The Power of Visual Thinking: Understanding and Utilizing Concept Mapping
Related Articles: The Power of Visual Thinking: Understanding and Utilizing Concept Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visual Thinking: Understanding and Utilizing Concept Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visual Thinking: Understanding and Utilizing Concept Mapping
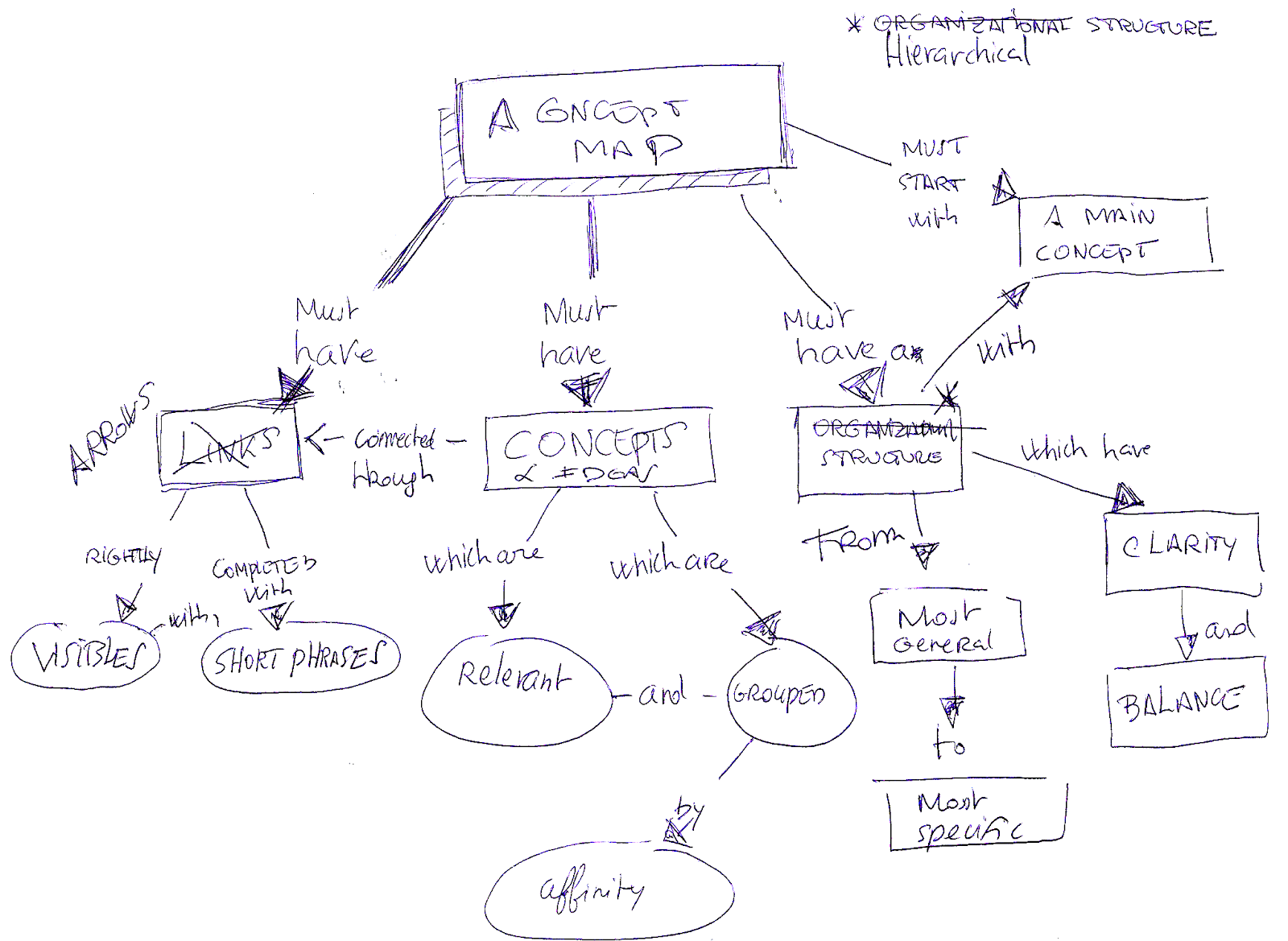
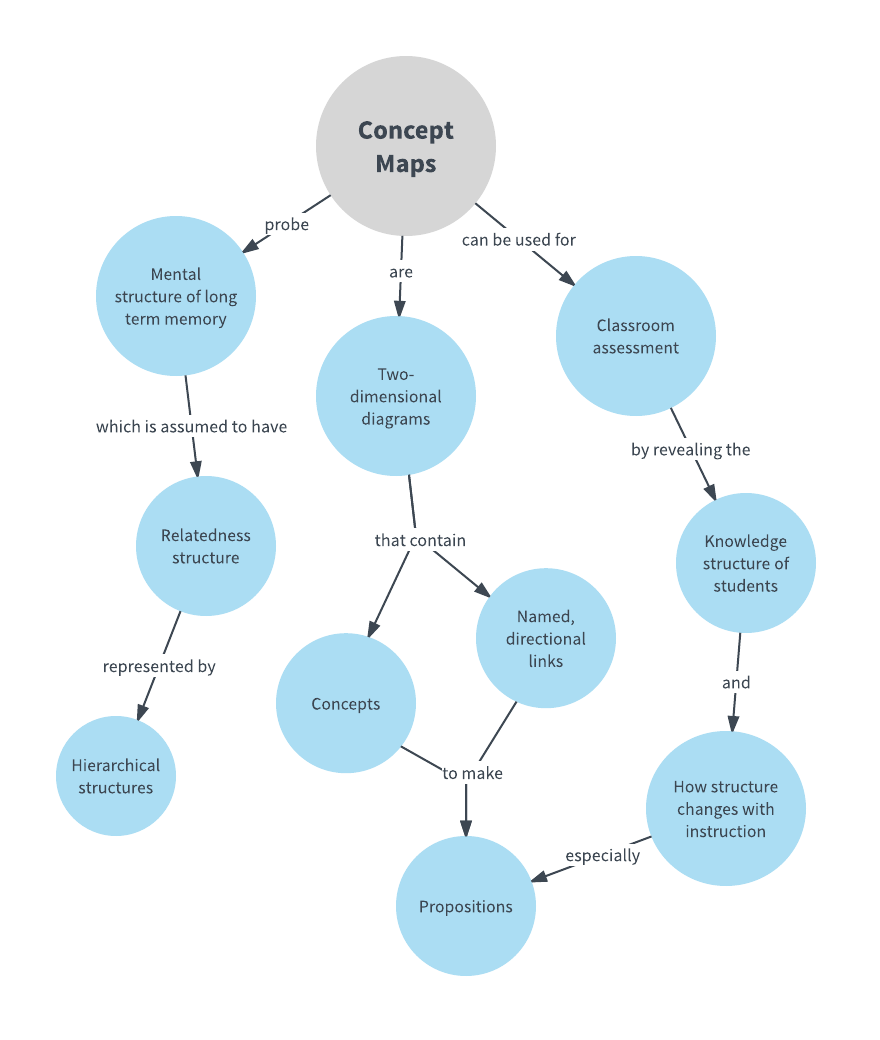
Concept mapping, a visual representation of knowledge, has emerged as a powerful tool for organizing, understanding, and communicating complex information. This technique, which utilizes nodes and connecting lines to illustrate relationships between concepts, has found applications across diverse fields, from education and research to business and personal development.
The Essence of Concept Mapping
At its core, concept mapping is a method of visually representing knowledge structures. It involves breaking down complex information into smaller, interconnected concepts, each represented by a node. These nodes are then linked together using lines, each signifying a specific relationship between the concepts. The result is a visually appealing and easily digestible representation of the information, revealing the underlying connections and hierarchical relationships.
Key Components of a Concept Mapping Diagram
A typical concept map comprises the following elements:
- Nodes: These are the central components of a concept map, representing individual concepts or ideas. They can be words, phrases, or even images, depending on the complexity of the information being mapped.
- Links: These lines connect the nodes, signifying the relationships between them. Each link is labeled with a verb or preposition, indicating the nature of the connection.
- Hierarchy: Concept maps often exhibit a hierarchical structure, with more general concepts at the top and more specific concepts branching out downwards. This hierarchical arrangement helps in understanding the flow of information and the relationships between different levels of abstraction.
- Cross-links: These links connect nodes that are not directly related in the hierarchical structure but share a common connection. They help to reveal hidden relationships and create a more comprehensive understanding of the information.
