Understanding Maps with Radius: Visualizing Proximity and Defining Areas
Related Articles: Understanding Maps with Radius: Visualizing Proximity and Defining Areas
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Maps with Radius: Visualizing Proximity and Defining Areas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Maps with Radius: Visualizing Proximity and Defining Areas
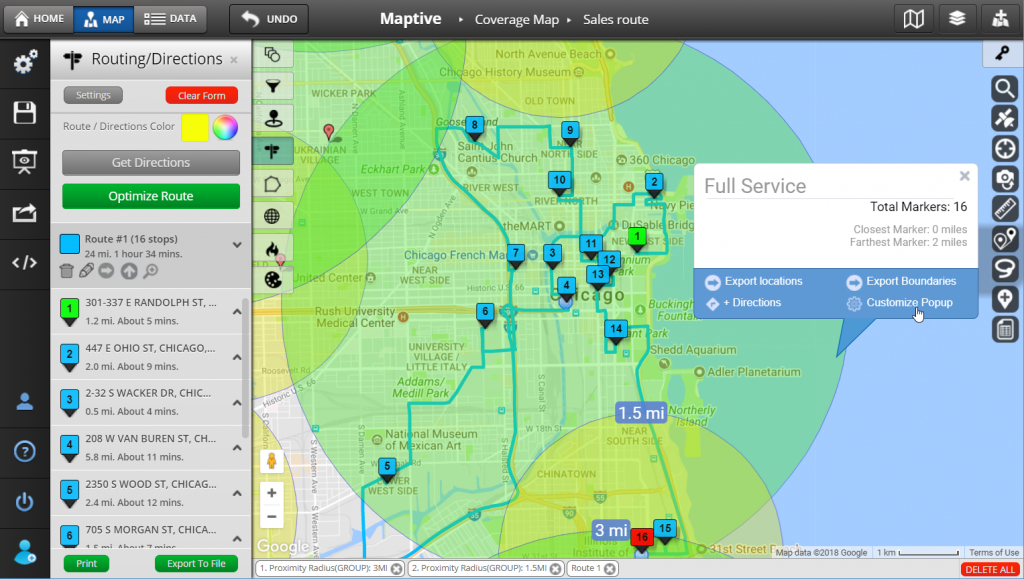
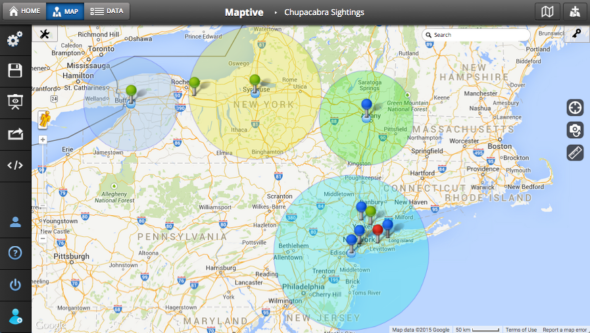
