The Silent Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
Related Articles: The Silent Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Silent Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silent Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
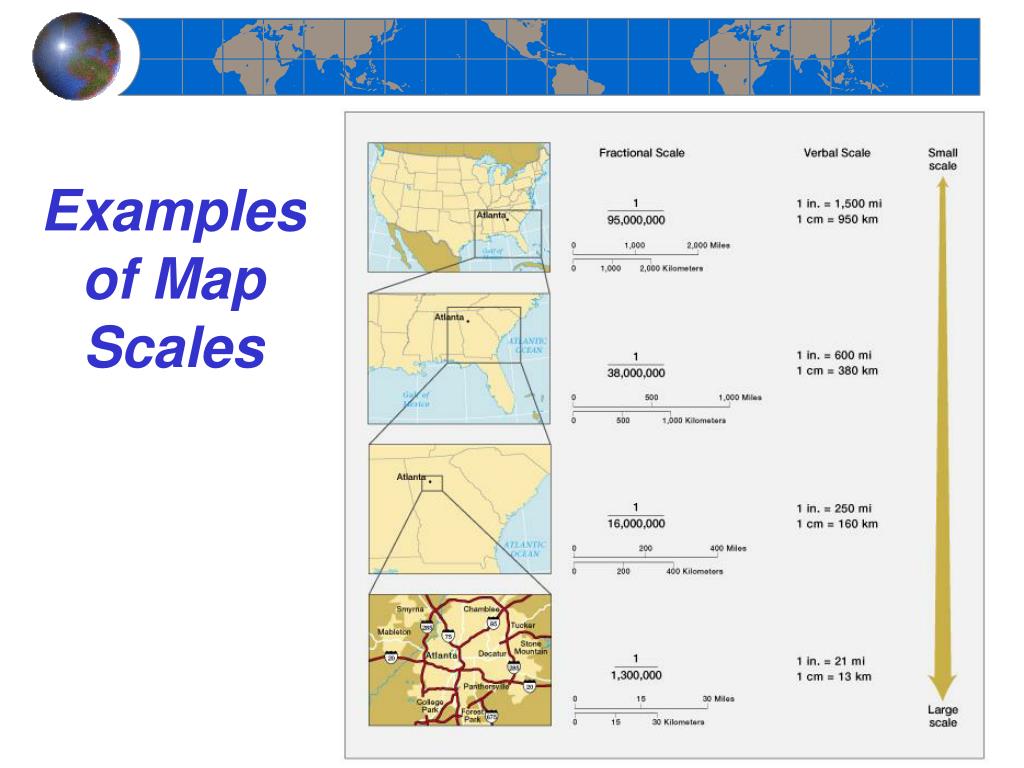
A map is a powerful tool, capable of conveying vast amounts of information in a concise and visually engaging manner. However, its effectiveness hinges on one crucial element: the map scale. This seemingly simple concept serves as the bridge between the vastness of the real world and the confined space of a map, allowing us to comprehend the distances and proportions depicted.
Defining the Map Scale
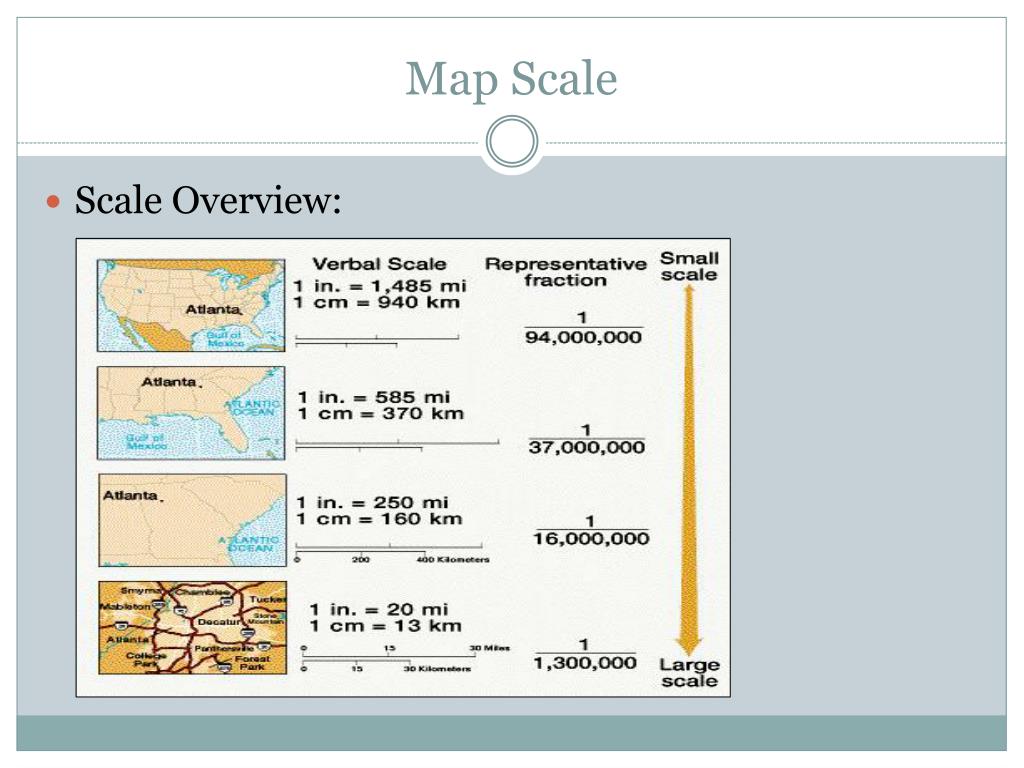
A map scale represents the relationship between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This relationship is expressed in various forms, each offering a distinct perspective on the map’s representation of reality:
- Verbal Scale: This straightforward method describes the relationship using words, such as "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers," signifying that 1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground.
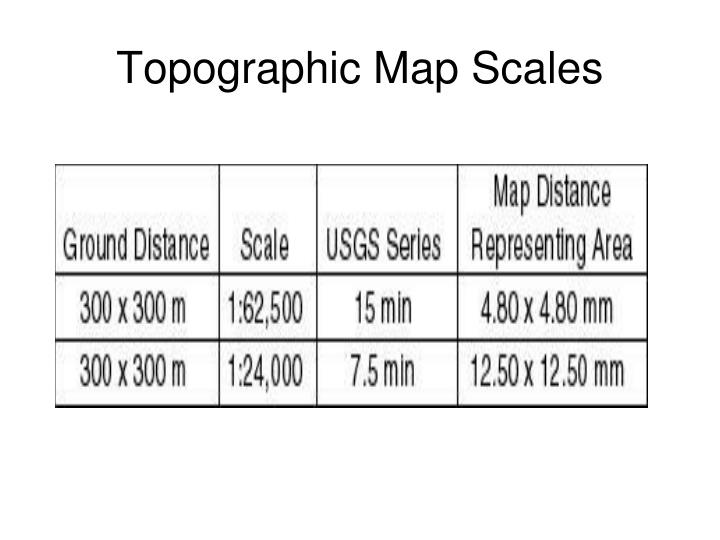
- Representative Fraction (RF): The RF expresses the scale as a ratio, typically in the form of 1:X. Here, the first number (1) always represents one unit on the map, while the second number (X) represents the equivalent number of units on the ground. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
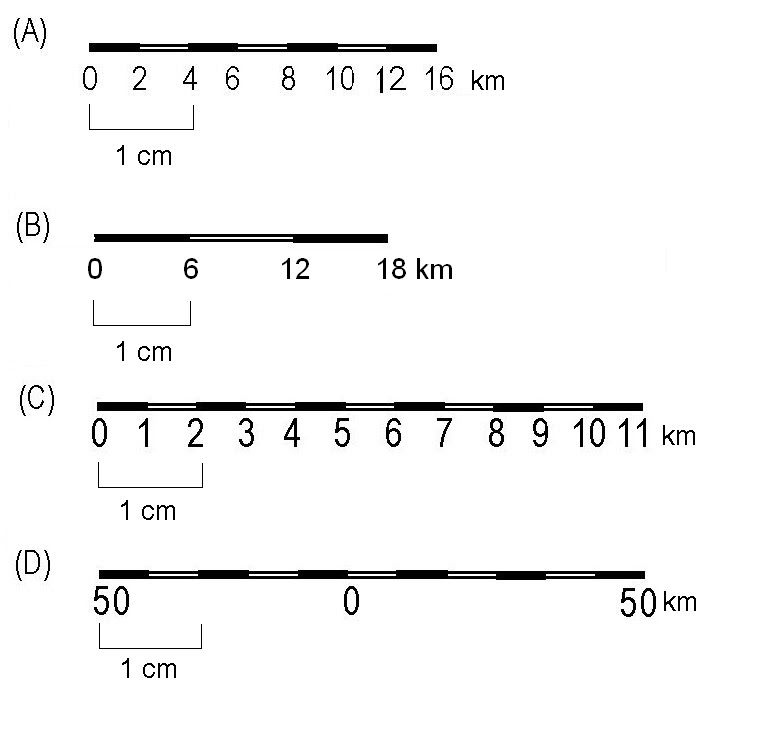
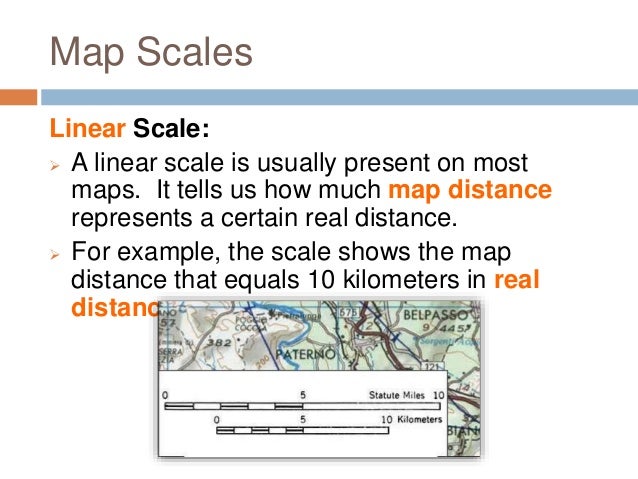
- Graphic Scale: This method employs a visual representation of the scale, typically a line divided into segments representing specific distances on the ground. This allows for quick visual estimation of distances without needing to perform calculations.
