The Role of Data Management in Modern Business: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Role of Data Management in Modern Business: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Role of Data Management in Modern Business: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Role of Data Management in Modern Business: A Comprehensive Overview

In today’s digital age, data has become the lifeblood of businesses. From understanding customer preferences to optimizing operations, data plays a crucial role in driving informed decision-making and achieving strategic goals. However, harnessing the power of data effectively requires a robust and efficient data management framework. This is where the concept of a "data management and analysis platform" (DMAP) comes into play.
A DMAP acts as a centralized hub for data collection, storage, processing, and analysis, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights from their data assets. It encompasses a wide range of tools and technologies that facilitate data governance, integration, transformation, and visualization, ultimately empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Understanding the Importance of Data Management:
Data management is not merely about storing information; it’s about ensuring data quality, accessibility, and security. A well-structured data management system offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights provide a foundation for informed and strategic decision-making, leading to better outcomes and reduced risks.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Understanding customer behavior and preferences through data analysis enables businesses to personalize interactions, improve customer satisfaction, and foster loyalty.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Data can be used to optimize processes, identify bottlenecks, and improve resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Competitive Advantage: Utilizing data effectively allows businesses to gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends, developing innovative products and services, and anticipating customer needs.
- Compliance and Security: Data management systems help ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards, safeguarding sensitive information and protecting against data breaches.
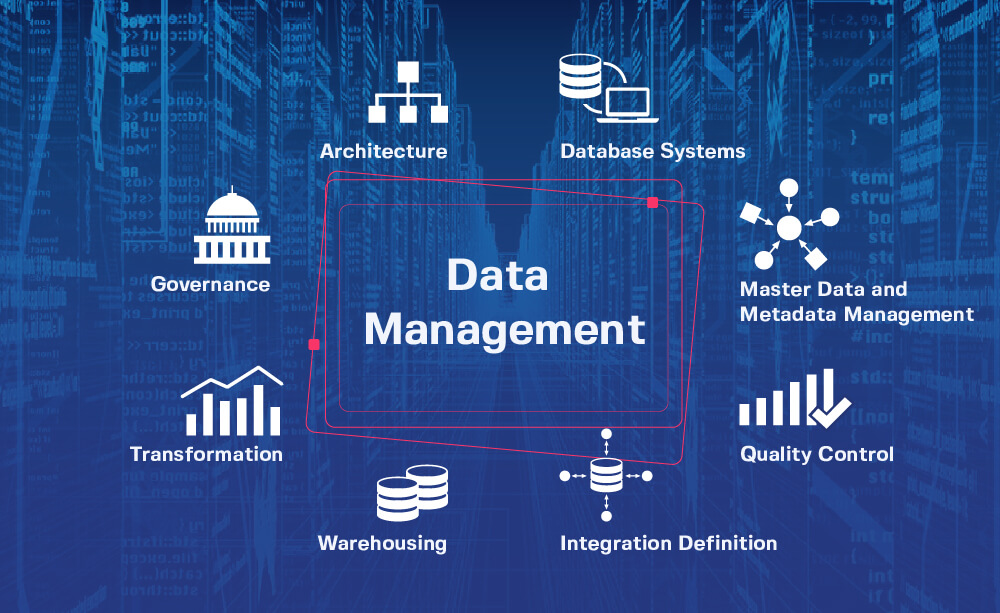
A Deep Dive into the Components of a DMAP:
A comprehensive DMAP typically comprises several key components, each contributing to the overall data management ecosystem:
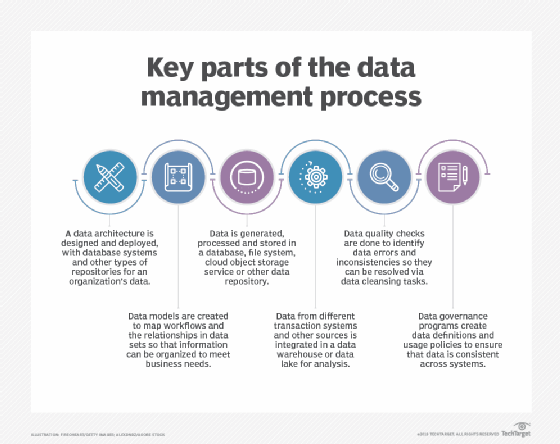
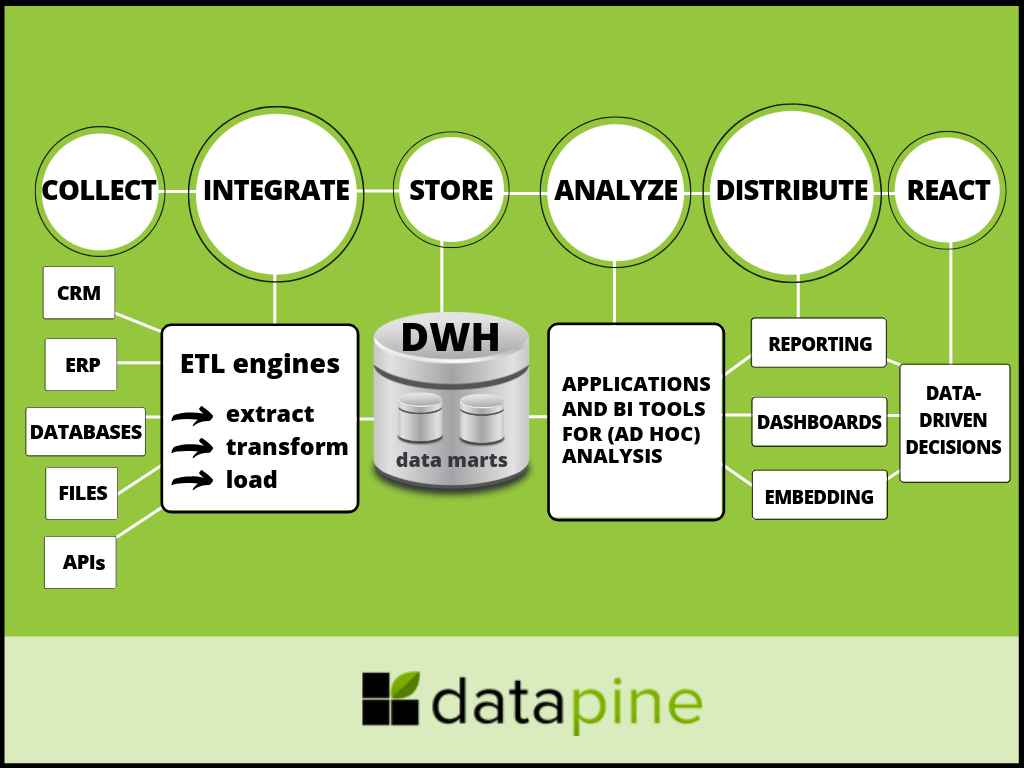
- Data Acquisition: This stage involves gathering data from various sources, including internal databases, external APIs, social media, and other relevant channels. Data acquisition tools ensure consistent and reliable data capture.
- Data Storage: Once acquired, data needs to be stored securely and efficiently. DMAPs utilize various storage solutions, such as relational databases, data warehouses, and cloud storage platforms, depending on the specific requirements.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from disparate sources is crucial for creating a unified view. DMAPs employ integration tools and techniques to harmonize data formats, structures, and schemas, ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
- Data Transformation: Raw data often requires transformation before it can be analyzed effectively. DMAPs include data cleansing, transformation, and enrichment capabilities to prepare data for analysis and reporting.
- Data Analysis: DMAPs provide advanced analytical tools and techniques for exploring data patterns, identifying trends, and generating insights. These tools can range from basic statistical analysis to sophisticated machine learning algorithms.
- Data Visualization: Visualizing data through charts, graphs, and dashboards helps communicate insights effectively and facilitates data exploration. DMAPs offer various visualization tools to present data in a clear and compelling manner.
