The Second Battle of Bull Run: A Turning Point in the American Civil War
Related Articles: The Second Battle of Bull Run: A Turning Point in the American Civil War
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Second Battle of Bull Run: A Turning Point in the American Civil War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Second Battle of Bull Run: A Turning Point in the American Civil War

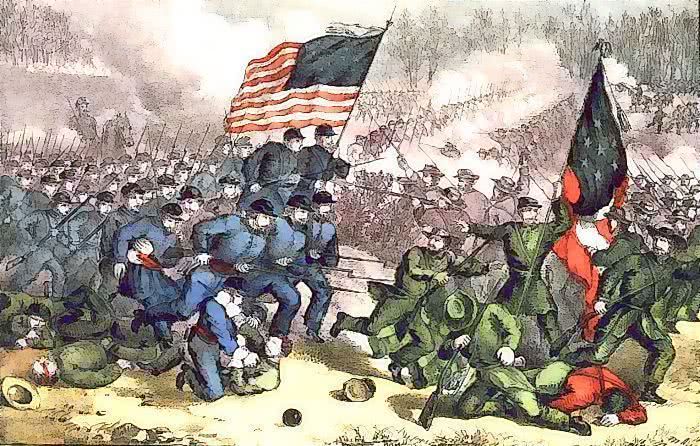
The Second Battle of Bull Run, also known as the Battle of Manassas, was a pivotal engagement in the American Civil War, fought on August 29-30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia. This battle marked a significant turning point in the war, shattering Union hopes for a swift victory and bolstering Confederate morale. The strategic importance of the battle is reflected in its enduring presence in historical narratives and its lasting impact on the course of the war.
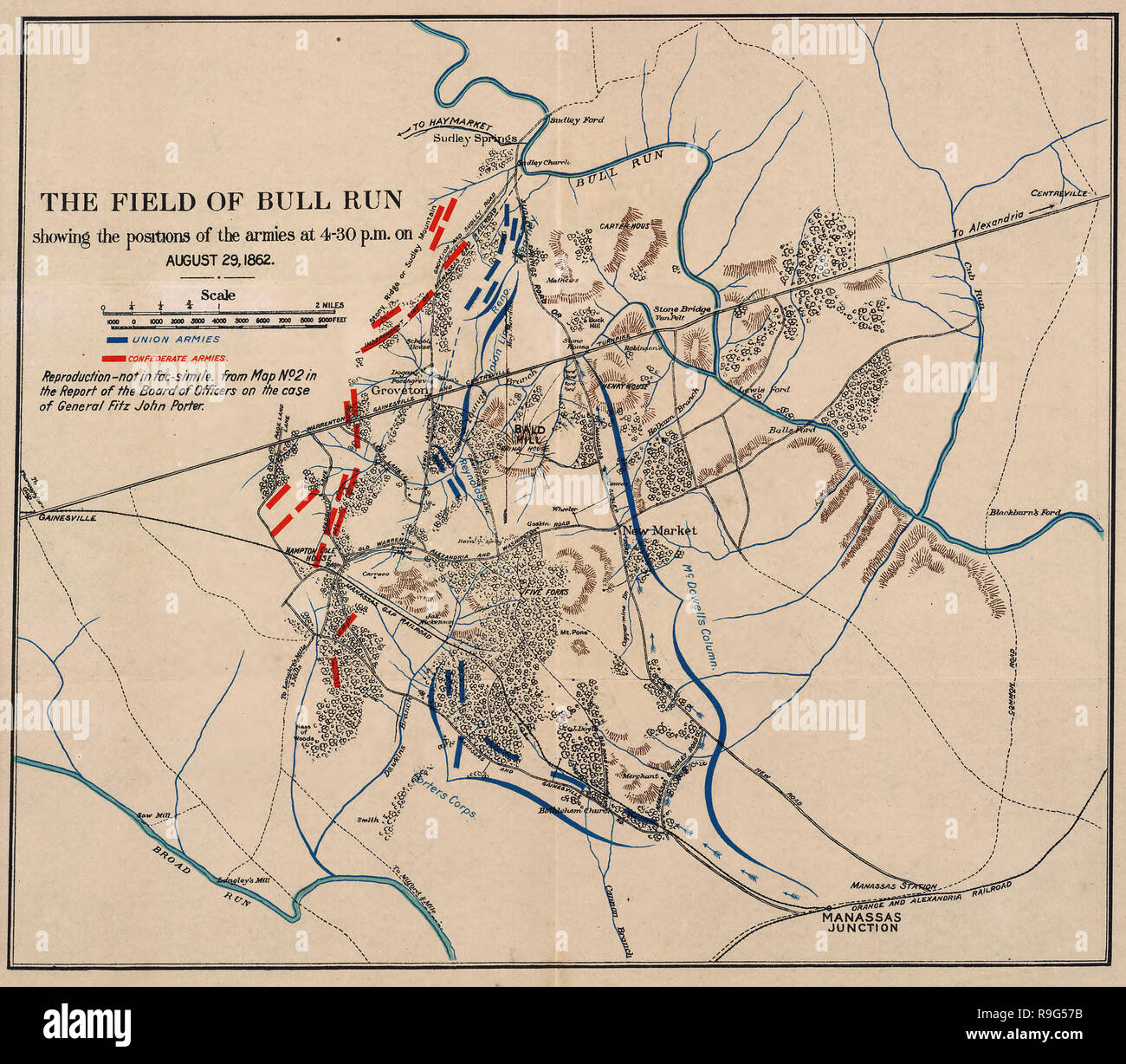
Understanding the Battlefield: A Map as a Window to History
To truly comprehend the Second Battle of Bull Run, a visual understanding of the battlefield is essential. A map of the area reveals the strategic significance of the terrain and the movements of both armies. The battle unfolded across a sprawling landscape, with the key geographical features playing a crucial role in the unfolding events.
- The Bull Run River: This natural barrier served as a strategic point for both armies, with the Union forces initially aiming to cross it and establish a foothold on the Confederate side.
- Henry House Hill: This prominent hill, located on the Confederate side of the Bull Run River, became a focal point for intense fighting, with the Union forces repeatedly attempting to capture it.
