Understanding Map Scale Conversion: A Guide to Navigating the Relationship Between Maps and Reality
Related Articles: Understanding Map Scale Conversion: A Guide to Navigating the Relationship Between Maps and Reality
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Scale Conversion: A Guide to Navigating the Relationship Between Maps and Reality. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map Scale Conversion: A Guide to Navigating the Relationship Between Maps and Reality
Maps, essential tools for navigation and understanding spatial relationships, represent the world in a reduced form. This reduction, known as the map scale, is a crucial factor in interpreting the information presented on a map. It establishes the mathematical relationship between distances on the map and the corresponding distances on the ground. Comprehending and converting map scales is essential for accurate measurements, calculations, and spatial analysis.
Defining Map Scale:
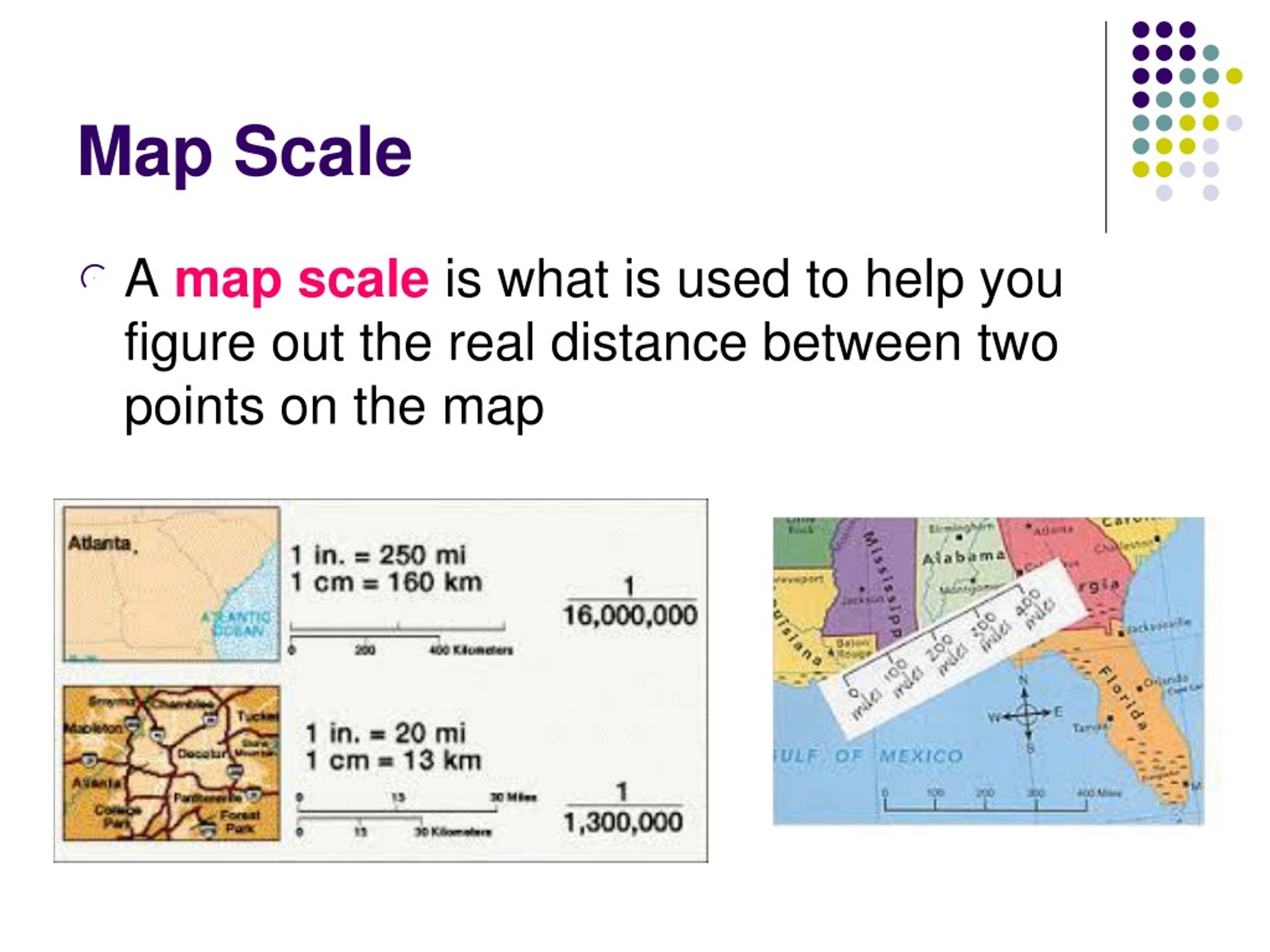
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio can be expressed in three primary forms:
- Verbal Scale: This form expresses the scale using words, for instance, "1 inch to 1 mile," indicating that one inch on the map represents one mile on the ground.