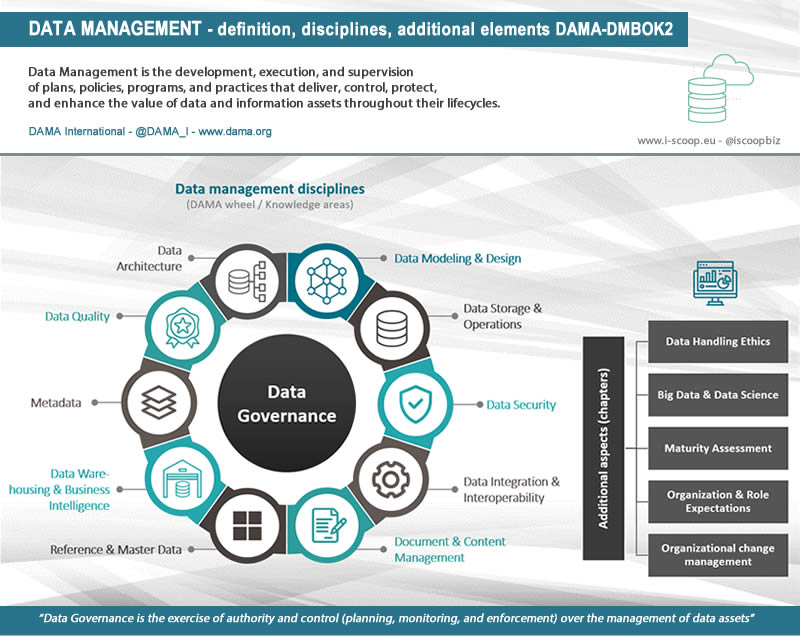
- Data Governance: Effective data management requires strong governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality, security, and compliance. DMAPs include tools for data access control, auditing, and data lineage tracking.
Leveraging DMAPs for Strategic Advantage:
By implementing a robust DMAP, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data assets and gain a significant competitive advantage. Here are some specific examples of how DMAPs can be leveraged for strategic purposes:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): DMAPs enable businesses to collect and analyze customer data, understand their needs and preferences, and personalize marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement and loyalty.
- Supply Chain Management: Data from various sources, such as suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers, can be integrated and analyzed to optimize inventory levels, improve delivery times, and reduce costs.
- Financial Analysis: DMAPs can help businesses track financial performance, identify trends, and make informed investment decisions. Data analysis can also be used to detect fraud and prevent financial risks.
- Product Development: Understanding customer feedback and market trends through data analysis can guide product development efforts, leading to the creation of innovative and successful products.
- Risk Management: DMAPs can be used to monitor risks, identify potential threats, and develop proactive mitigation strategies, enhancing overall business resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: What are the key considerations when choosing a DMAP?
A1: When selecting a DMAP, it is crucial to consider factors such as:
- Scalability: The platform should be able to handle growing data volumes and evolving business requirements.
- Security: Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Integration Capabilities: The DMAP should seamlessly integrate with existing systems and data sources.
- User-friendliness: The platform should be easy to use and navigate for both technical and non-technical users.
- Cost-effectiveness: The DMAP should provide a reasonable return on investment and align with the organization’s budget.
Q2: How can I ensure the success of my DMAP implementation?
A2: Successful DMAP implementation requires a well-defined strategy and a collaborative approach. Key steps include:
- Clear Business Objectives: Define clear goals and objectives for the DMAP implementation.
- Data Governance Framework: Establish a robust data governance framework to ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
- User Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to effectively leverage the DMAP.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly monitor the DMAP performance and identify areas for improvement.
Tips for Effective Data Management:
- Data Quality is Paramount: Invest in data quality initiatives to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
- Embrace Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies and procedures to ensure data integrity and compliance.
- Foster Data Literacy: Promote data literacy within the organization to empower employees to utilize data effectively.
- Leverage Automation: Utilize automation tools to streamline data management processes and improve efficiency.
- Stay Updated with Emerging Technologies: Keep abreast of advancements in data management technologies to enhance capabilities and gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion:
In the data-driven world, effective data management is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for business success. A well-designed and implemented DMAP provides the foundation for harnessing the power of data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive advantage. By embracing data management principles, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data assets and drive sustainable growth in the digital age.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Role of Data Management in Modern Business: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
