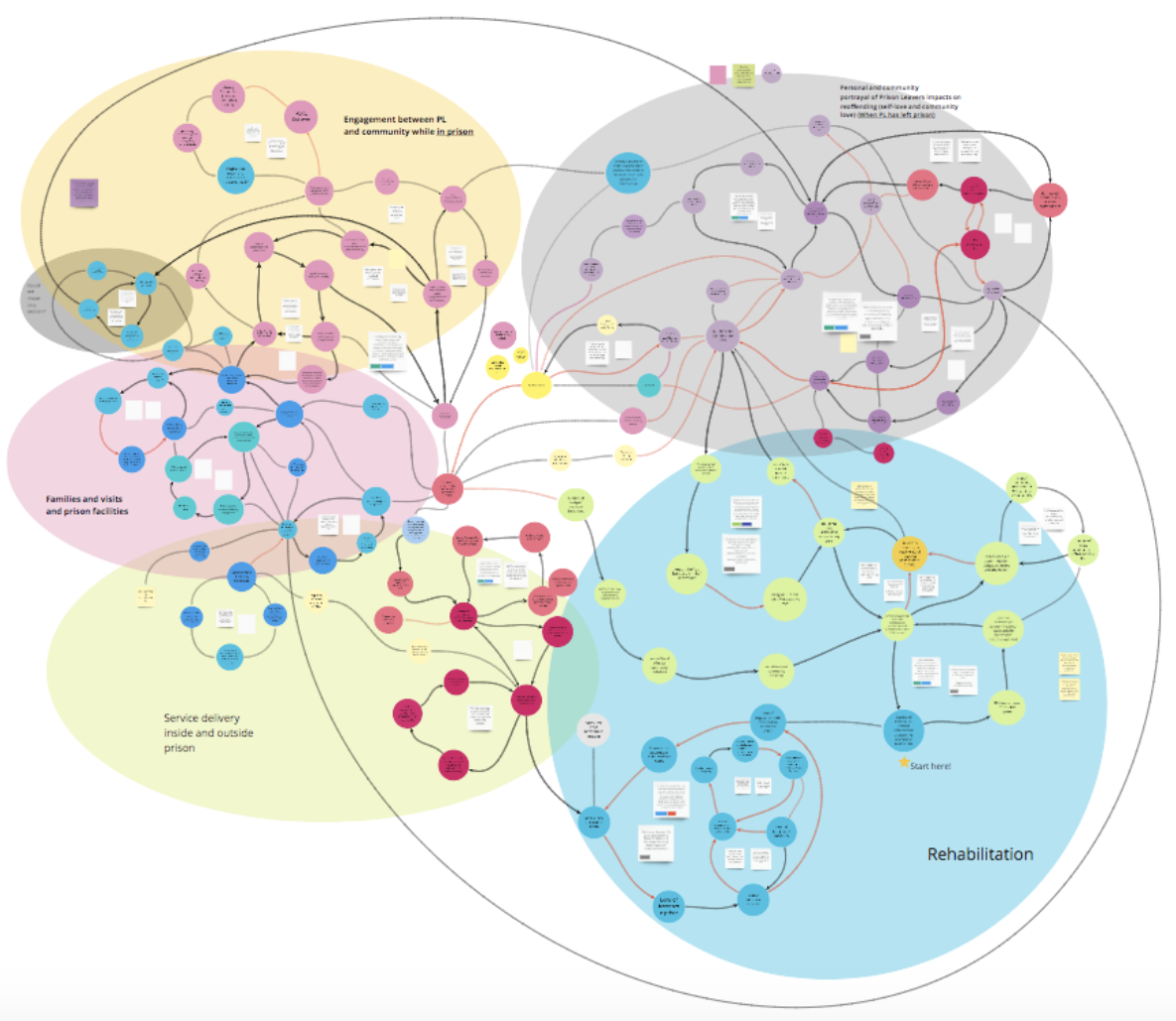
The essence of B-maps lies in their ability to visually represent data relationships and dependencies. Unlike traditional charts and graphs that focus on presenting individual data points, B-maps emphasize the interconnectedness of data elements. They create a visual map that reveals the underlying structure of a dataset, enabling users to identify clusters, outliers, and hidden trends.
