The Tropic of Cancer: A Line Dividing Worlds in the Sahara
Related Articles: The Tropic of Cancer: A Line Dividing Worlds in the Sahara
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Tropic of Cancer: A Line Dividing Worlds in the Sahara. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Tropic of Cancer: A Line Dividing Worlds in the Sahara
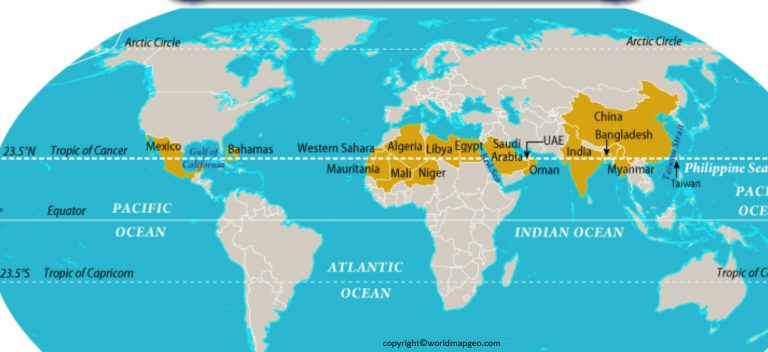
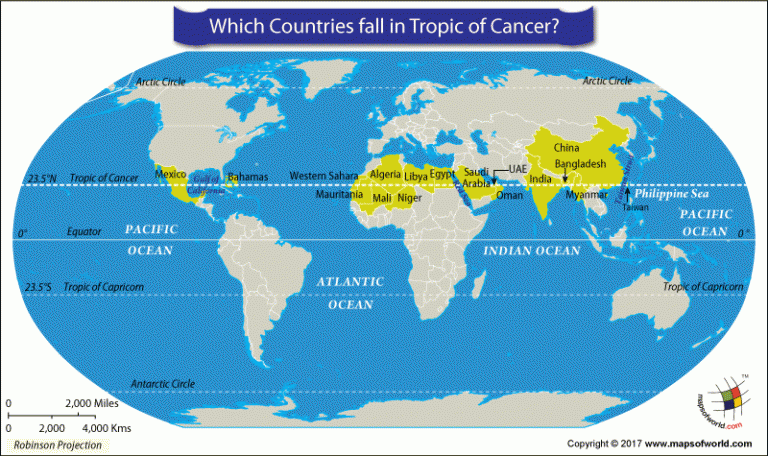
The Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of sand and rock stretching across North Africa, is a region defined by its extreme aridity and harsh conditions. While its physical boundaries are fluid and constantly shifting, a key geographical marker that intersects this desert is the Tropic of Cancer. This imaginary line, located at approximately 23.5 degrees north latitude, plays a significant role in understanding the Sahara’s climate, biodiversity, and human history.
A Line of Latitude and Solar Influence:
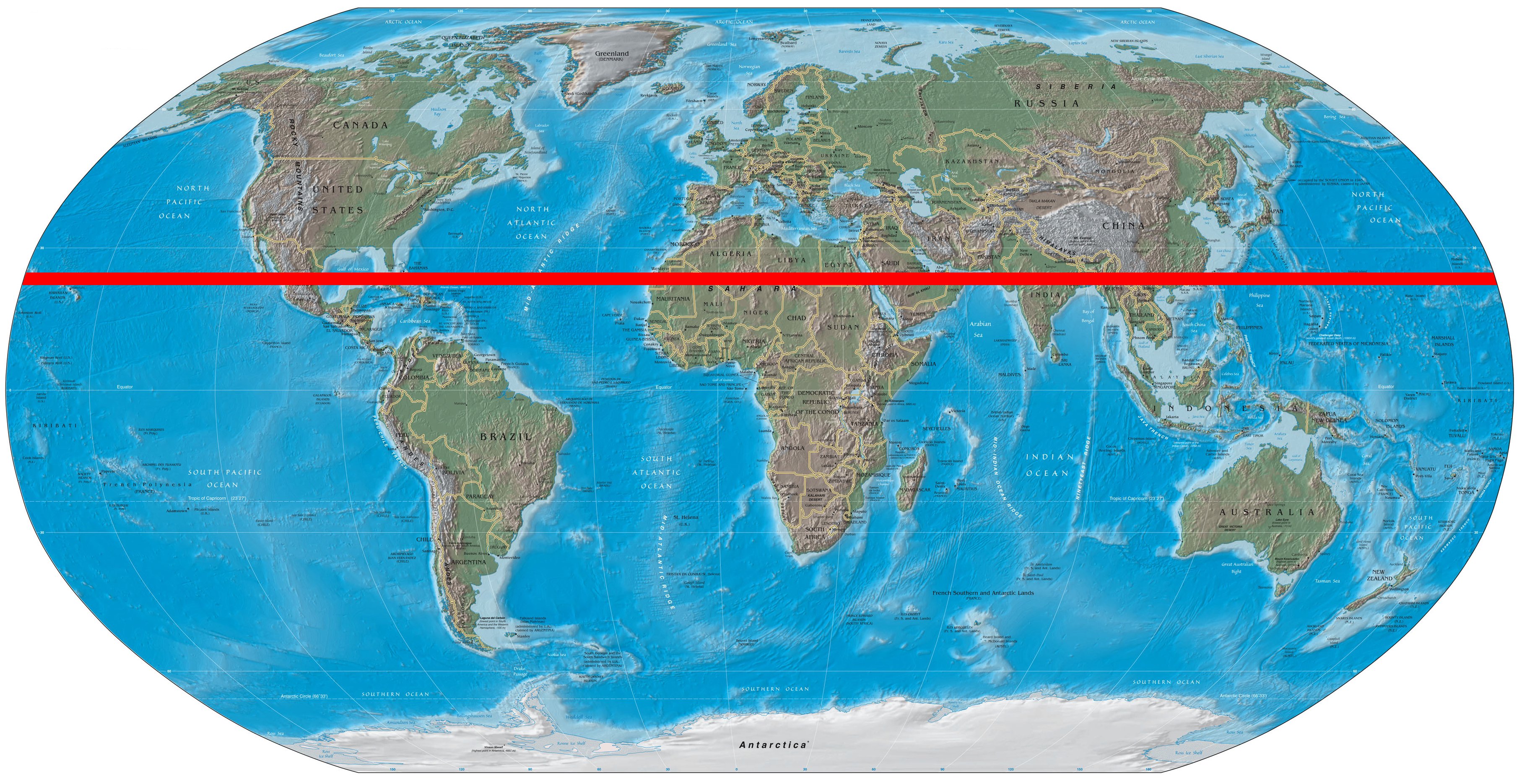
The Tropic of Cancer is not a physical barrier but a line of latitude that circles the Earth, marking the northernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead at noon during the summer solstice. This astronomical phenomenon has significant implications for the Sahara.
