Understanding Scotland’s Debt Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding Scotland’s Debt Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Scotland’s Debt Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Scotland’s Debt Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis
Scotland’s financial landscape is a complex tapestry woven from various threads, including its relationship with the United Kingdom, its economic performance, and its public finances. One crucial element of this landscape is the concept of "debt," a term that often evokes anxieties and necessitates careful understanding. This article delves into the intricacies of Scotland’s debt, exploring its various facets, the underlying factors contributing to its accumulation, and its implications for the Scottish economy and its people.
Defining Scotland’s Debt:
Firstly, it is essential to clarify what constitutes "Scotland’s debt." The term encompasses various forms of financial obligations, including:
- Public Sector Net Debt: This represents the total amount of money borrowed by the Scottish Government, local authorities, and public corporations. It is a key indicator of the government’s financial health and its ability to meet its spending commitments.
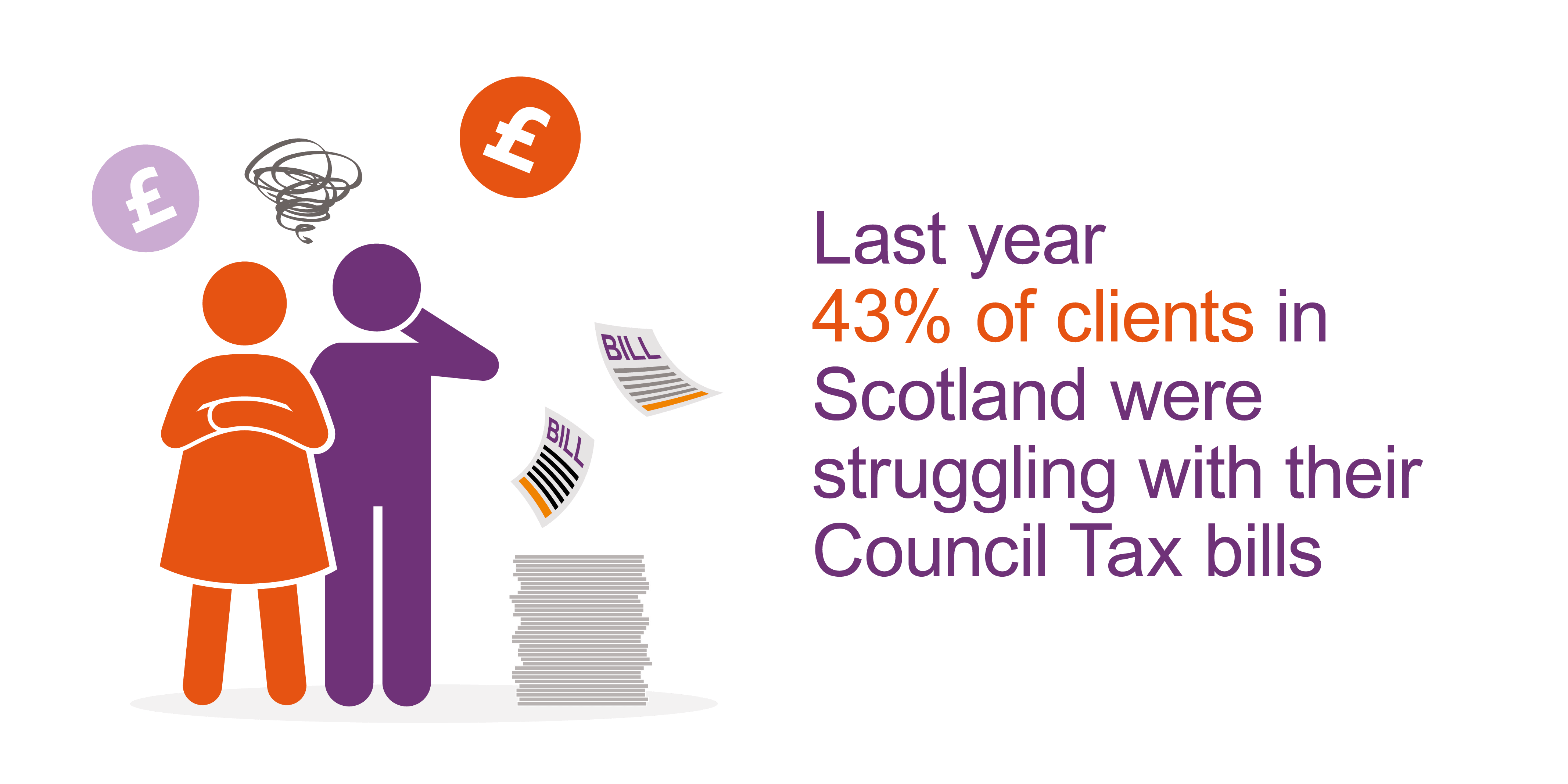
- Private Sector Debt: This encompasses the sum of money owed by individuals and businesses in Scotland. It includes mortgages, loans, credit card debt, and other financial obligations.
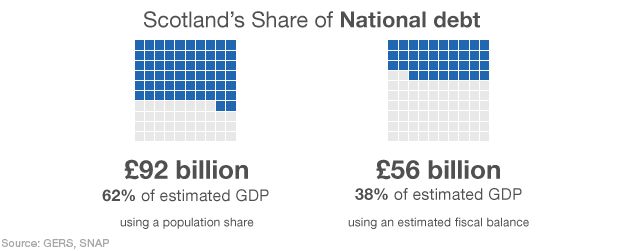
- National Debt: This refers to the total amount of money owed by the UK government, including Scotland’s share. While Scotland does not have independent control over this debt, it is a significant factor influencing the Scottish economy.
