Understanding Map Scale Ratios: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Map Scale Ratios: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Scale Ratios: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map Scale Ratios: A Comprehensive Guide
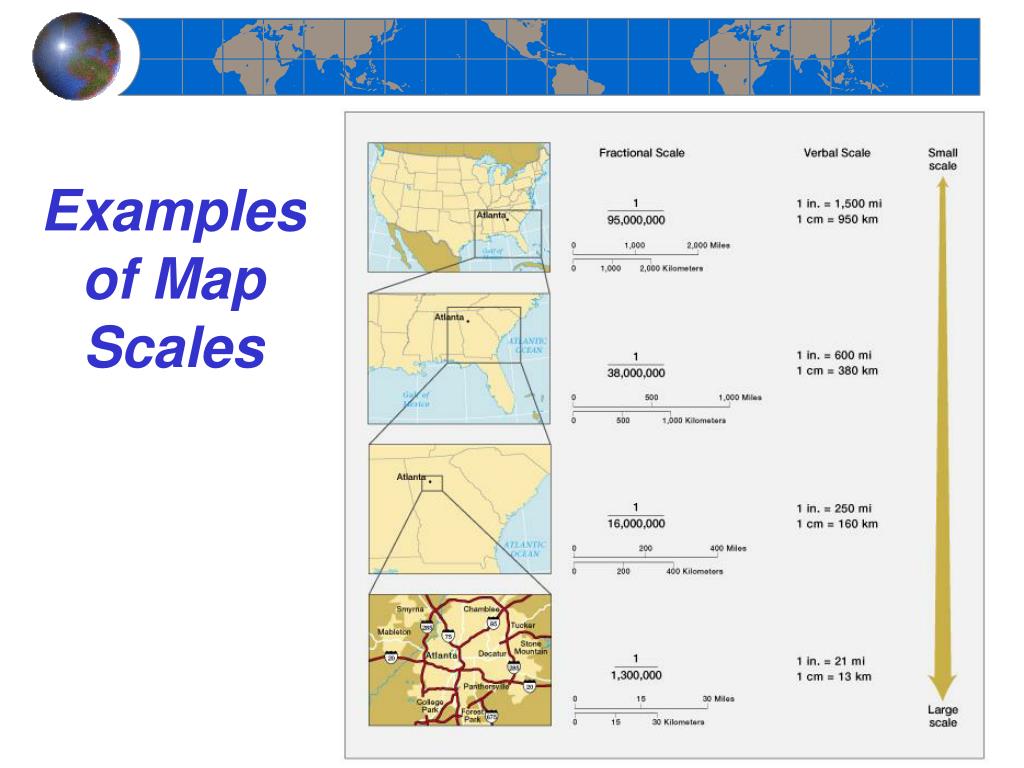
Maps are essential tools for navigating the world, understanding geographic relationships, and planning journeys. They provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, scaled down to a manageable size. However, the accuracy and usefulness of a map depend heavily on its scale, which defines the relationship between distances on the map and their corresponding distances in reality. This relationship is expressed through scale ratios, a fundamental concept in cartography.
What is a Map Scale Ratio?
A map scale ratio is a numerical representation of the relationship between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It is typically expressed as a fraction, a verbal statement, or a graphic scale.