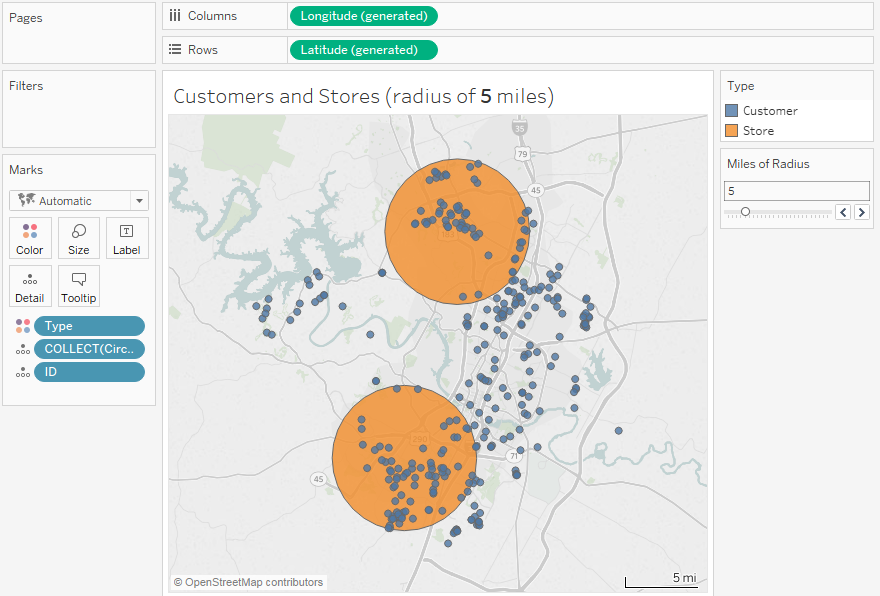
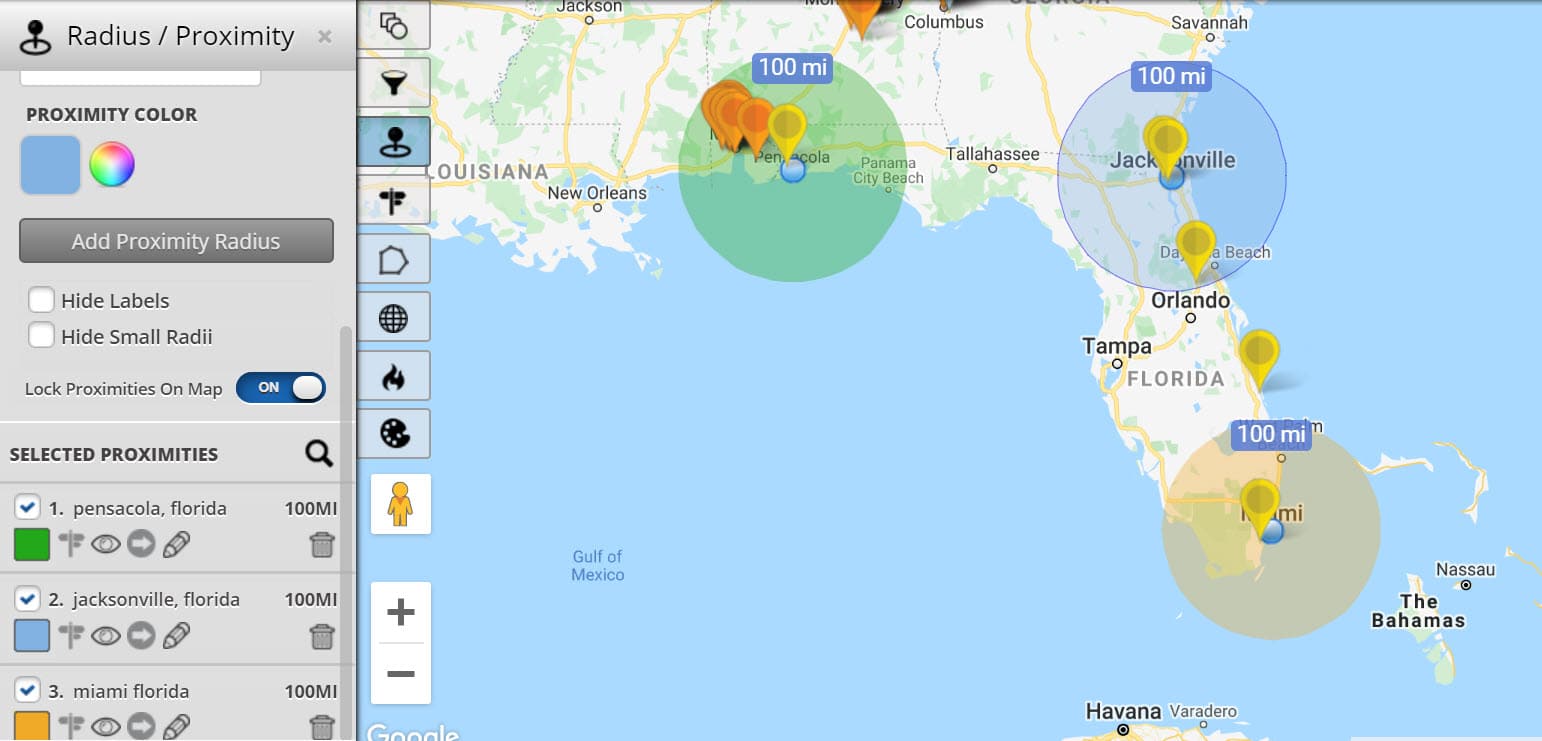
Maps with radius, often referred to as "radius maps" or "circle maps," are powerful tools for visualizing proximity and defining areas based on a central point. They provide a clear and intuitive representation of the spatial relationship between a location and its surrounding environment, making them indispensable for various applications across different fields.