Factors Contributing to Scotland’s Debt:
Several factors contribute to the accumulation of debt in Scotland, reflecting broader economic and political realities:
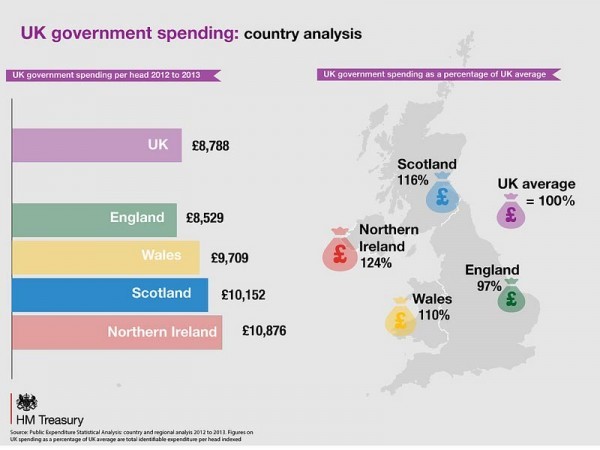
- Public Spending: The Scottish Government’s expenditure on public services, such as healthcare, education, and social security, plays a significant role in shaping its debt levels. This spending is often influenced by political priorities and the need to address social and economic challenges.
- Economic Performance: The overall health of the Scottish economy, including factors like employment levels, productivity, and investment, influences both public and private sector debt. Economic downturns can lead to increased borrowing by individuals, businesses, and the government to mitigate financial difficulties.
- Fiscal Policy: The Scottish Government’s fiscal policy, which encompasses its taxation and spending decisions, directly impacts its debt levels. Choices regarding tax rates, spending priorities, and the allocation of resources can influence the government’s financial position.
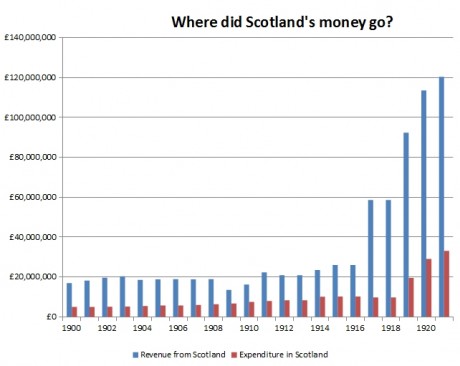
- UK Government Borrowing: Scotland’s share of the UK national debt is a significant factor in its overall debt burden. This debt is influenced by the UK government’s fiscal policy and spending decisions, which can impact Scotland’s financial situation.
- Demographic Trends: Aging populations, with their associated healthcare and pension costs, can contribute to increased public sector debt. Similarly, changes in birth rates and migration patterns can impact the demand for public services and influence government spending.
Analyzing the Impact of Debt:
Understanding the impact of debt on Scotland requires considering its various implications:
- Economic Growth: High levels of debt can negatively impact economic growth by increasing borrowing costs for businesses and individuals, hindering investment and discouraging entrepreneurship.
- Public Services: Debt can constrain the government’s ability to fund public services, potentially leading to cuts in essential services or reduced quality of care.
- Taxation: Increased debt can necessitate higher taxes to service the debt, potentially impacting individuals and businesses through reduced disposable income and higher business costs.
- Financial Stability: Excessive debt can pose a risk to financial stability, potentially leading to government defaults or economic crises.
Navigating the Debt Landscape:
Managing Scotland’s debt effectively requires a multifaceted approach:
- Fiscal Responsibility: The Scottish Government must maintain fiscal responsibility by balancing spending and revenue, avoiding excessive borrowing, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Economic Growth: Fostering economic growth through policies that promote investment, innovation, and job creation can generate revenue and reduce the burden of debt.
- Structural Reforms: Implementing structural reforms to address underlying economic challenges, such as improving productivity, enhancing skills, and fostering a more competitive business environment, can contribute to debt reduction.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency and accountability in government finances is crucial to building public trust and enabling effective management of debt.
FAQs on Scotland’s Debt:
Q: Does Scotland have its own currency?
A: No, Scotland does not have its own currency. It uses the British Pound Sterling, which is controlled by the Bank of England.
Q: How does Scotland’s debt compare to other countries?
A: Scotland’s debt levels are comparable to other developed nations, but they are influenced by the UK’s overall debt.
Q: What are the implications of independence for Scotland’s debt?
A: Independence would likely lead to a complex process of debt apportionment between Scotland and the UK, with significant implications for both economies.
Q: How can I learn more about Scotland’s debt?
A: You can access information from sources like the Scottish Government, the UK Office for National Statistics, and independent economic think tanks.
Tips for Understanding Scotland’s Debt:
- Focus on the Long Term: Debt is a complex issue that requires a long-term perspective. Avoid short-term fixes that may lead to greater problems later.
- Consider the Underlying Causes: Understanding the factors driving debt accumulation is crucial for developing effective solutions.
- Engage in Informed Debate: Participate in public discussions about debt management and policy solutions, contributing to informed decision-making.
Conclusion:
Scotland’s debt landscape is dynamic and complex, influenced by a multitude of factors. It is essential to approach this issue with a clear understanding of its various facets, its impact on the Scottish economy, and the potential strategies for managing it effectively. By fostering informed discussions, promoting fiscal responsibility, and implementing sound economic policies, Scotland can navigate its debt challenges and strive towards a more sustainable and prosperous future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Scotland’s Debt Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