1. Fractional Scale:
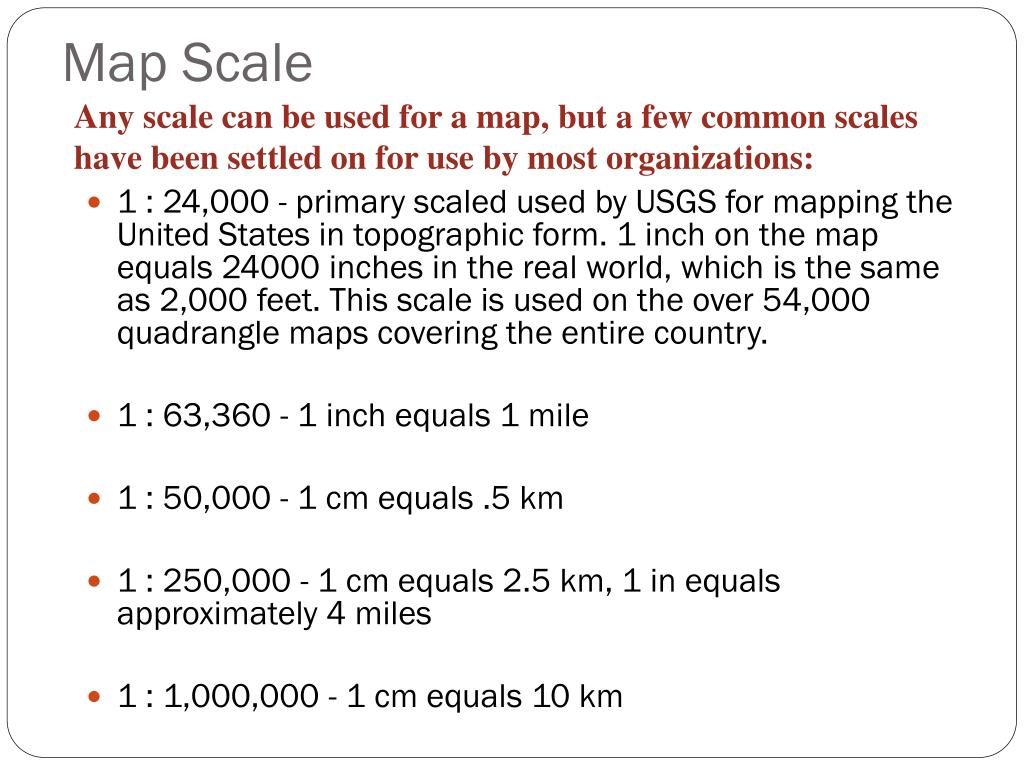
The fractional scale is the most common form, written as a fraction where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the corresponding ground distance. For example, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit of measurement on the map represents 100,000 of the same units on the ground. This means that one centimeter on the map corresponds to 100,000 centimeters (or one kilometer) in reality.
2. Verbal Scale:
The verbal scale expresses the relationship in words, stating that "one inch on the map equals one mile on the ground," or "one centimeter on the map equals ten kilometers on the ground." This method is straightforward and easily understood but less precise than the fractional scale.
3. Graphic Scale:
A graphic scale is a visual representation of the map scale, typically a bar with marked distances. This bar allows users to directly measure distances on the map and compare them to the corresponding distances on the ground. Graphic scales are particularly useful when working with maps that may have been enlarged or reduced, as they remain accurate regardless of the map’s size.
Understanding the Importance of Map Scale Ratios:
Map scale ratios are crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Measurement: They enable users to accurately measure distances, areas, and other geographical features on the map and translate them to real-world values. This is essential for navigation, planning, and research.
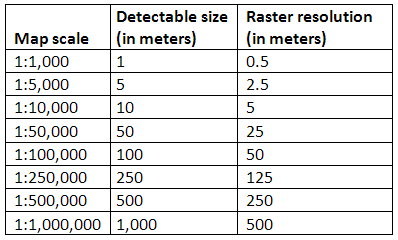
- Visual Representation: Scale ratios determine the level of detail and clarity on a map. A larger scale (e.g., 1:10,000) represents a smaller area with greater detail, while a smaller scale (e.g., 1:100,000) depicts a larger area with less detail.
- Comparative Analysis: Scale ratios allow for comparisons between different maps or sections of the same map, ensuring that observations and measurements are consistent and meaningful.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding the scale ratio is vital for interpreting map data and making informed decisions. For example, a map with a small scale may not accurately represent the distribution of small features, while a map with a large scale might be too detailed for a broad overview.
Working with Map Scale Ratios: Key Concepts and Calculations
1. Determining the Scale Ratio:
If the scale ratio is not explicitly stated on the map, it can be determined using the following steps:
- Measure a known distance on the map: Select a recognizable feature with a known ground distance, such as a road or a river.
