Understanding Scale on Maps: Decoding the Relationship Between Distance on a Map and Reality
Related Articles: Understanding Scale on Maps: Decoding the Relationship Between Distance on a Map and Reality
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Scale on Maps: Decoding the Relationship Between Distance on a Map and Reality. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Scale on Maps: Decoding the Relationship Between Distance on a Map and Reality
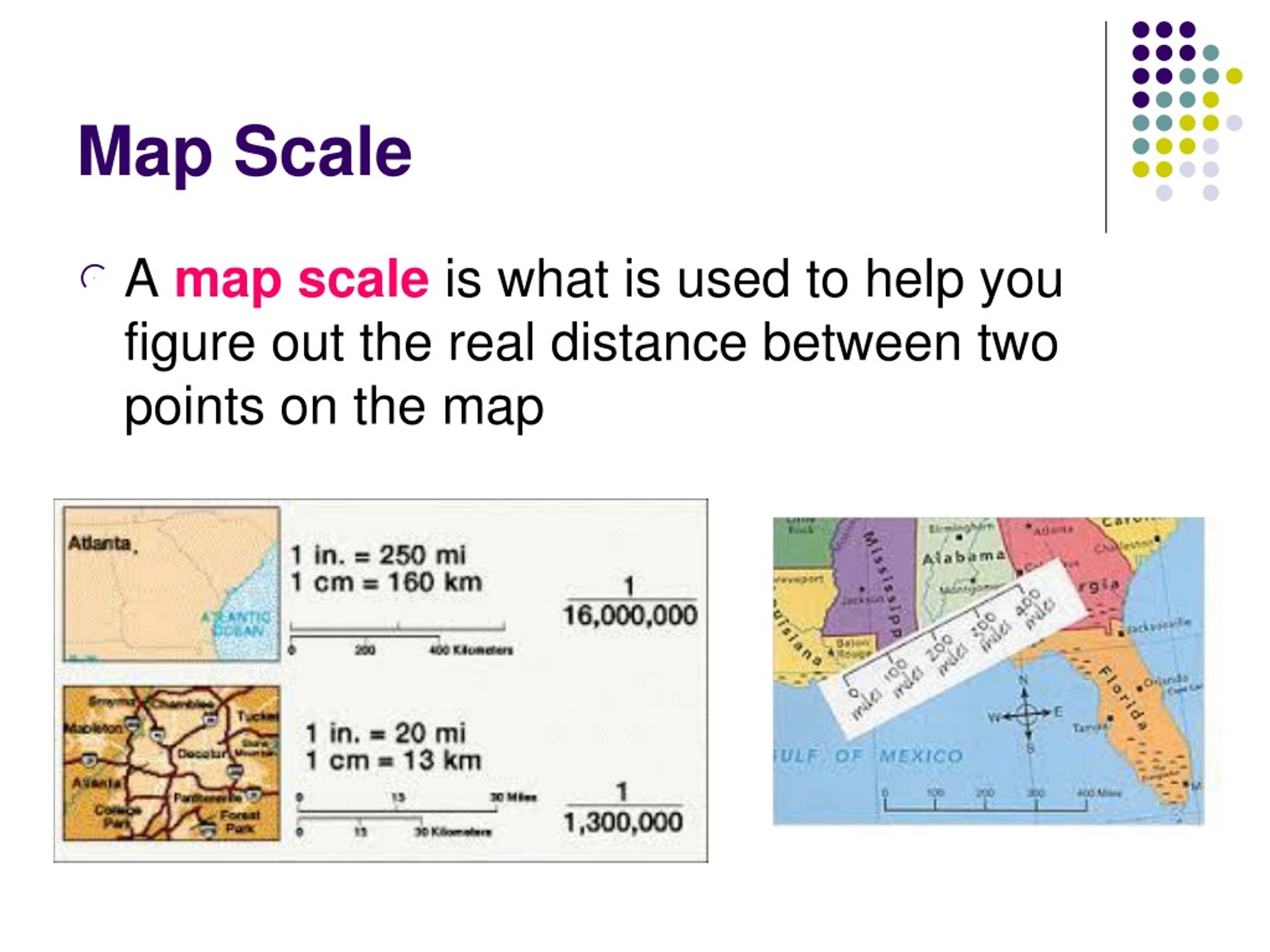
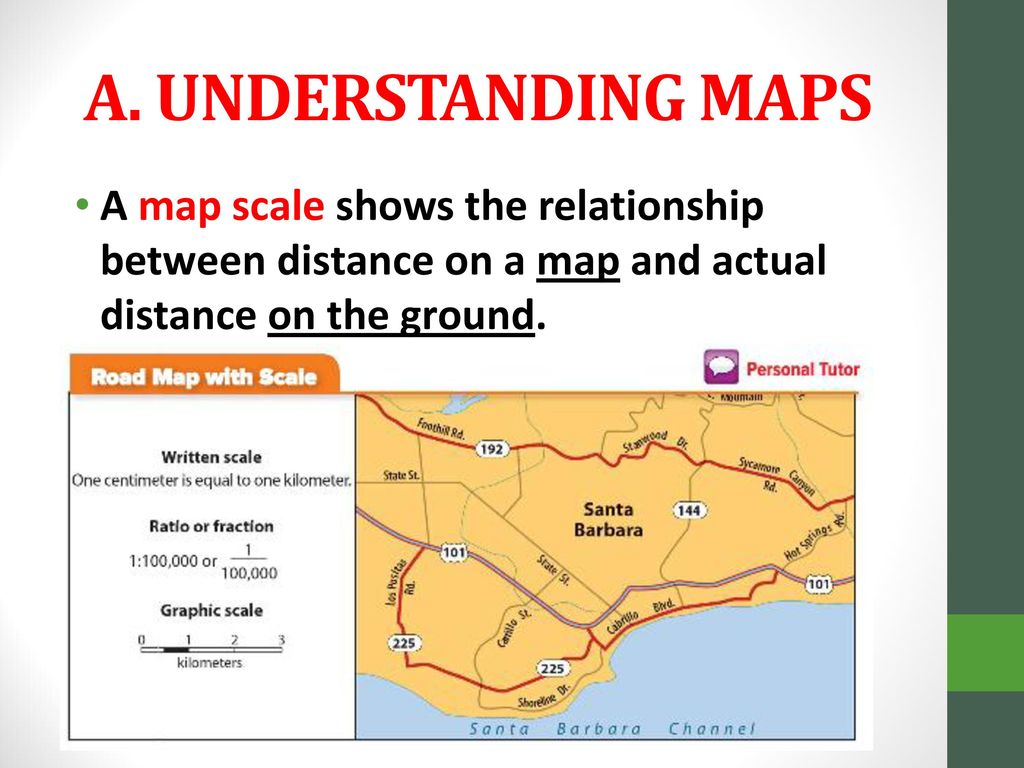
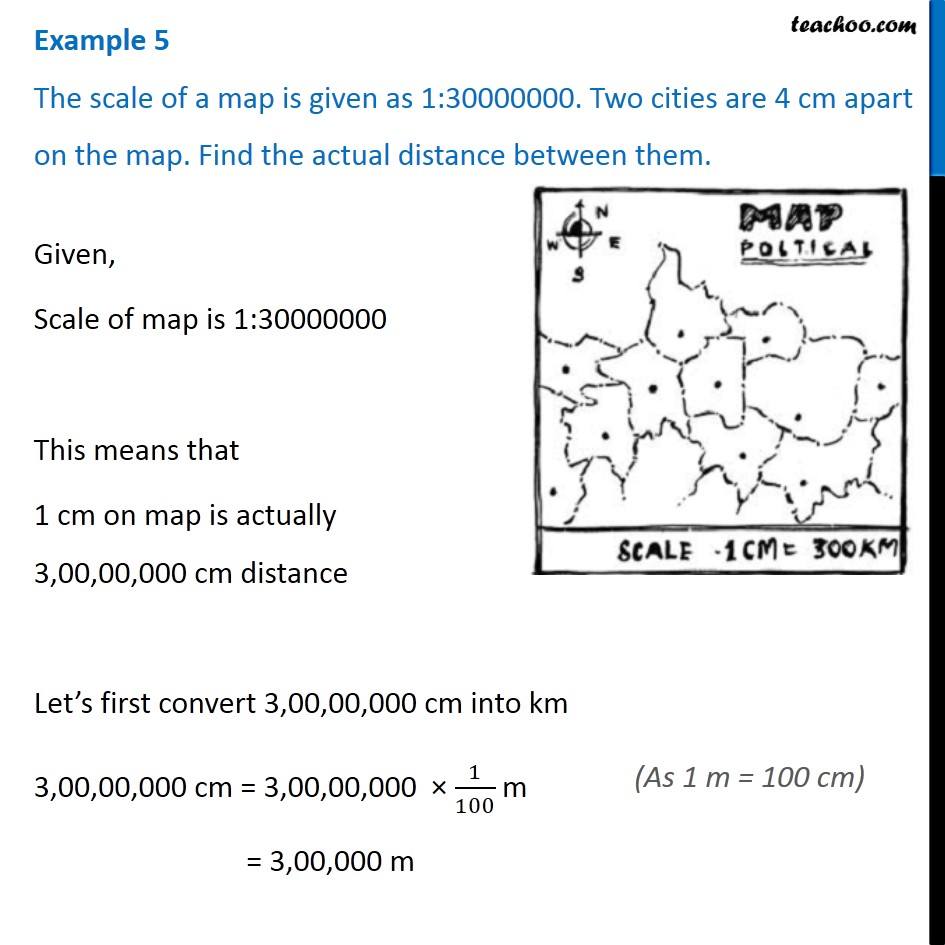
Maps are powerful tools for navigating the world, providing a miniature representation of vast landscapes. Their effectiveness hinges on the accurate portrayal of distances, achieved through the use of scale. A map’s scale defines the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance in the real world. This article explores the significance of map scales, particularly focusing on a scale of 1:25,000, and demonstrates how to determine real-world distances from measurements on a map.
