Understanding Linear Scales on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Linear Scales on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Linear Scales on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Linear Scales on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

Maps are essential tools for navigating the world, providing visual representations of geographical features and their relative locations. An integral component of many maps is the scale, which establishes a clear relationship between distances on the map and the corresponding distances in the real world. Among the various types of map scales, linear scales stand out for their simplicity and ease of use, offering a straightforward way to measure distances directly on the map.
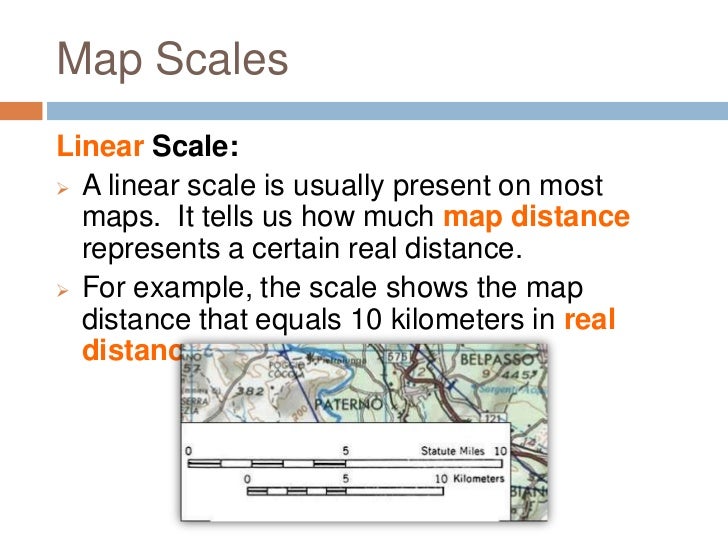
Defining the Linear Scale
A linear scale, also known as a graphic scale, is a visual representation of the map’s scale. It typically appears as a straight line divided into segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground. This line is accompanied by numerical markings, usually in units like kilometers, miles, or meters, indicating the corresponding real-world distances.
Advantages of Linear Scales
Linear scales offer several advantages over other types of scales, making them a preferred choice for many maps:
- Direct Measurement: Linear scales allow for direct measurement of distances on the map. Users can simply use a ruler or other measuring tool to determine the distance between two points on the map and then correlate that measurement to the corresponding distance on the ground using the scale.
- Simplicity and Clarity: Linear scales are easy to understand and use, even for individuals unfamiliar with map reading. Their visual representation eliminates the need for complex calculations or conversions, simplifying the process of determining distances.
- Flexibility: Linear scales can be easily adjusted to accommodate different map sizes and scales. They can be scaled up or down to fit the specific needs of a particular map, ensuring accurate representation of distances regardless of the map’s dimensions.
- Independence from Map Projection: Unlike verbal scales, which express the scale as a ratio, linear scales are independent of the map’s projection. This makes them particularly useful for maps that employ different projections, as the scale remains consistent regardless of the distortion introduced by the projection.
Types of Linear Scales
Linear scales can be broadly categorized into two main types:
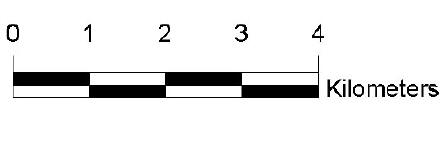
- Simple Linear Scale: This is the most basic type of linear scale, consisting of a single line divided into equal segments. Each segment represents a specific distance on the ground, and the numerical markings indicate the corresponding values.
- Bar Scale: A bar scale is similar to a simple linear scale but features a bar divided into segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground. The bar is often labeled with the corresponding distances, making it easier to read and interpret.