- Measure the corresponding distance on the ground: Use a ruler or other measuring tool to determine the distance on the map.
- Calculate the scale ratio: Divide the ground distance by the map distance to obtain the scale ratio. For example, if a 5-centimeter road on the map represents a 10-kilometer road in reality, the scale ratio is 10,000 meters / 5 centimeters = 1:200,000.
2. Converting between Units:
When working with scale ratios, it is crucial to ensure that the units of measurement are consistent. To convert between units, use the following guidelines:
- Kilometers to Meters: Multiply by 1000 (1 kilometer = 1000 meters)
- Meters to Centimeters: Multiply by 100 (1 meter = 100 centimeters)
- Centimeters to Millimeters: Multiply by 10 (1 centimeter = 10 millimeters)
3. Calculating Ground Distances:
Given a map distance and the scale ratio, the corresponding ground distance can be calculated using the following formula:
Ground Distance = Map Distance x Scale Ratio
4. Calculating Map Distances:
Given a ground distance and the scale ratio, the corresponding map distance can be calculated using the following formula:
Map Distance = Ground Distance / Scale Ratio
5. Using Scale Ratios for Area Calculations:
Scale ratios can also be used to calculate the area of features on a map. The formula for calculating area is:
Area on Ground = Area on Map x (Scale Ratio)^2
Examples of Map Scale Ratio Applications:
- Navigation: A traveler uses a map with a scale of 1:50,000 to plan a hiking route. They measure a 5-centimeter distance on the map, which translates to a 2.5-kilometer distance on the ground.
- Land Management: A surveyor uses a map with a scale of 1:25,000 to assess the size of a plot of land. They measure a 10-centimeter area on the map, which represents a 625,000 square meter area on the ground.
- Environmental Monitoring: A scientist uses a map with a scale of 1:1,000,000 to study the distribution of a particular species. They observe a cluster of points representing the species on the map and use the scale ratio to estimate the real-world area covered by the species.
FAQs on Map Scale Ratios:
1. How do I determine which scale ratio is appropriate for a particular map?
The appropriate scale ratio depends on the purpose of the map and the level of detail required. For large-scale maps that depict small areas with high detail, a larger scale ratio (e.g., 1:10,000) is suitable. For small-scale maps that represent large areas with less detail, a smaller scale ratio (e.g., 1:100,000) is appropriate.
2. What are the limitations of using map scale ratios?
While map scale ratios provide a valuable tool for understanding geographic relationships, they have limitations:
- Earth’s Curvature: Maps are flat representations of a curved surface, which introduces distortion, particularly at larger scales.
- Projection Errors: Different map projections distort distances and shapes in different ways, making it challenging to obtain precise measurements.
- Scale Variation: Some maps may have varying scale ratios across different areas, making it crucial to consider the specific scale at the location of interest.
3. How can I improve my understanding of map scale ratios?
- Practice using different scales: Experiment with maps of various scales to gain a sense of how different ratios affect the visual representation and the accuracy of measurements.
- Use online tools: Several online tools and calculators are available to convert between different scale ratios, calculate distances, and perform other map-related calculations.
- Explore different types of maps: Examine maps with different scales and purposes to understand the relationship between scale ratio and map content.
Tips for Using Map Scale Ratios Effectively:
- Always check the map’s scale: Ensure that the scale ratio is clearly indicated on the map before using it for measurements or calculations.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool: Accurate measurements are essential for obtaining reliable results.
- Pay attention to units: Ensure that the units of measurement are consistent throughout the calculations.
- Consider map distortion: Recognize that maps are not perfect representations of reality and that distortion can affect measurements.
Conclusion:
Map scale ratios are fundamental to understanding and interpreting maps. By mastering the concepts and techniques associated with scale ratios, users can accurately measure distances, calculate areas, and make informed decisions based on map data. Whether for navigation, planning, or research, a solid grasp of map scale ratios empowers individuals to navigate the world with greater confidence and precision.