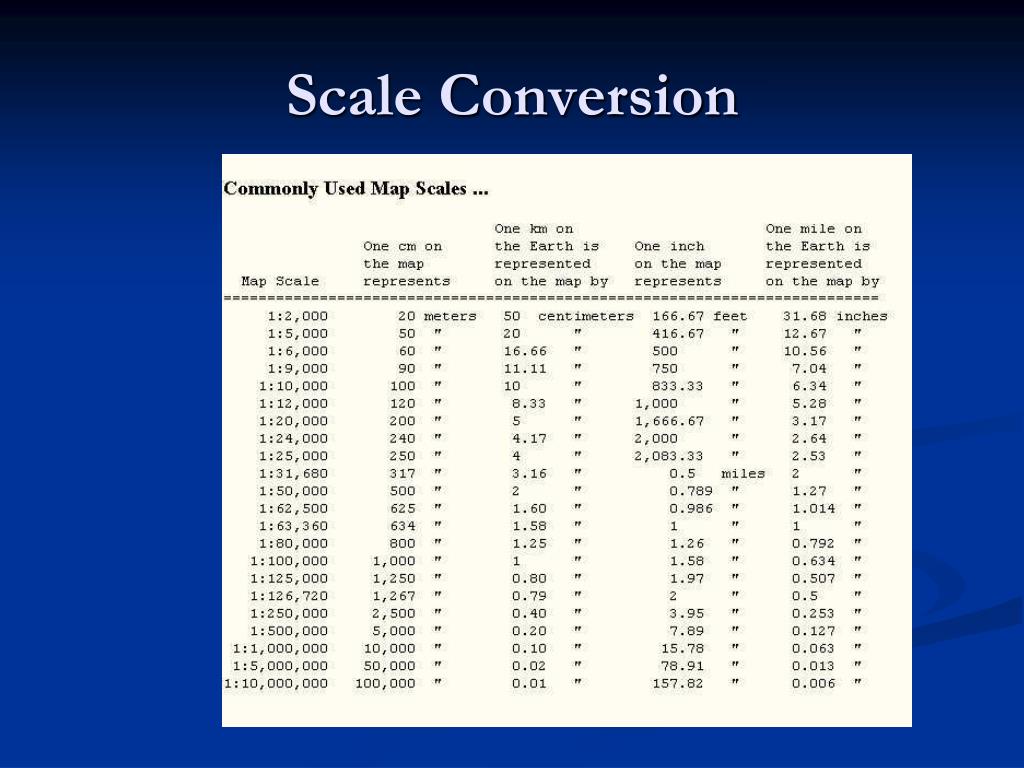
- Representative Fraction (RF): This form uses a fraction, such as 1:100,000, where the numerator (1) represents one unit on the map, and the denominator (100,000) represents the same unit on the ground.
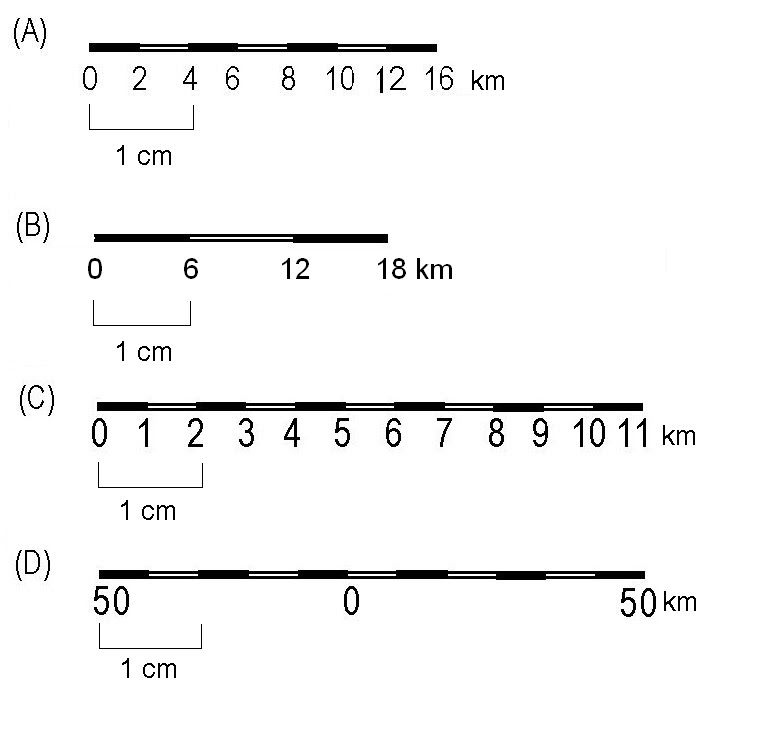
- Graphic Scale: This form utilizes a visual representation of the scale, typically a bar with marked distances representing specific distances on the ground.
The Importance of Map Scale Conversion:
Map scale conversion is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Measurements: Converting between different scale representations allows for precise measurements of distances, areas, and other spatial features on the map.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing maps with different scales requires conversion to ensure consistency and accurate analysis of spatial data.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from different sources often necessitates scale conversion to ensure compatibility and meaningful analysis.
- Effective Communication: Converting map scales facilitates clear and concise communication of spatial information across various audiences.
