The Power of Scale: Understanding the Influence of Map Scale in Cartography
Related Articles: The Power of Scale: Understanding the Influence of Map Scale in Cartography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Scale: Understanding the Influence of Map Scale in Cartography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Scale: Understanding the Influence of Map Scale in Cartography

Maps are powerful tools that allow us to navigate the world, understand spatial relationships, and visualize complex data. However, the effectiveness of a map hinges on a crucial element: its scale. Map scale, the ratio between a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground, dictates how much detail a map can display and influences its intended use. This article explores the multifaceted influence of map scale, highlighting its crucial role in cartography and its impact on various applications.
Defining Map Scale: A Foundation for Understanding
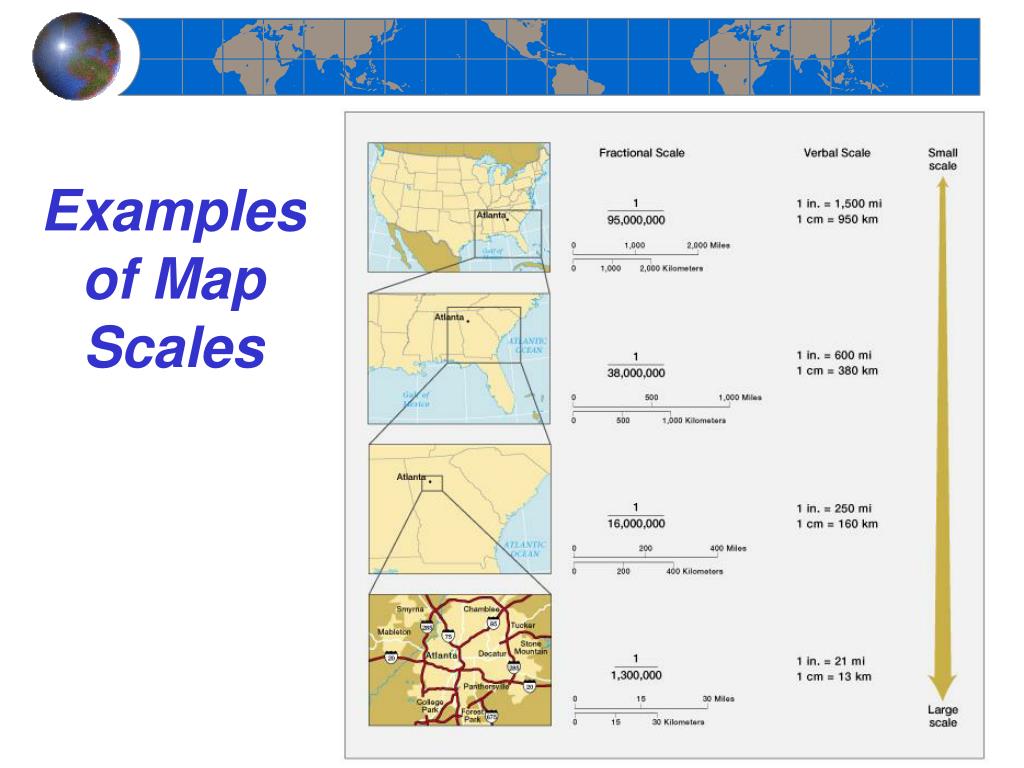
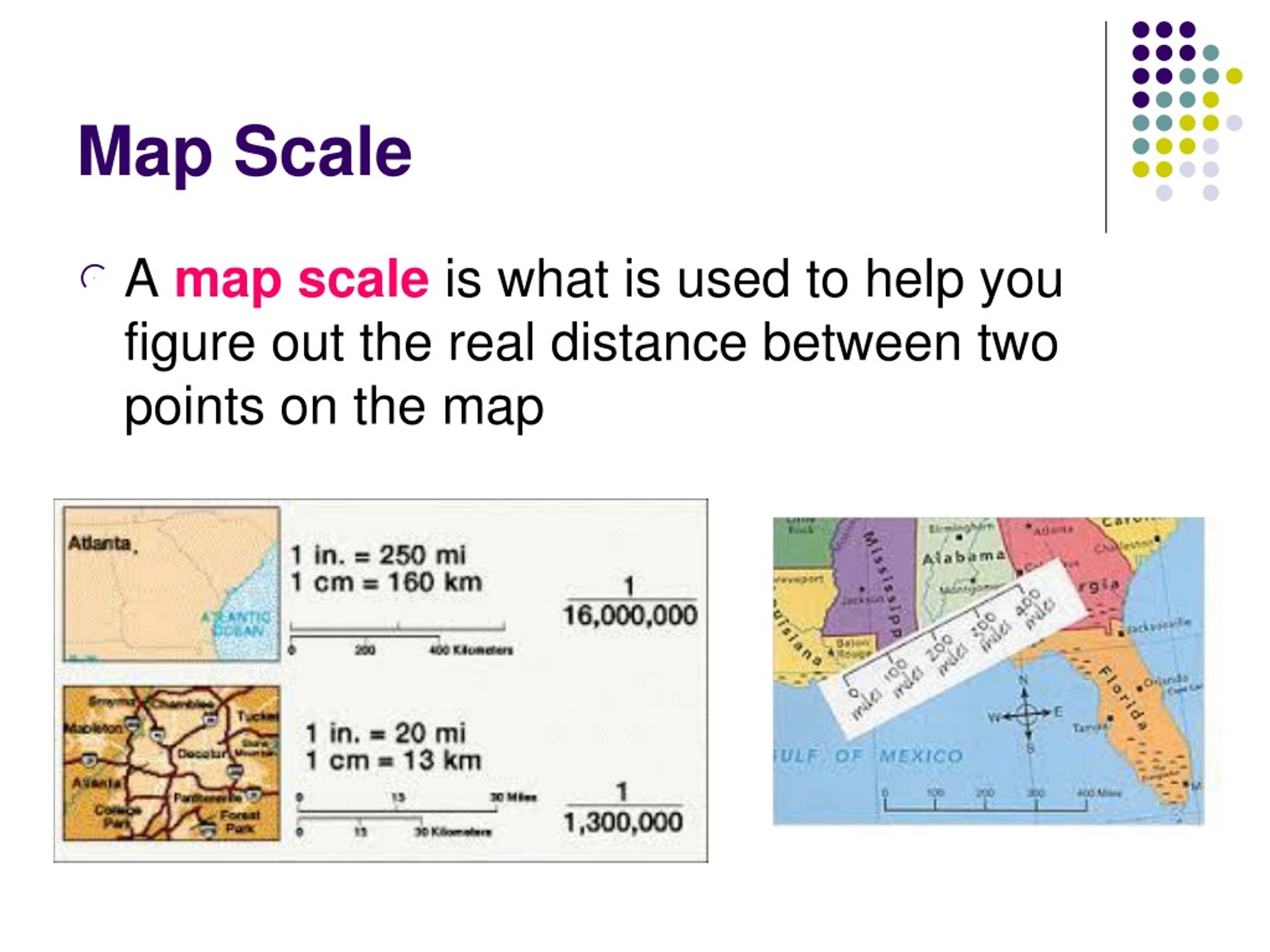
Map scale is expressed in three primary ways:
- Verbal Scale: A simple statement describing the relationship, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): A ratio of map distance to ground distance, typically written as a fraction like 1:100,000. This indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: A visual representation of the scale using a bar marked with distances corresponding to real-world distances.
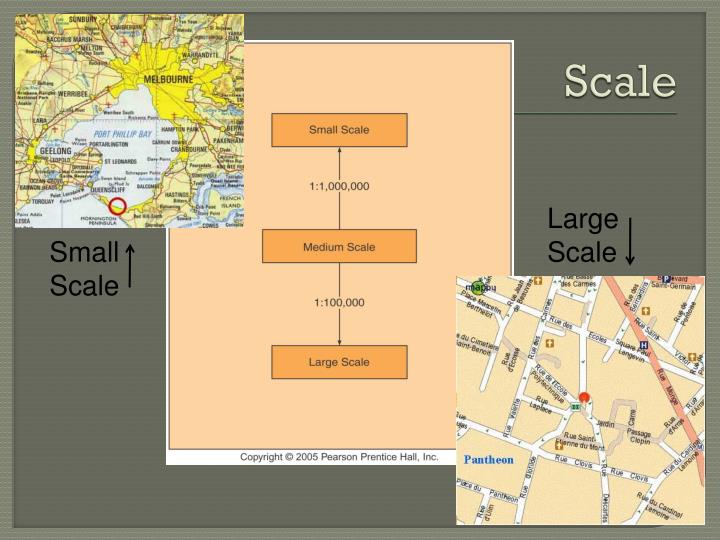
Understanding map scale is crucial for interpreting the information presented on a map. A map with a large scale (e.g., 1:10,000) represents a small area in great detail, while a map with a small scale (e.g., 1:1,000,000) encompasses a larger region but with less detail. This fundamental concept underlies the diverse influence of map scale on various aspects of cartography.