Understanding the Concept of Scale
The scale of a map is expressed as a ratio, typically written as 1:x, where:
- 1 represents one unit of measurement on the map.
- x represents the equivalent number of units of measurement in the real world.
For instance, a scale of 1:25,000 indicates that one centimeter on the map represents 25,000 centimeters (or 250 meters) in the real world. This means that every centimeter measured on the map corresponds to 250 meters on the ground.
The Significance of Scale in Map Interpretation
The scale of a map is crucial for accurate interpretation and measurement. It allows us to:
- Determine real-world distances: By measuring distances on the map and applying the scale, we can calculate the actual distance on the ground.
- Compare sizes and distances: The scale provides a consistent reference point for comparing the relative sizes and distances of different features on the map.
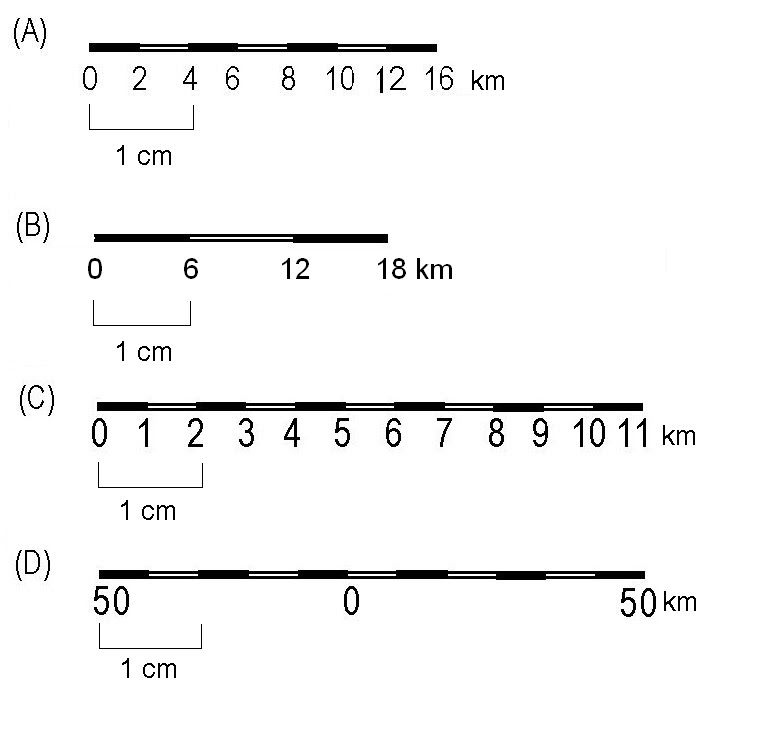
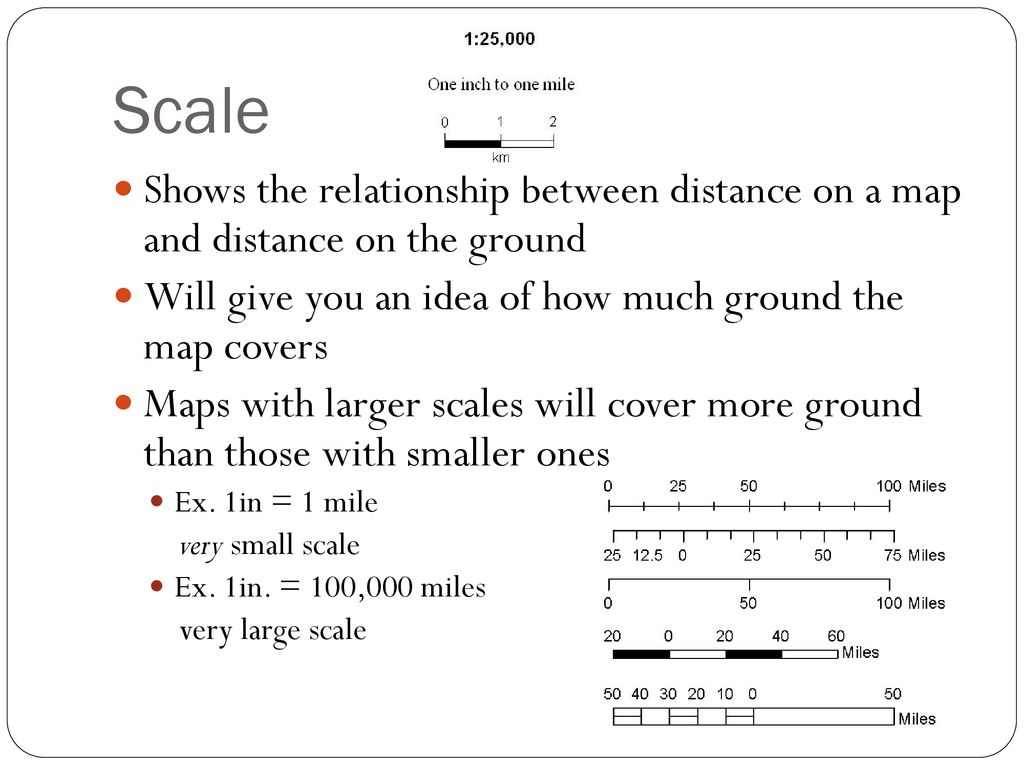
