Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance
Related Articles: Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance
- 3.1 Defining Earth’s Radius
- 3.2 Factors Influencing Earth’s Radius
- 3.3 Significance of Earth’s Radius
- 3.4 FAQs about Earth’s Radius
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding Earth’s Radius
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance
The Earth, our home planet, is a near-spherical celestial body with a complex structure. One of its fundamental characteristics is its radius, a crucial parameter for various scientific and practical applications. This article delves into the concept of Earth’s radius, exploring its different measurements, the factors influencing its variation, and its significance in various fields.
Defining Earth’s Radius
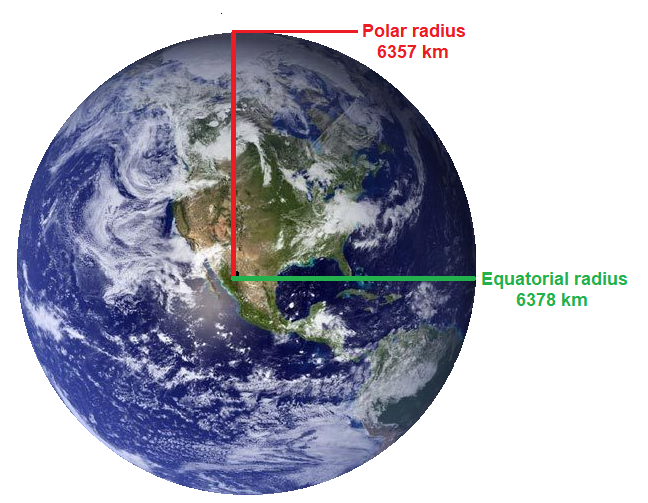
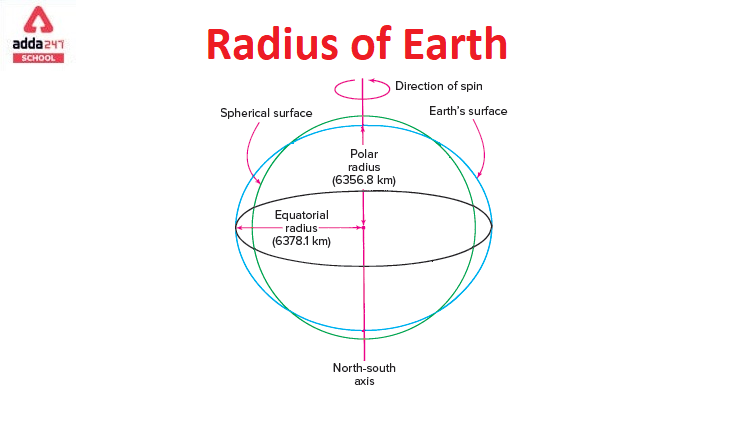
Earth’s radius refers to the distance from its center to its surface. Due to the planet’s slightly oblate shape, meaning it bulges at the equator and is flattened at the poles, there are multiple ways to define the radius:
- Equatorial Radius: This represents the distance from the Earth’s center to a point on the equator, measuring approximately 6,378.1 kilometers (3,963.2 miles).
- Polar Radius: This refers to the distance from the Earth’s center to a point on the North or South Pole, measuring approximately 6,356.8 kilometers (3,949.9 miles).
- Mean Radius: This is an average value of the Earth’s radius, calculated as the geometric mean of the equatorial and polar radii, approximately 6,371 kilometers (3,959 miles).
These variations in radius are crucial for understanding the Earth’s shape and its gravitational field.
Factors Influencing Earth’s Radius
The Earth’s radius is not a static value but is influenced by various factors, including:
- Rotation: The Earth’s rotation causes a centrifugal force, which pushes matter outwards at the equator, leading to the equatorial bulge.
- Gravity: The Earth’s gravitational field attracts matter towards its center, influencing the overall shape and radius.
- Tectonic Activity: Plate tectonics, the movement of the Earth’s crust, can cause changes in elevation and, consequently, local variations in radius.
- Melting and Freezing of Ice Caps: Fluctuations in ice cover can affect the distribution of mass and alter the Earth’s shape and radius.
These factors contribute to a dynamic Earth, where its radius is constantly evolving, albeit on a geological timescale.
Significance of Earth’s Radius
The Earth’s radius plays a significant role in various fields, including:
- Navigation and Mapping: Accurate measurements of the Earth’s radius are essential for precise navigation systems, satellite mapping, and geographical information systems (GIS).
- Space Exploration: Understanding the Earth’s radius is crucial for launching satellites into orbit, calculating orbital parameters, and planning space missions.
- Geophysics and Geology: The Earth’s radius provides insights into the planet’s internal structure, composition, and dynamics.
- Climate Modeling: Variations in the Earth’s radius can influence atmospheric circulation patterns and climate change.
- Astronomy: The Earth’s radius is used as a reference point for measuring distances to other celestial objects.
FAQs about Earth’s Radius
1. How is Earth’s radius measured?
Earth’s radius is measured using various techniques, including:
- Satellite Altimetry: Satellites measure the distance between themselves and the Earth’s surface using radar signals.
- Gravity Measurements: Variations in Earth’s gravitational field provide information about its shape and radius.
- Geodetic Surveys: Precise measurements of distances and angles on the Earth’s surface are used to calculate its radius.
2. What is the difference between Earth’s radius and diameter?
The diameter of a sphere is the distance across its center, while the radius is the distance from the center to its surface. Therefore, the diameter is twice the radius.
3. Does Earth’s radius change over time?
While Earth’s radius is constantly evolving, the changes are very slow and occur over geological timescales. The primary factors influencing these changes are tectonic activity, ice cap melting and freezing, and gravitational forces.
4. How does Earth’s radius affect its gravitational force?
The Earth’s gravitational force is directly proportional to its mass and inversely proportional to the square of its radius. Therefore, a larger radius would result in a weaker gravitational force.
5. What are some applications of Earth’s radius in everyday life?
Earth’s radius is used in numerous applications, including:
- GPS navigation: Accurate calculation of distances and locations relies on precise measurements of the Earth’s radius.
- Weather forecasting: Atmospheric models use the Earth’s radius to simulate weather patterns and predict climate change.
- Construction projects: Understanding the Earth’s curvature is essential for designing large-scale structures like bridges and tunnels.
Tips for Understanding Earth’s Radius
- Visualize the Earth’s shape: Imagine a slightly squashed sphere, with a bulge at the equator and a flattened area at the poles.
- Remember the different radii: Understand the distinction between equatorial, polar, and mean radius and their respective values.
- Consider the factors influencing the radius: Recognize that the Earth’s radius is not static and is influenced by various factors, including rotation, gravity, and tectonic activity.
- Explore the applications of Earth’s radius: Understand how the radius is used in different fields, from navigation to climate modeling.
- Engage with resources: Explore online resources, textbooks, and documentaries to deepen your understanding of Earth’s radius and its significance.
Conclusion
The Earth’s radius is a fundamental parameter that plays a crucial role in various scientific and practical applications. Understanding its different measurements, the factors influencing its variation, and its significance in different fields is essential for comprehending our planet’s shape, gravity, and dynamics. As we continue to explore and study Earth, our understanding of its radius will undoubtedly evolve, leading to further discoveries and applications in various fields.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Concept of Earth’s Radius and its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