The Influence of Map Scale: Shaping the Scope and Detail of Maps
1. Level of Detail:
The most direct influence of map scale is on the level of detail that can be displayed. Large-scale maps, with their smaller areas of representation, can depict intricate features like individual buildings, street names, and even specific vegetation. Conversely, small-scale maps, due to their larger coverage, are forced to generalize features, often representing cities as points, rivers as lines, and forests as shaded areas.
2. Purpose and Application:
The intended use of a map dictates its appropriate scale. For instance, a detailed street map designed for navigation would employ a large scale to accurately depict street networks and landmarks. Conversely, a world map, intended for a general overview of global geography, necessitates a small scale to encompass the entire Earth.
3. Data Representation:
Map scale influences the choice of data representation methods. Large-scale maps can incorporate detailed geographic data, including topographic contours, elevation data, and even 3D models. Small-scale maps, however, require simplified representations, often relying on color gradients, symbols, and statistical data to convey information about large areas.
4. Cartographic Generalization:
The process of cartographic generalization, simplifying features to fit the scale of a map, is heavily influenced by map scale. As scale decreases, generalization becomes more pronounced, requiring decisions about which features to omit, simplify, or merge. This process ensures that maps remain legible and avoid overcrowding while still conveying essential information.
5. Accuracy and Distortion:
The Earth’s spherical shape presents challenges for accurately representing it on a flat map. All map projections introduce some form of distortion, and the degree of distortion is influenced by map scale. Large-scale maps, covering smaller areas, exhibit less distortion, while small-scale maps, encompassing larger areas, necessitate more significant compromises in accuracy.
6. Visual Communication:
Map scale plays a crucial role in visual communication. The choice of scale can influence the reader’s perception of distance, area, and the relative importance of different features. A large-scale map can emphasize the density of urban areas, while a small-scale map can highlight the vastness of deserts or oceans.
The Benefits of Understanding Map Scale:
- Effective Map Interpretation: Understanding map scale allows users to accurately interpret the information presented, recognizing the limitations of detail and generalization at different scales.
- Informed Map Selection: Knowing the appropriate scale for a specific purpose enables users to choose maps that meet their needs, ensuring relevant information is available.
- Critical Analysis of Cartographic Representations: Understanding the influence of scale allows users to critically analyze maps, recognizing potential biases and distortions inherent in cartographic generalization.
- Enhanced Spatial Reasoning: Familiarity with map scale fosters spatial reasoning skills, allowing users to visualize and understand spatial relationships more effectively.
FAQs Regarding Map Scale Influence:
1. What are the limitations of using a small-scale map for navigation?
Small-scale maps lack the detail necessary for precise navigation. They may not depict specific streets, landmarks, or local features needed for accurate route planning.
2. Can a large-scale map be used to understand global trends?
Large-scale maps are not suitable for analyzing global trends due to their limited spatial coverage. They focus on localized details rather than broader patterns.
3. How does map scale affect the accuracy of representing elevation?
Large-scale maps can incorporate detailed elevation data, allowing for precise representations of topographic features. Small-scale maps, however, often use generalized contour lines or shading, leading to less accurate elevation depictions.
4. Why is it important to consider the map projection when interpreting map scale?
Different map projections distort the Earth’s surface in different ways, influencing the accuracy of distances and areas. Understanding the projection used for a map is crucial for correctly interpreting its scale.
5. What are the implications of using a map with a scale that is too small for the intended purpose?
Using a map with a scale that is too small can lead to misinterpretation, inaccurate navigation, and a lack of essential detail for the intended task.
Tips for Using Map Scale Effectively:
- Always check the scale of a map before using it. Understanding the scale helps you interpret the information correctly and avoid misinterpretations.
- Choose the appropriate scale for your needs. Select a map with a scale that provides the level of detail necessary for your specific task.
- Be aware of the limitations of different scales. Recognize that small-scale maps generalize features, while large-scale maps offer more detail but cover smaller areas.
- Use different scales to analyze different aspects of a region. Combining maps with varying scales can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a place.
- Consider the intended audience when choosing a map scale. The level of detail and complexity should be appropriate for the target audience’s understanding and needs.
Conclusion:
Map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, profoundly influencing the representation of spatial information. It dictates the level of detail, purpose, and accuracy of maps, impacting their effectiveness in communication, navigation, and data analysis. Understanding the influence of map scale empowers users to interpret maps critically, make informed choices about map selection, and utilize these powerful tools effectively for various applications. As we continue to explore and understand our world, the ability to interpret and utilize map scale remains a vital skill for navigating the complexities of spatial information.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Scale: Understanding the Influence of Map Scale in Cartography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