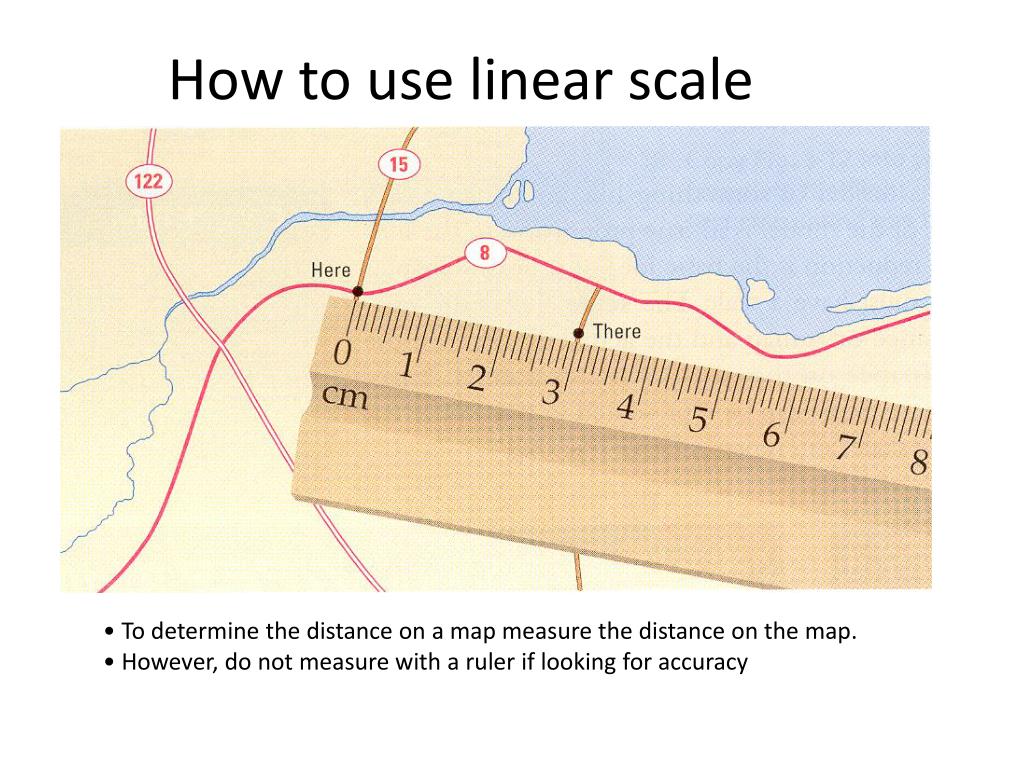
How to Use a Linear Scale
Using a linear scale is straightforward:
- Locate the Scale: Identify the linear scale on the map, usually found in a corner or margin.
- Select the Unit: Choose the unit of measurement that aligns with your needs (e.g., kilometers, miles, or meters).
- Measure the Distance: Use a ruler or other measuring tool to measure the distance between the two points on the map.
- Convert to Real-World Distance: Align the measured distance on the map with the corresponding segment on the linear scale. The numerical markings on the scale will indicate the equivalent distance on the ground.
Examples of Linear Scales in Action
Linear scales are widely used in various maps, including:
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict detailed terrain features and are often equipped with linear scales to facilitate accurate distance measurements for hiking, surveying, or land management.
- Road Maps: Linear scales are commonly used in road maps to help travelers estimate distances between cities or towns, aiding in route planning and travel time estimation.
- Nautical Charts: Linear scales are essential for nautical charts, allowing mariners to measure distances between navigational points, calculate course headings, and ensure safe navigation.
FAQs about Linear Scales
Q: What is the difference between a linear scale and a verbal scale?
A: A linear scale is a visual representation of the map’s scale, while a verbal scale expresses the scale as a ratio. For example, a verbal scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground. Linear scales provide a more direct and visual way to measure distances.
Q: Can linear scales be used for maps with different projections?
A: Yes, linear scales are independent of the map’s projection. This makes them particularly useful for maps that employ different projections, as the scale remains consistent regardless of the distortion introduced by the projection.
Q: How accurate are linear scales?
A: The accuracy of a linear scale depends on the precision of the map and the measuring tool used. However, linear scales generally provide a reasonably accurate representation of distances, especially when used in conjunction with a precise ruler or other measuring device.
Tips for Using Linear Scales
- Ensure the scale is appropriate for the map: Use a linear scale designed for the specific map you are using.
- Use a precise measuring tool: A ruler or other measuring device with clear markings is essential for accurate distance measurements.
- Account for distortion: Be aware that map projections can introduce distortion, especially at larger scales.
- Double-check your measurements: It is always a good practice to double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Linear scales are invaluable tools for understanding and interpreting maps, providing a straightforward and accurate method for measuring distances. Their simplicity, clarity, and flexibility make them a preferred choice for a wide range of maps, from topographic maps to road maps and nautical charts. By understanding the principles and applications of linear scales, users can effectively navigate the world, make informed decisions, and gain a deeper appreciation for the power of maps as visual representations of our environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Linear Scales on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!

