The Power of Open Data: Navigating the World with Free and Accessible Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Open Data: Navigating the World with Free and Accessible Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Open Data: Navigating the World with Free and Accessible Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Open Data: Navigating the World with Free and Accessible Maps
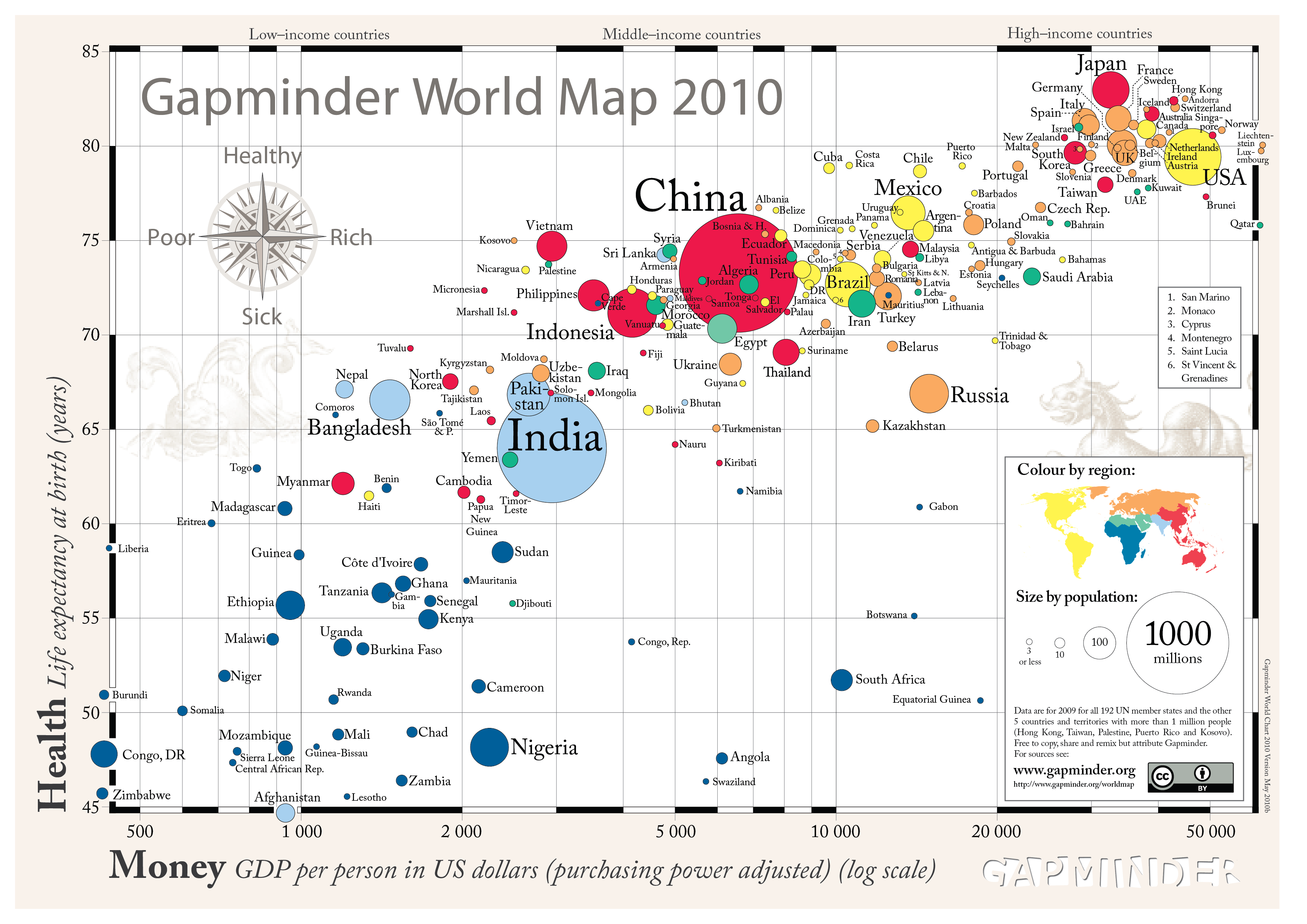
In the digital age, access to information is paramount. This is particularly true in the realm of geographic data, which underpins countless applications, from navigation and urban planning to environmental monitoring and disaster response. The concept of "free and open maps" is not merely a technical detail, but a powerful tool for empowering individuals, businesses, and governments alike. This article explores the significance of open map data, its various applications, and the benefits it offers to society.
Understanding Open Map Data
Open map data refers to geographic information that is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute. It stands in contrast to proprietary map data, which is often restricted by licensing agreements and may come at a significant cost. The principles of open data advocate for transparency, accessibility, and collaboration, fostering innovation and promoting a more equitable access to geographic information.
The Foundations of Open Map Data
The foundation of open map data rests on several key principles:
- Open Licensing: Open map data is typically released under open licenses, such as the Open Database License (ODbL) or Creative Commons licenses. These licenses allow for free use, modification, and distribution, fostering a collaborative environment for data sharing and improvement.
- Open Standards: Open map data adheres to open standards, such as GeoJSON, KML, and Shapefile formats. This ensures interoperability and allows different applications and platforms to easily access and process the data.
- Community Collaboration: Open map data thrives on community contributions. Individuals, organizations, and governments can contribute to the data, ensuring its accuracy, completeness, and relevance.