Conversion Formula and its Application:
The fundamental principle of map scale conversion lies in maintaining the proportional relationship between map distances and ground distances. The conversion process involves manipulating the scale ratio to achieve the desired representation.
Conversion Formula:
The conversion formula utilizes the following relationship:
Map Distance / Ground Distance = Scale RatioTo convert between different scale representations, we can rearrange the formula to solve for the desired quantity. For instance, to convert a verbal scale to a representative fraction, we can use:
RF = Map Distance / Ground DistanceExample:
Let’s consider a map with a verbal scale of "1 inch to 10 miles." To convert this to a representative fraction, we need to determine the equivalent distance in inches for one mile.
- Ground Distance: 1 mile
- Map Distance: 1 inch
- RF: 1 inch / 10 miles = 1:10 miles
To express the RF in a standard format, we need to convert miles to inches:
- 1 mile = 63,360 inches
- RF: 1: (10 miles x 63,360 inches/mile) = 1:633,600
Therefore, the representative fraction for the map scale "1 inch to 10 miles" is 1:633,600.
Conversion Between Different Scale Representations:
The conversion formula can be applied to convert between any two scale representations. Here’s a breakdown of common conversion scenarios:
- Verbal Scale to Representative Fraction: As demonstrated in the previous example, this involves expressing the verbal scale as a ratio of map distance to ground distance.
- Representative Fraction to Verbal Scale: This requires converting the RF to a ratio where the map distance is expressed in a common unit (e.g., inches) and the ground distance in a convenient unit (e.g., miles).
- Graphic Scale to Representative Fraction: This involves measuring the distance on the graphic scale corresponding to a known ground distance. The RF can then be calculated by dividing the measured map distance by the known ground distance.
- Representative Fraction to Graphic Scale: This involves constructing a graphic scale based on the RF. This is typically done by choosing a convenient ground distance and calculating the corresponding map distance using the RF.
Understanding the Impact of Scale Conversion:
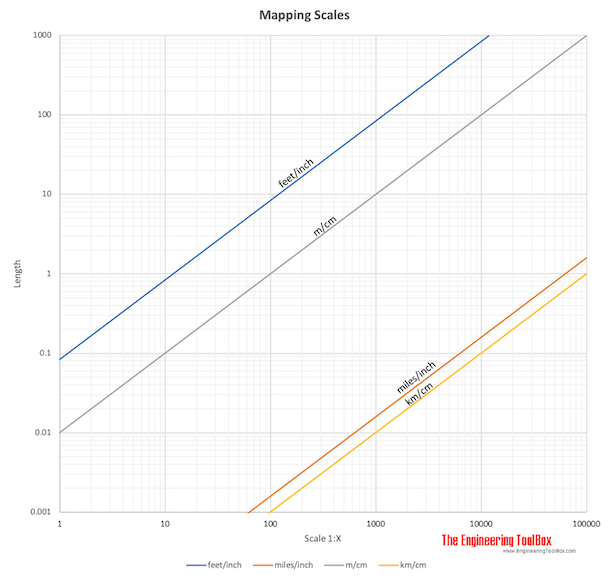
Scale conversion significantly impacts the accuracy and interpretation of map data. Larger scales (e.g., 1:10,000) represent smaller areas in greater detail, while smaller scales (e.g., 1:1,000,000) represent larger areas with less detail.
Key Considerations for Scale Conversion:
- Units: Ensure consistency in units used for both map and ground distances.
- Precision: The level of precision required for the conversion will determine the number of significant figures used in the calculation.
- Context: Consider the purpose of the map and the intended use of the converted scale.
FAQs Regarding Map Scale Conversion:
Q: What happens if the units for map distance and ground distance are different?
A: When units differ, you must convert them to a common unit before applying the conversion formula. For example, if the map distance is in centimeters and the ground distance is in kilometers, convert kilometers to centimeters before calculating the RF.
Q: Can I convert between different types of graphic scales?
A: Yes, you can convert between different types of graphic scales. The process involves measuring the distances on each scale corresponding to a known ground distance and then calculating the corresponding RFs.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate map scale for my needs?
A: The appropriate map scale depends on the specific application. For detailed analysis of small areas, a large scale is suitable. For overview maps of large regions, a small scale is more appropriate.
Tips for Effective Map Scale Conversion:
- Use a consistent unit system: Stick to either metric or imperial units throughout the conversion process.
- Double-check your calculations: Verify your calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Consider the context: Choose the appropriate scale for the intended use of the map.
- Utilize online conversion tools: Numerous online resources can assist in converting map scales quickly and accurately.
Conclusion:
Understanding and applying map scale conversion is crucial for accurately interpreting and analyzing spatial data. By mastering the conversion formula and its applications, users can effectively navigate the relationship between maps and the real world, ensuring accurate measurements, meaningful comparisons, and effective communication of spatial information. The ability to convert between different scale representations empowers users to leverage the power of maps for diverse applications in cartography, geography, and other fields that rely on spatial data.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Scale Conversion: A Guide to Navigating the Relationship Between Maps and Reality. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