The Tropic of Cancer acts as a dividing line between two distinct climatic zones: the subtropical desert climate north of it and the tropical savanna climate to the south. The Sahara, situated north of this line, experiences high temperatures year-round, with minimal rainfall. The intense solar radiation that the region receives, a direct result of the sun’s position during the summer solstice, contributes to its aridity and high evaporation rates.
The Tropic’s Influence on the Sahara’s Landscape:
The Tropic of Cancer’s influence extends beyond the climate to shape the Sahara’s diverse landscape. The desert’s vast sand seas, rocky plateaus, and oases are all products of the region’s aridity and the interplay of geological forces influenced by solar radiation.
The sand dunes, a defining feature of the Sahara, are shaped by the prevailing winds, which themselves are influenced by the solar energy that drives atmospheric circulation. The rocky plateaus, formed by ancient volcanic eruptions and erosion, are a testament to the long geological history of the region, shaped by the harsh conditions created by the Tropic’s influence.
Human History and the Tropic of Cancer:
The Tropic of Cancer has also played a crucial role in the human history of the Sahara. Early civilizations, like the ancient Egyptians, developed along the Nile River, which flows south of the Tropic, taking advantage of its fertile lands and proximity to water. The Tropic, however, presented a formidable barrier to migration and settlement, forcing early humans to adapt to the harsh desert environment.
The Tropic’s influence on human settlement patterns is evident in the distribution of nomadic tribes and the development of unique adaptations to desert life, including sophisticated water management techniques and the use of camels for transportation.
The Tropic of Cancer: A Symbol of Adaptation and Resilience:
The Tropic of Cancer, while an invisible line on a map, represents a critical geographical marker that has shaped the Sahara’s climate, landscape, and human history. It is a symbol of the harsh realities of desert life and the remarkable resilience of the people and ecosystems that have adapted to its challenges.
FAQs:
Q: Is the Tropic of Cancer a physical barrier?
A: No, the Tropic of Cancer is an imaginary line of latitude, not a physical barrier. It represents the northernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead at noon during the summer solstice.
Q: Why is the Sahara so dry?
A: The Sahara’s aridity is primarily due to its location north of the Tropic of Cancer, which results in high temperatures and minimal rainfall. The intense solar radiation contributes to high evaporation rates, further reducing moisture levels.
Q: How does the Tropic of Cancer influence the Sahara’s landscape?
A: The Tropic’s influence on the Sahara’s landscape is evident in its sand dunes, shaped by the prevailing winds; its rocky plateaus, formed by geological processes influenced by the region’s aridity; and its oases, which provide vital water sources in the otherwise barren desert.
Q: How has the Tropic of Cancer affected human history in the Sahara?
A: The Tropic of Cancer has acted as a barrier to migration and settlement, forcing early humans to adapt to the desert environment. It has influenced the distribution of nomadic tribes and the development of unique adaptations to desert life, such as water management techniques and the use of camels.
Tips:
- Visualize the Tropic of Cancer: Use a globe or online maps to understand its position and how it intersects the Sahara.
- Explore the Sahara’s diverse landscape: Research the region’s sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and oases to appreciate the impact of the Tropic on its geography.
- Learn about the adaptations of desert life: Investigate the strategies employed by nomadic tribes and desert wildlife to survive in the harsh conditions of the Sahara.
Conclusion:
The Tropic of Cancer, while an invisible line on a map, holds immense significance for the Sahara Desert. Its influence on the region’s climate, landscape, and human history highlights the intricate relationship between geography, environment, and human adaptation. Understanding the Tropic’s role in shaping the Sahara provides valuable insights into the resilience of life in extreme environments and the enduring power of human ingenuity in overcoming geographical challenges.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tropic of Cancer: A Line Dividing Worlds in the Sahara. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