The Importance of Map Scales
The map scale is not merely a technical detail; it is the cornerstone of map interpretation. It dictates the level of detail a map can portray and influences how we perceive the world around us.
- Determining Distances: A map scale enables us to accurately measure distances between points on a map and translate them into real-world distances. This is crucial for planning trips, navigating unfamiliar territories, and understanding the spatial relationships between different locations.
- Comprehending Relative Size: The map scale allows us to appreciate the relative sizes of features, such as cities, rivers, or mountains. A map with a large scale (e.g., 1:10,000) will show a greater level of detail for a smaller area, while a map with a small scale (e.g., 1:1,000,000) will depict a wider region but with less detail.
- Understanding Spatial Relationships: The map scale plays a vital role in understanding the spatial relationships between different features. A small-scale map might show the overall layout of a country, while a large-scale map might depict the detailed street network of a city.
Map Scales in Action: Everyday Applications
Map scales are ubiquitous in our daily lives, often operating in the background without explicit recognition. They are essential in various fields, including:
- Navigation: Maps used in GPS systems, navigation apps, and paper atlases rely on scales to guide us through unfamiliar environments.
- Urban Planning: City planners utilize maps with different scales to understand the layout of neighborhoods, assess infrastructure needs, and plan for future development.
- Environmental Studies: Maps with scales tailored to specific environmental features help scientists analyze land cover, monitor deforestation, and study the impact of climate change.