The Core Components of a B-map:
- Nodes: These represent individual data points, entities, or concepts within the dataset.
- Edges: These connect nodes, indicating relationships or dependencies between them. The strength of these connections can be represented through varying line thickness or color intensity.
- Attributes: Each node can have associated attributes, providing additional information about the data point it represents.
Benefits of Utilizing B-maps:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: B-maps offer a more comprehensive and intuitive way to visualize data compared to traditional methods. They provide a holistic view of the data structure, highlighting relationships that might not be apparent in tabular formats.
- Improved Data Understanding: By revealing hidden connections and patterns, B-maps facilitate a deeper understanding of the underlying data relationships. This can lead to more insightful analysis and informed decision-making.
- Pattern Recognition: B-maps facilitate the identification of clusters, outliers, and other patterns within the data. This can be particularly useful for tasks like anomaly detection, market segmentation, and social network analysis.
- Data Exploration and Discovery: B-maps provide a powerful tool for exploratory data analysis, enabling users to discover unexpected relationships and insights. This can lead to new hypotheses and avenues for further investigation.
Applications of B-maps in Diverse Fields:
B-maps find applications across various fields, including:
- Business Analytics: Understanding customer behavior, market trends, and supply chain dynamics.
- Social Network Analysis: Identifying influential nodes, community structures, and information flow in social networks.
- Bioinformatics: Studying protein-protein interactions, gene regulatory networks, and disease pathways.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing ecological networks, climate change impacts, and resource management.
- Cybersecurity: Detecting malicious activity, identifying network vulnerabilities, and understanding threat actors.
Creating Effective B-maps:
While the concept of B-maps is straightforward, creating effective visualizations requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Data Selection: Choose relevant data that accurately represents the phenomenon being studied.
- Relationship Definition: Clearly define the relationships between data points and represent them appropriately through edges.
- Attribute Selection: Choose attributes that provide meaningful insights and contribute to the overall understanding of the data.
- Visualization Techniques: Select appropriate visualization techniques to effectively communicate the data structure and patterns.
- Interactive Exploration: Allow users to interact with the B-map, zooming in on specific areas, filtering data, and exploring different perspectives.
FAQs about B-maps:
Q: What are the limitations of B-maps?
A: While B-maps offer a powerful tool for data visualization, they have limitations:
- Complexity: Large and complex datasets can lead to cluttered and difficult-to-interpret B-maps.
- Data Quality: The quality of the input data directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the B-map.
- Subjectivity: The interpretation of B-maps can be subjective, depending on the user’s perspective and analytical approach.
Q: How can I create B-maps?
A: Several software tools and libraries can be used to create B-maps, including:
- Gephi: A free and open-source visualization software for network and graph analysis.
- Cytoscape: A popular platform for visualizing complex networks and biological pathways.
- NetworkX: A Python library for creating, manipulating, and analyzing networks.
Q: How can I learn more about B-maps?
A: There are numerous resources available for learning more about B-maps, including:
- Online tutorials: Search for tutorials on platforms like YouTube and Coursera.
- Books and articles: Explore books and articles on data visualization, network analysis, and graph theory.
- Online communities: Engage with communities on platforms like Stack Overflow and Reddit to exchange knowledge and learn from others.
Tips for Effective B-map Creation:
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the B-map and the insights you want to extract from the data.
- Choose the right visualization techniques: Select techniques that best represent the relationships and patterns within the data.
- Use color and size effectively: Employ color and size variations to highlight important nodes, edges, and attributes.
- Maintain clarity and simplicity: Avoid cluttering the B-map with excessive information or unnecessary details.