- Understand the level of detail: Larger scale maps (e.g., 1:10,000) depict a smaller area with greater detail, while smaller scale maps (e.g., 1:100,000) show a larger area with less detail.
Applying the Scale: Calculating Real-World Distance
To calculate the real-world distance corresponding to a measurement on a map, we use the following formula:
Real-world distance = Map distance x Scale
Example:
Let’s consider a map with a scale of 1:25,000. If we measure a distance of 9 centimeters on the map, the corresponding real-world distance can be calculated as follows:
Real-world distance = 9 cm x 25,000 = 225,000 cm
Converting centimeters to meters, we get:
Real-world distance = 225,000 cm / 100 cm/m = 2,250 meters
Therefore, a 9 centimeter distance on the map represents a real-world distance of 2,250 meters.
The Importance of Scale in Different Applications
The choice of scale for a map depends on its intended purpose. For example:
- Topographical maps: These maps often use large scales (e.g., 1:25,000) to provide detailed information about terrain, elevation, and features in a specific area.
- Road maps: These maps generally employ smaller scales (e.g., 1:100,000) to cover larger regions and focus on major roads and cities.
- World maps: These maps use extremely small scales (e.g., 1:100,000,000) to represent the entire globe, sacrificing detail for broad coverage.
Conclusion
Understanding the scale of a map is essential for accurate interpretation and measurement. By applying the scale, we can translate distances on the map into their real-world equivalents, allowing us to gain a deeper understanding of the landscape and navigate effectively. Whether exploring a local park or planning a cross-country road trip, the scale of the map remains a crucial tool for deciphering the relationship between the miniature representation and the vast reality it portrays.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Scale on Maps: Decoding the Relationship Between Distance on a Map and Reality. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