- Stone Bridge: This historical landmark, located near the Bull Run River, served as a crossing point for both armies and witnessed fierce battles throughout the engagement.
- The Confederate Lines: The Confederate army established a strong defensive line across the battlefield, utilizing the terrain to their advantage and effectively repelling Union attacks.
- Union Advance: The Union army, under the command of General John Pope, aimed to outflank the Confederate forces and capture Richmond, the Confederate capital. Their initial advance was successful, but they ultimately fell victim to a series of Confederate counterattacks.
The Battle’s Progression: A Clash of Strategies and Tactics
The Second Battle of Bull Run unfolded in a series of engagements, each with its own unique strategic significance.
- August 29th: A Union Advance and Confederate Counterattack: The Union forces, under the command of General John Pope, launched a series of attacks against the Confederate lines, aiming to secure a foothold across the Bull Run River. The Confederate army, led by General Robert E. Lee, responded with a series of counterattacks, successfully repelling the Union advance.
- August 30th: A Turning Point: The second day of the battle witnessed a dramatic shift in momentum. The Confederate forces, reinforced by General Stonewall Jackson’s arrival, launched a coordinated attack on the Union flank. The Union army, caught off guard and outnumbered, was forced to retreat in disarray.
- The Confederate Victory: The Confederate army, led by General Robert E. Lee, emerged victorious from the battle, inflicting a decisive defeat on the Union forces. The Union army suffered heavy casualties, while the Confederate army sustained significantly fewer losses. The battle’s outcome significantly boosted Confederate morale and hindered Union efforts to capture Richmond.