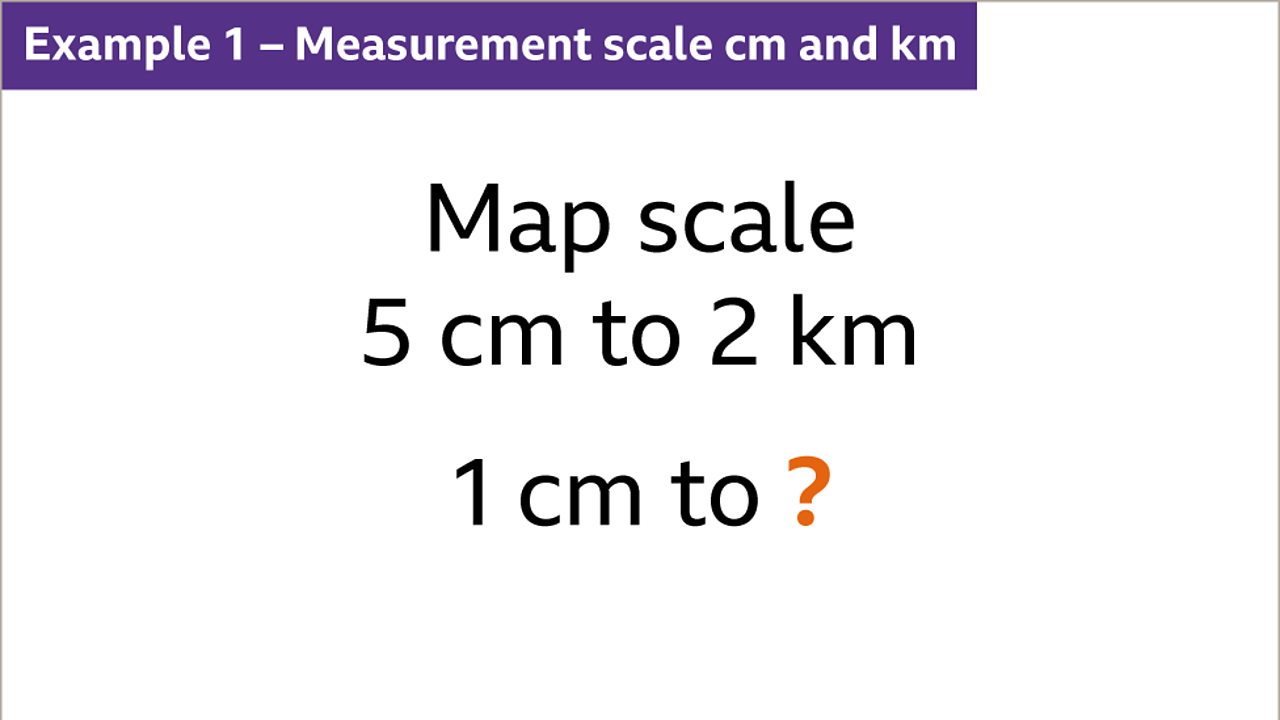
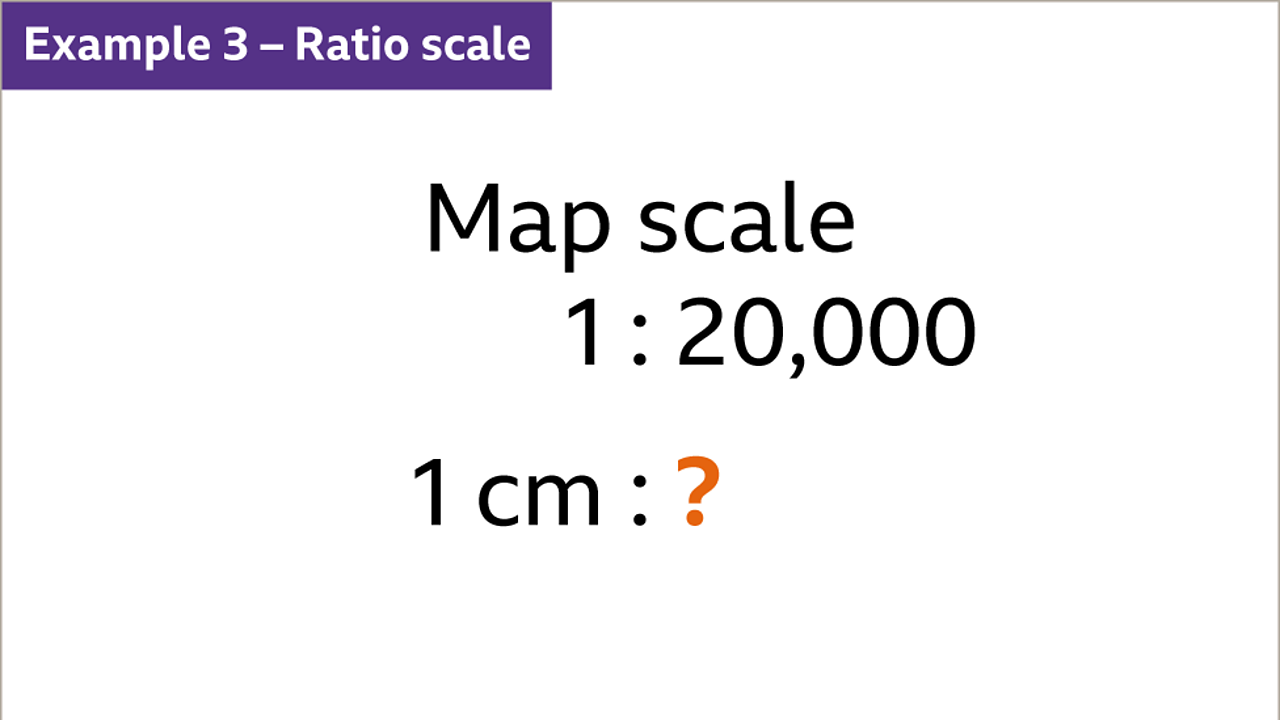



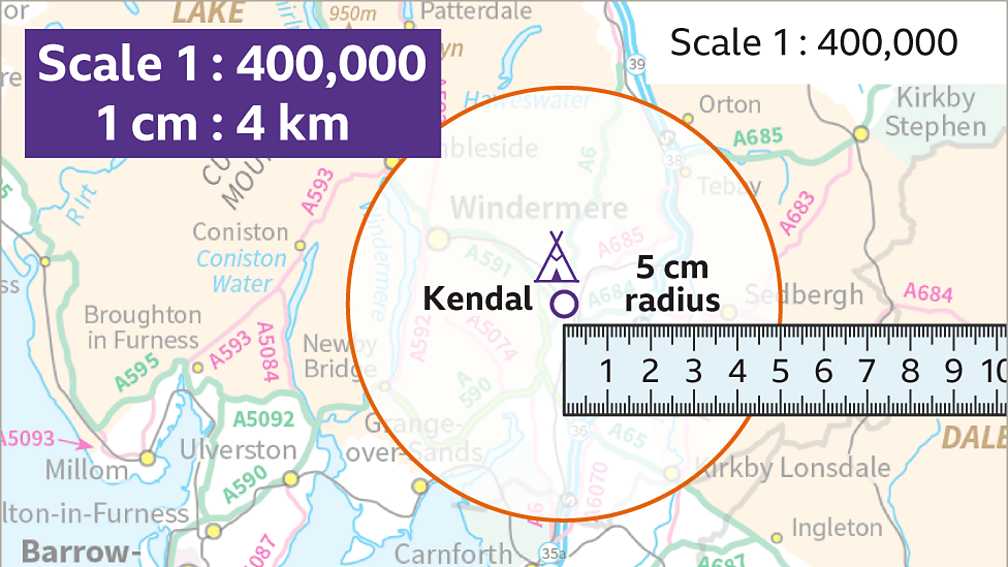
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Scale Ratios: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