Benefits of Open Map Data
The availability of open map data offers numerous benefits, ranging from individual empowerment to societal progress:
- Enhanced Navigation and Location Services: Open map data empowers individuals to navigate their surroundings with greater ease. It fuels the development of mapping applications, providing accurate and up-to-date information on roads, landmarks, and points of interest.
- Improved Urban Planning and Development: Open map data enables planners and developers to gain insights into urban landscapes, facilitating informed decisions regarding infrastructure development, transportation planning, and resource allocation.
- Environmental Monitoring and Conservation: Open map data allows researchers and environmental organizations to monitor environmental changes, track deforestation, and manage natural resources effectively.
- Disaster Response and Emergency Management: In times of crisis, open map data plays a crucial role in facilitating relief efforts. It provides real-time information on affected areas, infrastructure damage, and evacuation routes, enabling swift and efficient response.
- Economic Development and Innovation: Open map data fuels innovation and economic growth. It empowers businesses to develop location-based services, optimize logistics, and target specific customer segments.
Examples of Open Map Data Initiatives
The concept of open map data has gained considerable traction, resulting in a plethora of initiatives aimed at promoting its use:
- OpenStreetMap (OSM): OSM is a collaborative project that produces a free and open map of the world. It relies on contributions from volunteers who collect and edit data, making it one of the most comprehensive and widely used open map data sources.
- OpenStreetMap Foundation: The OpenStreetMap Foundation is a non-profit organization dedicated to supporting the development and promotion of OpenStreetMap. It provides resources, infrastructure, and legal support to the OSM community.
- GeoNode: GeoNode is an open-source platform for managing and sharing geospatial data. It enables users to publish, edit, and access open map data, fostering collaboration and data exchange.
- Government Open Data Initiatives: Many governments around the world have embraced open data principles, releasing a wide range of geographic data, including maps of infrastructure, demographics, and environmental data.
FAQs on Open Map Data
1. Is open map data accurate and reliable?
While open map data is generally accurate and reliable, its quality can vary depending on the source and level of community involvement. However, the collaborative nature of open map data initiatives allows for continuous improvement through community contributions and validation.
2. How can I contribute to open map data?
Contributing to open map data initiatives is relatively straightforward. Users can contribute by:
- Editing and correcting existing data: Users can identify and correct inaccuracies in existing maps through online platforms like OpenStreetMap.
- Adding new data: Users can contribute new data, such as points of interest, road closures, or building footprints.
- Supporting the development of tools and resources: Users can contribute to the development of open-source tools and resources that enhance the usability and accessibility of open map data.
3. Are there any limitations to using open map data?
While open map data offers significant benefits, it also has some limitations:
- Data completeness: The completeness of open map data can vary depending on the region and the level of community involvement.
- Data accuracy: While open map data is generally accurate, it can be prone to errors, especially in areas with low community involvement.
- Data currency: Open map data is constantly being updated, but it may not always reflect the most recent changes.
Tips for Utilizing Open Map Data
- Choose the right data source: Selecting the appropriate data source is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and relevance of the information. Consider the purpose of your project and the specific geographic area of interest.
- Understand data formats and standards: Familiarize yourself with the various data formats and standards used for open map data. This will enable you to effectively process and utilize the information.
- Utilize available tools and resources: There are numerous open-source tools and resources available for working with open map data. Explore these options to streamline your workflow and enhance your data analysis capabilities.
Conclusion
Open map data is a powerful tool for empowering individuals, businesses, and governments. It fosters innovation, promotes transparency, and enables informed decision-making across a wide range of sectors. By embracing the principles of open data, we can unlock the full potential of geographic information, paving the way for a more connected, sustainable, and equitable future.





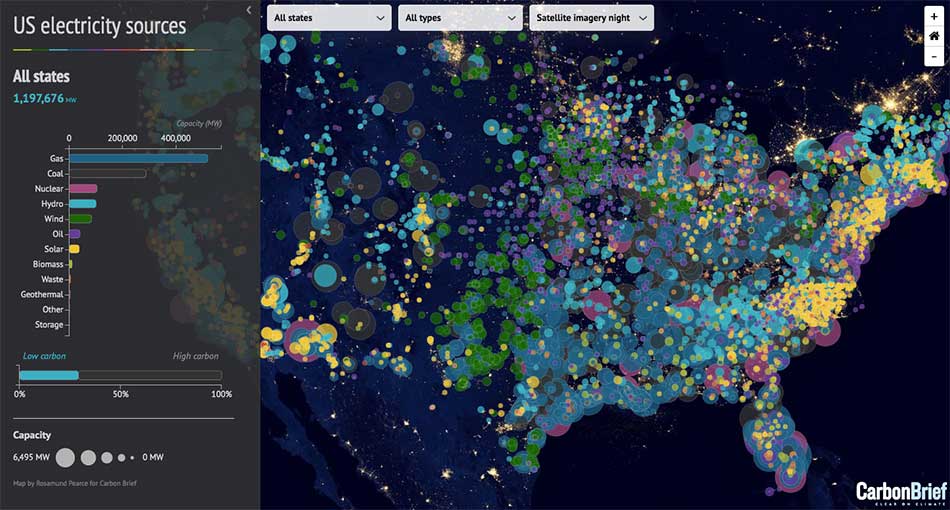
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Open Data: Navigating the World with Free and Accessible Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