The Essence of Radius Maps:
At their core, radius maps depict a circular area centered on a specific point, with the radius defining the distance from that point to the boundary of the circle. This simple yet effective concept allows for the representation of:
- Proximity: Radius maps clearly show which locations fall within a specified distance from a central point, facilitating analysis of accessibility, coverage, or influence.
- Areas of Interest: They define specific geographic regions based on their distance from a reference point, enabling targeted analysis and decision-making.
- Visual Communication: Radius maps provide a visually engaging and easily comprehensible way to present spatial information, making complex data accessible to a wider audience.
Applications of Radius Maps:
The versatility of radius maps extends across a wide range of disciplines and applications, including:
- Urban Planning: Analyzing the impact of new infrastructure projects, identifying service coverage areas, and optimizing the location of public amenities.
- Business and Marketing: Defining target markets, optimizing delivery routes, and analyzing customer proximity to retail locations.
- Emergency Response: Mapping evacuation zones, identifying the reach of emergency services, and coordinating rescue efforts.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the impact of pollution sources, defining wildlife habitat ranges, and tracking the spread of invasive species.
- Healthcare: Determining the catchment areas of hospitals and clinics, optimizing healthcare access, and identifying underserved communities.
- Education: Visualizing school district boundaries, analyzing student travel patterns, and optimizing school location planning.
Construction and Interpretation:
Creating radius maps involves the following steps:
- Defining the Central Point: The starting point for the map, which could be a specific location, a landmark, or a geographic coordinate.
- Specifying the Radius: The distance from the central point to the boundary of the circle, measured in units like kilometers, miles, or meters.