- Provide context and labels: Include labels and explanations to guide users in interpreting the visualization.
Conclusion:
B-maps offer a powerful tool for navigating the complexities of data, revealing hidden relationships and patterns that can lead to deeper insights and informed decision-making. Their ability to visualize data structures and dependencies makes them invaluable across various fields, enabling users to explore data in new ways and extract meaningful information. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, B-maps will play an increasingly important role in unlocking the potential of data and driving innovation across diverse disciplines.
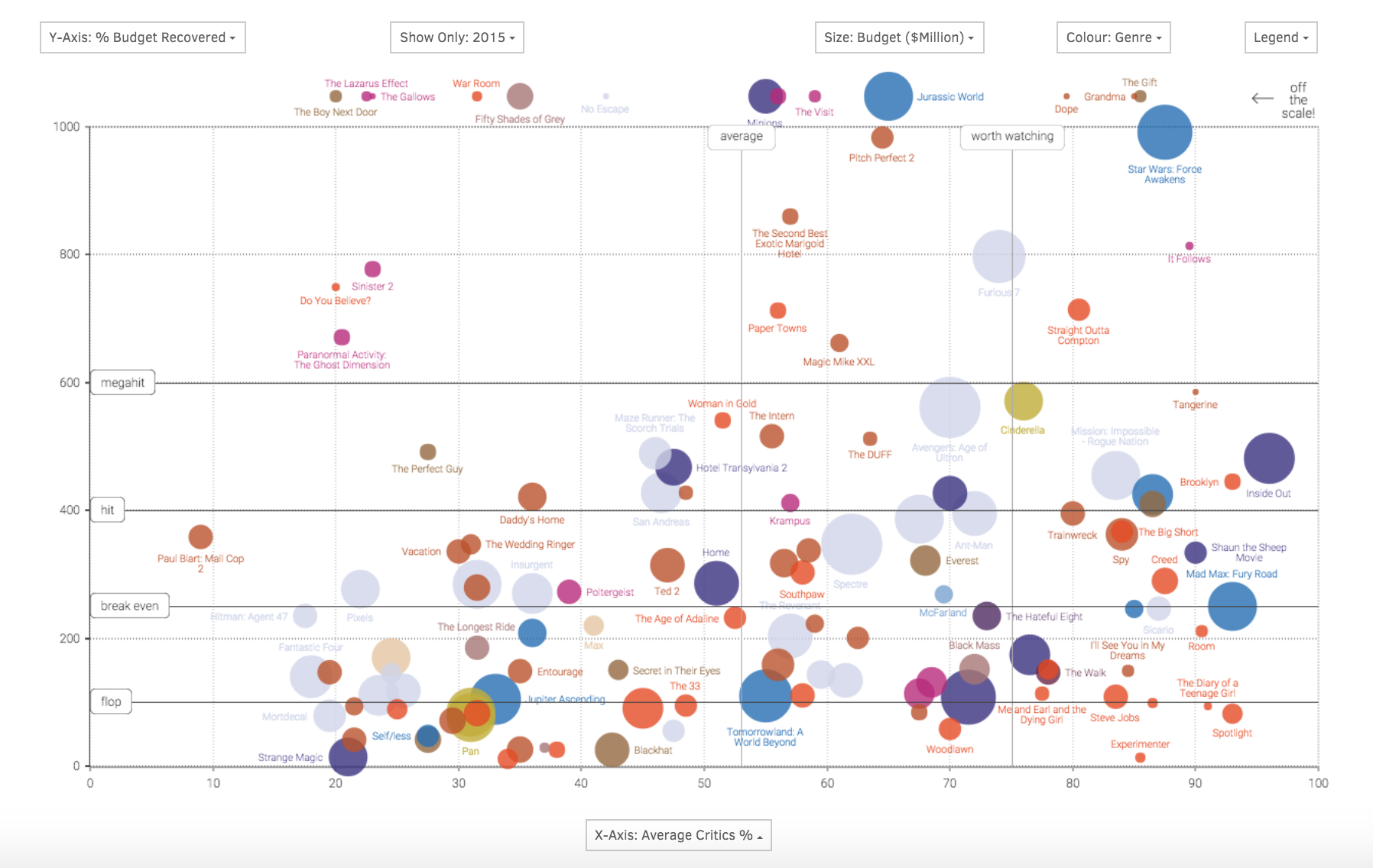

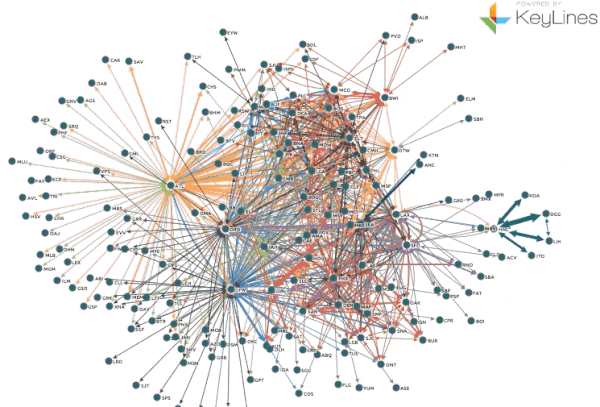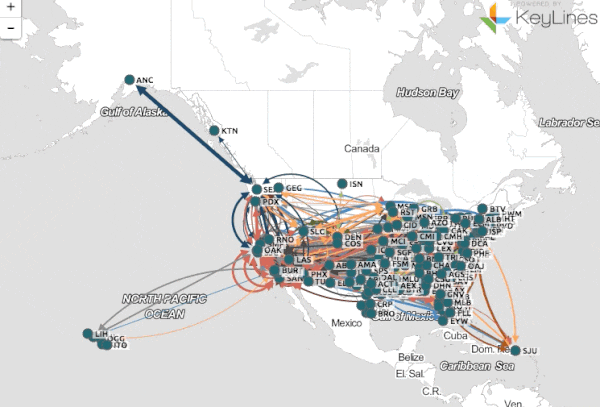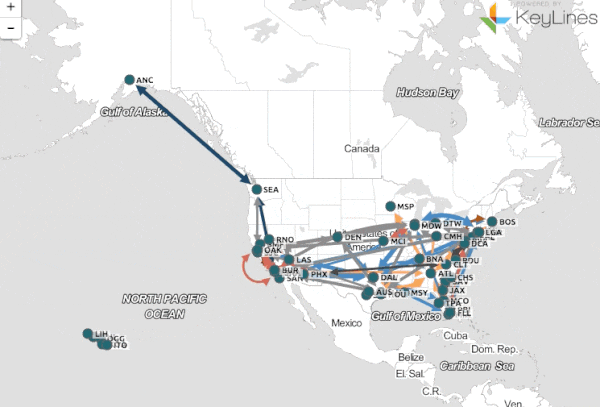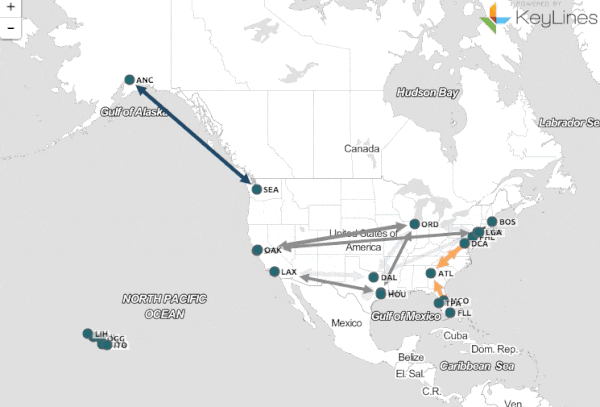



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Mapping: Navigating the Complexities of Data with B-Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