- Military Operations: Military maps are meticulously crafted with precise scales to support strategic planning, troop movements, and targeting operations.
FAQs about Map Scales
Q: How do I choose the right map scale for my needs?
A: The ideal map scale depends on the specific task or purpose. For detailed exploration of a small area, a large-scale map is preferred. Conversely, for a broad overview of a vast region, a small-scale map is more suitable.
Q: Can I convert between different map scales?
A: Yes, you can convert between different scales using simple calculations. For example, to convert a scale of 1:50,000 to 1:100,000, you need to double the distance measured on the 1:50,000 map.
Q: What are the limitations of map scales?
A: While map scales are essential for understanding the world, they have limitations. They can distort the shape and size of features, especially at smaller scales. Additionally, they cannot accurately represent the Earth’s curvature, leading to inaccuracies in distances and areas, particularly over large distances.
Tips for Using Map Scales
- Always check the map scale before interpreting any information.
- Use a ruler to measure distances accurately.
- Be aware of the limitations of the map scale and its potential for distortion.
- Consider using multiple maps with different scales for a comprehensive understanding of an area.
Conclusion: A Silent Yet Powerful Tool
The map scale is a silent yet powerful element that underpins the effectiveness of maps. It enables us to bridge the gap between the real world and its representation on paper, facilitating understanding, navigation, and informed decision-making. By mastering the language of map scales, we unlock the potential of maps to illuminate our world and guide our actions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silent Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