The Benefits of Concept Mapping
Concept mapping offers a multitude of benefits, making it an invaluable tool for various purposes:
- Enhanced Understanding: By visually representing complex information, concept maps facilitate deeper comprehension and retention. The interconnected nature of the nodes and links allows for a holistic understanding of the topic, revealing connections that might otherwise remain hidden.
- Improved Learning: Concept mapping promotes active learning by encouraging students to engage with the material, analyze relationships, and synthesize information. The process of creating a concept map itself reinforces learning and helps in identifying areas of confusion or gaps in knowledge.
- Effective Communication: Concept maps provide a clear and concise way to communicate complex information to others. Their visual nature makes them easily accessible and understandable, facilitating effective knowledge sharing and collaboration.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: Concept mapping can be a valuable tool for problem-solving and decision-making. By visually representing the problem, its components, and potential solutions, concept maps enable a structured approach to identifying the most effective course of action.
- Creativity and Innovation: Concept mapping encourages creative thinking and brainstorming by fostering connections between seemingly unrelated ideas. The visual representation of concepts allows for a more flexible and open approach to problem-solving and idea generation.
Applications of Concept Mapping
The versatility of concept mapping extends across various domains:
- Education: Concept mapping is widely used in classrooms to enhance student understanding, promote active learning, and facilitate knowledge retention. It is particularly effective for teaching complex subjects like science, history, and literature.
- Research: Researchers utilize concept maps to organize research findings, identify gaps in knowledge, and develop new hypotheses. They can also be used to create literature reviews, visualize research methodologies, and communicate research results effectively.
- Business: Concept mapping is employed in business for strategic planning, problem-solving, decision-making, and project management. It helps in identifying key stakeholders, analyzing market trends, and developing effective marketing strategies.
- Personal Development: Concept mapping can be used for personal goal setting, planning, and reflection. It allows individuals to visualize their aspirations, break them down into smaller steps, and track their progress.
FAQs About Concept Mapping
1. What are the different types of concept maps?
Concept maps can be categorized based on their structure and purpose. Common types include:
- Hierarchical Maps: These maps exhibit a hierarchical structure, with more general concepts at the top and more specific concepts branching out downwards.
- Spider Maps: These maps radiate outward from a central concept, with related concepts branching out in different directions.
- Flow Maps: These maps illustrate the flow of information or processes, showing the sequence of events or steps.
- Matrix Maps: These maps use a grid format to represent relationships between concepts along two or more dimensions.
2. How do I create a concept map?
Creating a concept map involves a series of steps:
- Identify the central concept: Begin by identifying the main topic or idea that you want to map.
- Brainstorm related concepts: Generate a list of concepts related to the central concept.
- Organize concepts hierarchically: Arrange the concepts in a hierarchical structure, with more general concepts at the top and more specific concepts branching out downwards.
- Connect concepts with links: Use lines to connect the nodes, labeling each link with a verb or preposition indicating the relationship between the concepts.
- Refine and revise: Review the map and refine it as needed, adding or removing concepts, adjusting the hierarchy, and clarifying the relationships between concepts.
3. What are some tools for creating concept maps?
There are numerous software tools available for creating concept maps, both online and offline. Popular options include:
- CmapTools: This free and open-source software allows for collaborative concept mapping, offering features like hierarchical mapping, cross-linking, and image integration.
- MindManager: This commercial software offers a wide range of features, including mind mapping, concept mapping, and project planning.
- XMind: This software provides a user-friendly interface for creating concept maps, with features like freehand drawing, templates, and collaboration capabilities.
- FreeMind: This free and open-source software focuses on mind mapping, but it also supports concept mapping with features like hierarchical mapping and cross-linking.
Tips for Effective Concept Mapping
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the concept map before you begin.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overloading the map with too much information.
- Use clear and concise language: Choose words and phrases that are easily understood.
- Use visual cues: Incorporate images, symbols, and colors to enhance the map’s visual appeal and clarity.
- Review and revise: Don’t be afraid to revise the map as needed to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Concept mapping is a powerful tool for organizing, understanding, and communicating complex information. Its visual nature and ability to reveal hidden relationships make it an effective method for learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Whether used in education, research, business, or personal development, concept mapping can significantly enhance our ability to process information, generate ideas, and communicate effectively. By embracing the power of visual thinking, we can unlock new insights and achieve greater clarity in a world overflowing with complex information.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visual Thinking: Understanding and Utilizing Concept Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
