The Unsung Hero of Engine Control: A Comprehensive Look at the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of Engine Control: A Comprehensive Look at the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Unsung Hero of Engine Control: A Comprehensive Look at the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unsung Hero of Engine Control: A Comprehensive Look at the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor

The internal combustion engine, a marvel of engineering, relies on a delicate dance of air, fuel, and spark to generate power. While the spark plugs and fuel injectors are often in the spotlight, a crucial component quietly orchestrates this symphony: the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This unassuming sensor plays a vital role in determining the engine’s air intake, directly influencing fuel delivery and ultimately impacting performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The MAP Sensor: A Window into the Engine’s Breath
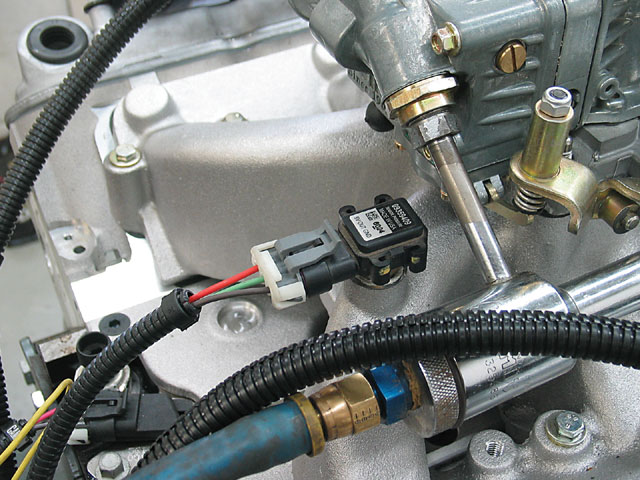
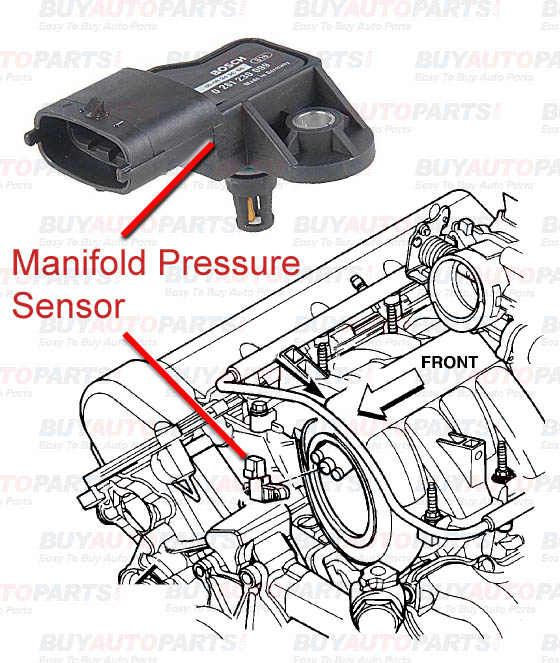
The MAP sensor is a pressure transducer, a device that converts pressure changes into an electrical signal. Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This manifold, a complex network of tubes, acts as the engine’s "lungs," channeling air from the air intake system into the combustion chambers. The pressure within the manifold directly reflects the amount of air entering the engine.
How the MAP Sensor Works: A Journey from Pressure to Signal
The MAP sensor, typically a small, cylindrical device, houses a diaphragm that flexes in response to pressure fluctuations within the intake manifold. This diaphragm is connected to a strain gauge, a device that translates the diaphragm’s movement into a measurable electrical resistance. The change in electrical resistance is then interpreted by the engine control unit (ECU) as a measure of manifold pressure.
The MAP Sensor’s Crucial Role: Fueling the Fire
The information provided by the MAP sensor is critical for the ECU to determine the optimal fuel-air mixture for combustion. The ECU uses the manifold pressure data, along with other sensor inputs like engine speed, air temperature, and throttle position, to calculate the precise amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. This precise fuel-air ratio is essential for efficient combustion, maximizing power output while minimizing emissions.
Benefits Beyond Fuel Efficiency: The MAP Sensor’s Multifaceted Role
The MAP sensor’s contribution extends beyond fuel management. Its data is utilized for various engine functions, including:
- Ignition Timing: The ECU uses manifold pressure data to adjust ignition timing, ensuring optimal spark delivery for efficient combustion.
- Boost Control: In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor helps regulate boost pressure, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in optimizing the air-fuel ratio, minimizing harmful emissions like carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons.
- Adaptive Learning: The ECU utilizes MAP sensor data for adaptive learning, constantly fine-tuning engine parameters for optimal performance.
Troubleshooting the MAP Sensor: Identifying and Addressing Issues
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a range of engine problems, including:
- Rough Idle: An inaccurate manifold pressure reading can disrupt the fuel-air mixture, causing the engine to run unevenly.
- Poor Acceleration: A faulty MAP sensor may prevent the ECU from delivering the correct fuel-air ratio, leading to sluggish acceleration.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: An inaccurate manifold pressure reading can lead to a rich fuel mixture, resulting in increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will often trigger the check engine light, indicating a potential issue.
Diagnosing MAP Sensor Problems: A Step-by-Step Approach
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves a combination of visual inspection, multimeter readings, and specialized diagnostic tools.
- Visual Inspection: Check for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections on the sensor itself and its wiring harness.
- Multimeter Readings: Use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s resistance and voltage output. Compare these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any discrepancies.
- Diagnostic Tools: Advanced diagnostic tools can provide real-time data from the MAP sensor, allowing technicians to analyze its performance and identify potential issues.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the MAP Sensor
Q: How often should a MAP sensor be replaced?
A: MAP sensors are generally very reliable and can last for the life of the vehicle. However, environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to contaminants, can shorten their lifespan. If you suspect a malfunctioning MAP sensor, it’s best to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Q: Can I replace the MAP sensor myself?
A: Replacing a MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward task, but it requires basic mechanical knowledge and tools. It’s important to consult your vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause engine damage?
A: While a faulty MAP sensor won’t directly damage the engine, it can lead to issues that could eventually cause damage. For example, an inaccurate fuel-air mixture can lead to detonation (engine knocking), which can damage engine components.
Q: What are the symptoms of a bad MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include rough idle, poor acceleration, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light.
Tips for Maintaining MAP Sensor Performance:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow your vehicle’s maintenance schedule, including air filter changes and engine tune-ups.
- Clean Air Intake: A dirty air intake can restrict airflow, affecting the MAP sensor’s readings.
- Avoid Contaminants: Protect the MAP sensor from exposure to oil, dirt, and other contaminants.
- Professional Inspection: Have your MAP sensor inspected by a qualified mechanic if you suspect any issues.
Conclusion: A Vital Component in the Engine’s Symphony
The MAP sensor, though often overlooked, plays a vital role in the intricate operation of modern internal combustion engines. Its accurate measurement of manifold pressure enables the ECU to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, boost control, and emissions, ultimately contributing to better performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Understanding the MAP sensor’s function and potential issues is crucial for maintaining optimal engine health and performance. By recognizing its importance and implementing proper maintenance practices, drivers can ensure that this unsung hero continues to play its vital role in the engine’s symphony.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unsung Hero of Engine Control: A Comprehensive Look at the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