- Choosing a Base Map: Selecting an appropriate map background, such as a road map, satellite imagery, or topographic map, depending on the application.
- Visualizing the Radius: Drawing the circle on the base map, either manually or using specialized software, to represent the defined area.
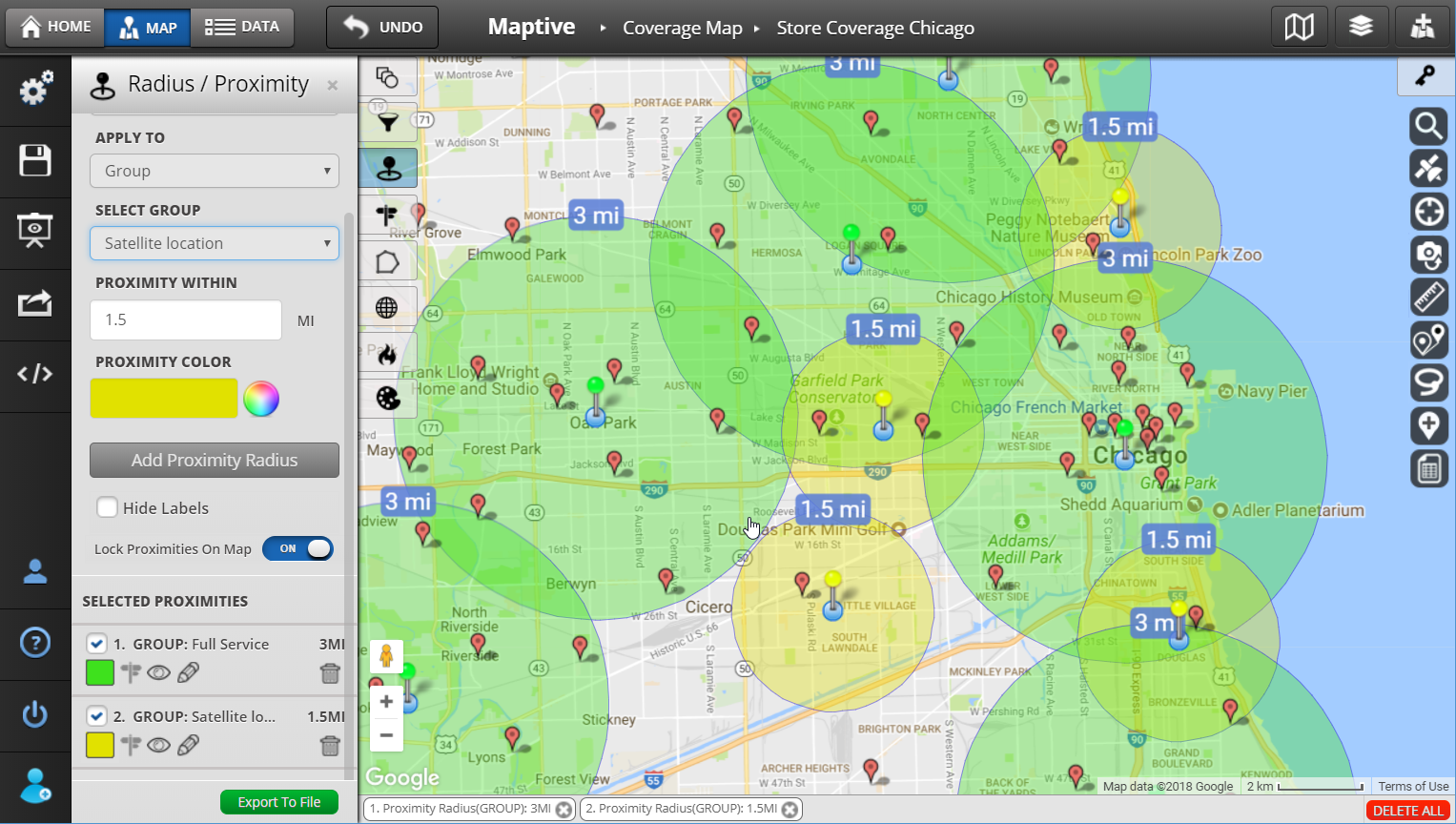
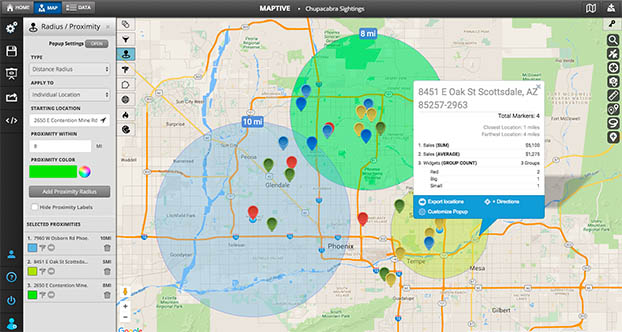
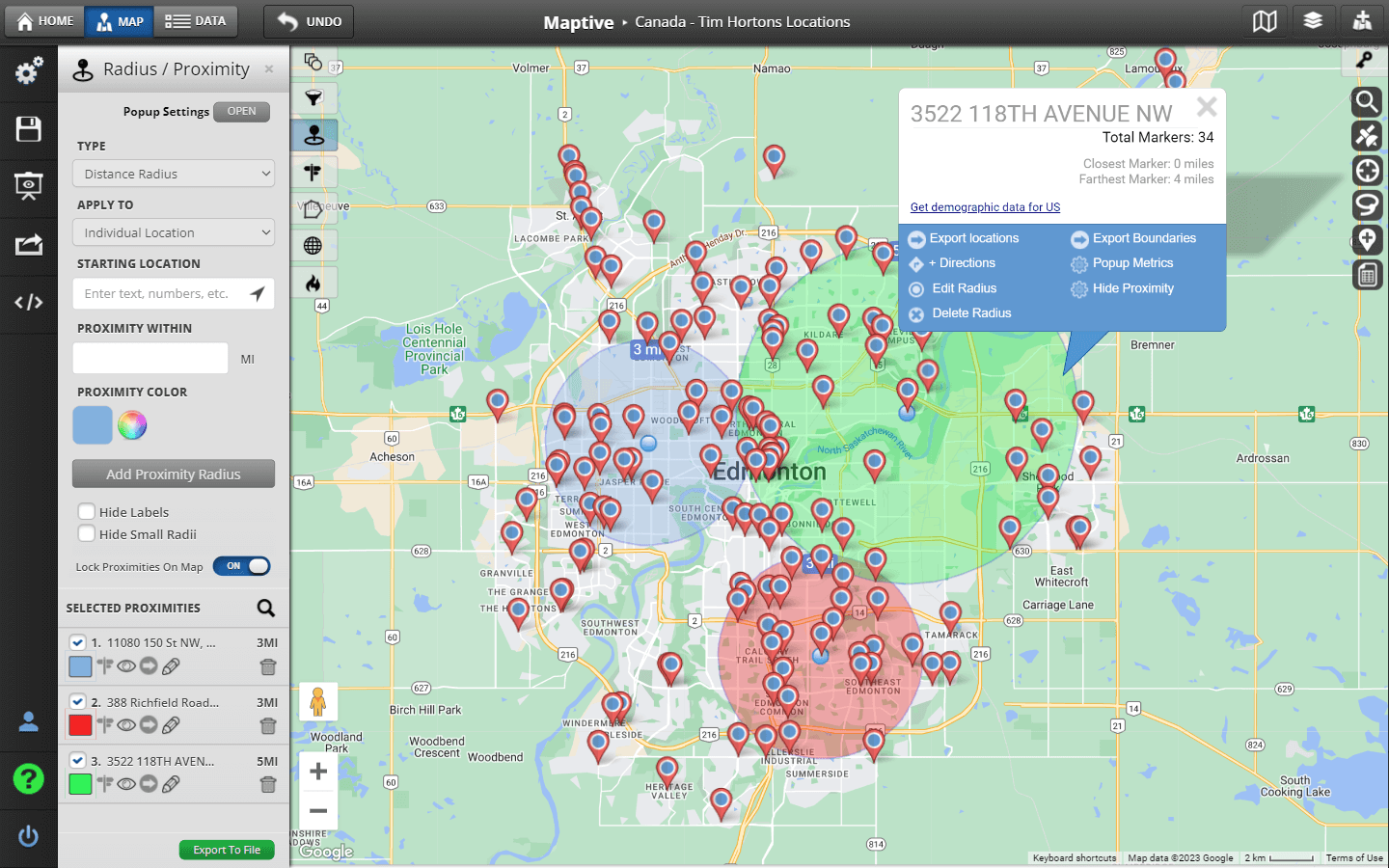
Interpreting radius maps involves understanding the relationship between the central point, the radius, and the locations within the circle. The size of the radius determines the extent of the area covered, and the placement of locations within the circle indicates their proximity to the central point.
Key Benefits of Radius Maps:
The use of radius maps offers numerous benefits:
- Clear and Intuitive Visualization: They provide a simple and readily understandable representation of spatial relationships, making complex data accessible to a wider audience.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Radius maps facilitate informed decision-making by providing a visual representation of proximity and coverage, enabling the analysis of various factors.
- Targeted Analysis: They allow for the focus on specific areas of interest defined by the radius, enabling efficient analysis and resource allocation.
- Improved Communication: Radius maps offer a powerful tool for conveying spatial information to stakeholders, facilitating collaboration and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the different types of radius maps?
Radius maps can be classified based on the type of data they represent:
- Simple Radius Maps: Depicting a single circle around a central point.
- Multi-Radius Maps: Showing multiple circles with different radii, representing varying distances from the central point.
- Buffer Maps: Similar to radius maps, but the boundary is not necessarily circular, allowing for more complex shapes based on factors like terrain or obstacles.
2. What software tools are available for creating radius maps?
Numerous software tools can be used to create radius maps, ranging from basic mapping applications to specialized Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software. Popular options include:
- Google Maps: Provides basic radius map functionality within its mapping platform.
- ArcGIS: A powerful GIS software offering advanced tools for creating and analyzing radius maps.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software with capabilities for creating radius maps.
3. What are some common applications of radius maps in different fields?
Radius maps find applications in various fields, including:
- Business: Analyzing customer proximity to retail locations, optimizing delivery routes, and defining target markets.
- Emergency Response: Mapping evacuation zones, identifying the reach of emergency services, and coordinating rescue efforts.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the impact of pollution sources, defining wildlife habitat ranges, and tracking the spread of invasive species.
Tips for Creating Effective Radius Maps:
- Choose an appropriate map background: Select a base map that aligns with the application and provides relevant contextual information.
- Use clear and consistent colors and symbols: Ensure the map is visually appealing and easy to interpret.
- Label the radius and central point: Clearly identify the distance represented by the radius and the location of the central point.
- Consider using multiple radii: Representing different distances from the central point can provide more detailed insights.
- Include relevant data layers: Overlaying additional data, such as population density or road networks, can enrich the map’s informational value.
Conclusion:
Radius maps are valuable tools for visualizing proximity and defining areas based on a central point. Their versatility and ease of interpretation make them applicable across various fields, facilitating data-driven decision-making, targeted analysis, and improved communication. By understanding the principles behind radius maps and leveraging the available software tools, users can harness their power to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions in diverse contexts.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Maps with Radius: Visualizing Proximity and Defining Areas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