The Aftermath: A Turning Point in the War’s Trajectory
The Second Battle of Bull Run had a profound impact on the course of the American Civil War.
- Union Morale: The Union suffered a major setback, with the defeat at Bull Run undermining public confidence in the war effort. This loss further fueled political divisions within the North, leading to calls for a change in leadership.
- Confederate Morale: The victory at Bull Run had a galvanizing effect on the Confederacy, boosting morale and providing a much-needed morale boost. The victory also solidified the reputation of General Robert E. Lee as a skilled military strategist.
- Strategic Implications: The Confederate victory at Bull Run effectively stalled Union efforts to capture Richmond and shifted the focus of the war to the Eastern Theater. The battle’s outcome also highlighted the importance of strategic planning and the need for effective coordination between different Union armies.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Battle’s Significance
1. What were the key strategic objectives of the Union and Confederate armies in the Second Battle of Bull Run?
The Union army, under General John Pope, aimed to outflank the Confederate forces and capture Richmond, the Confederate capital. The Confederate army, led by General Robert E. Lee, sought to defend Richmond and prevent the Union advance.
2. What were the major factors that contributed to the Confederate victory at Bull Run?
The Confederate victory was largely attributed to the arrival of General Stonewall Jackson’s forces, which significantly bolstered their numbers and allowed them to launch a coordinated attack on the Union flank. The Confederate army also effectively utilized the terrain to their advantage, establishing a strong defensive line and repelling Union attacks.
3. What were the long-term consequences of the Second Battle of Bull Run?
The Confederate victory at Bull Run significantly impacted the course of the war, boosting Confederate morale, hindering Union efforts to capture Richmond, and shifting the focus of the war to the Eastern Theater.
4. How did the Second Battle of Bull Run impact public opinion in the North and the South?
The Union defeat at Bull Run led to a decline in public confidence in the war effort and fueled political divisions within the North. The Confederate victory, on the other hand, boosted morale and solidified support for the Confederacy.
5. What lessons can be learned from the Second Battle of Bull Run?
The battle serves as a reminder of the importance of strategic planning, effective coordination between different armies, and the need to adapt to changing battlefield conditions. It also underscores the significance of morale and public support in shaping the outcome of a conflict.
Tips for Understanding the Second Battle of Bull Run
- Utilize Maps: Studying maps of the battlefield is crucial for understanding the strategic significance of the terrain and the movements of both armies.
- Research Key Figures: Gaining insight into the personalities and strategies of key figures like General John Pope, General Robert E. Lee, and General Stonewall Jackson is essential for comprehending the battle’s dynamics.
- Explore Primary Sources: Reading firsthand accounts from soldiers and civilians who participated in the battle provides a visceral understanding of the human cost of war.
- Engage with Historical Literature: Examining scholarly works on the Second Battle of Bull Run offers diverse perspectives and in-depth analysis of the battle’s significance.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Conflict and Change
The Second Battle of Bull Run stands as a testament to the brutality and complexity of the American Civil War. The battle’s outcome marked a turning point in the war’s trajectory, boosting Confederate morale, hindering Union efforts to capture Richmond, and shifting the focus of the war to the Eastern Theater. The battle’s legacy continues to inform our understanding of this pivotal period in American history, serving as a reminder of the human cost of conflict and the enduring impact of strategic decisions. By studying the battle, we gain a deeper appreciation for the sacrifices made by those who fought in this defining moment in American history.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-517359510-31c2246191964a04b9d55bf23c430940.jpg)




![Second Battle of Bull Run, U.S. Civil War (28 – 30 August 1862) [1600 x 1242] : r/warmaps](https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-JkmVjlSWEZg/UKFkt-lp7oI/AAAAAAAAA-k/pBgxksGl4Jo/s1600/Second_Bull_Run_Aug28.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Second Battle of Bull Run: A Turning Point in the American Civil War. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
