Understanding the Horizontal Lines on Maps: A Guide to Latitude and its Importance
Related Articles: Understanding the Horizontal Lines on Maps: A Guide to Latitude and its Importance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Horizontal Lines on Maps: A Guide to Latitude and its Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Horizontal Lines on Maps: A Guide to Latitude and its Importance

Maps are essential tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding the world around us. They provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, allowing us to comprehend spatial relationships, distances, and geographical features. While we often focus on the vertical lines that run north to south, the horizontal lines that traverse the globe from east to west are equally crucial. These lines, known as lines of latitude, play a vital role in defining locations, understanding climate patterns, and navigating the vast expanse of our planet.
Latitude: Defining Our Position on Earth
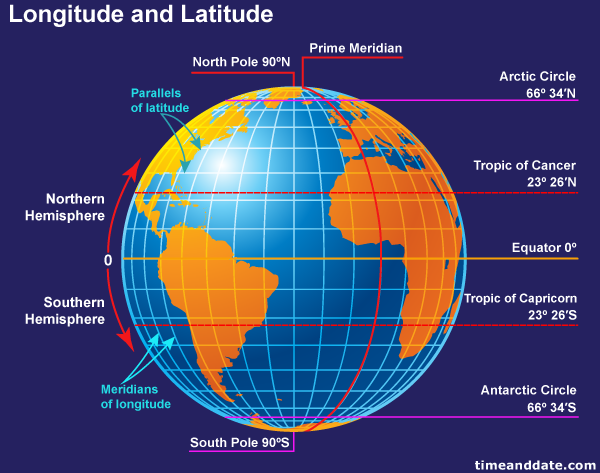
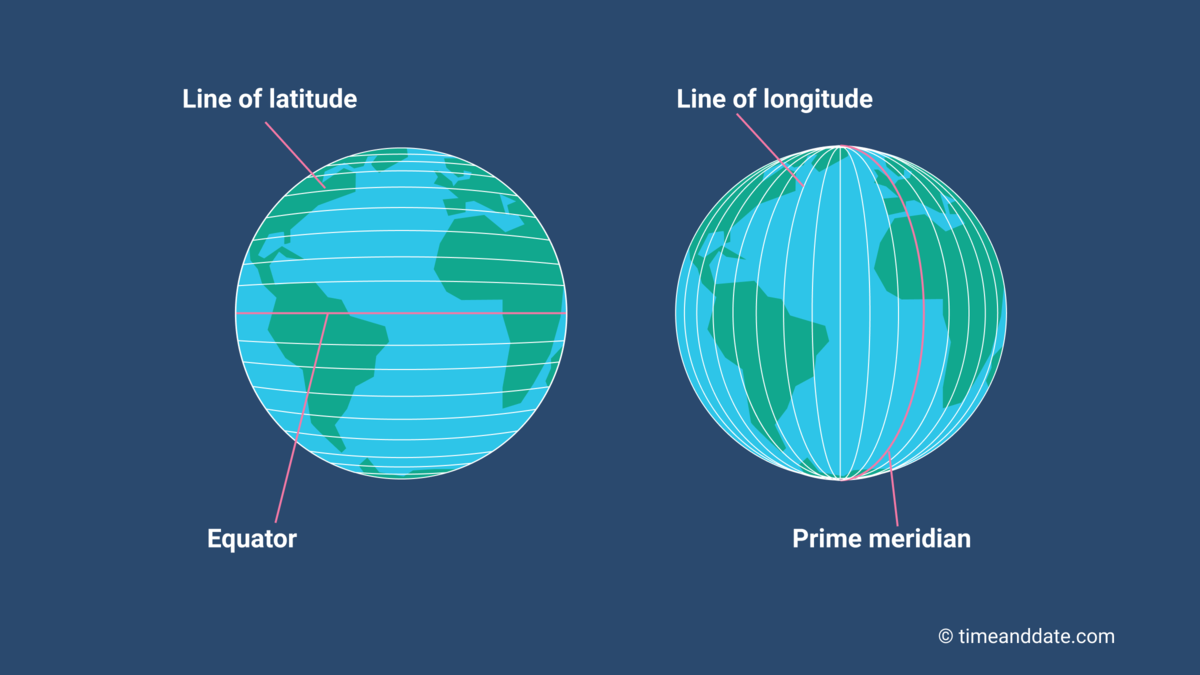
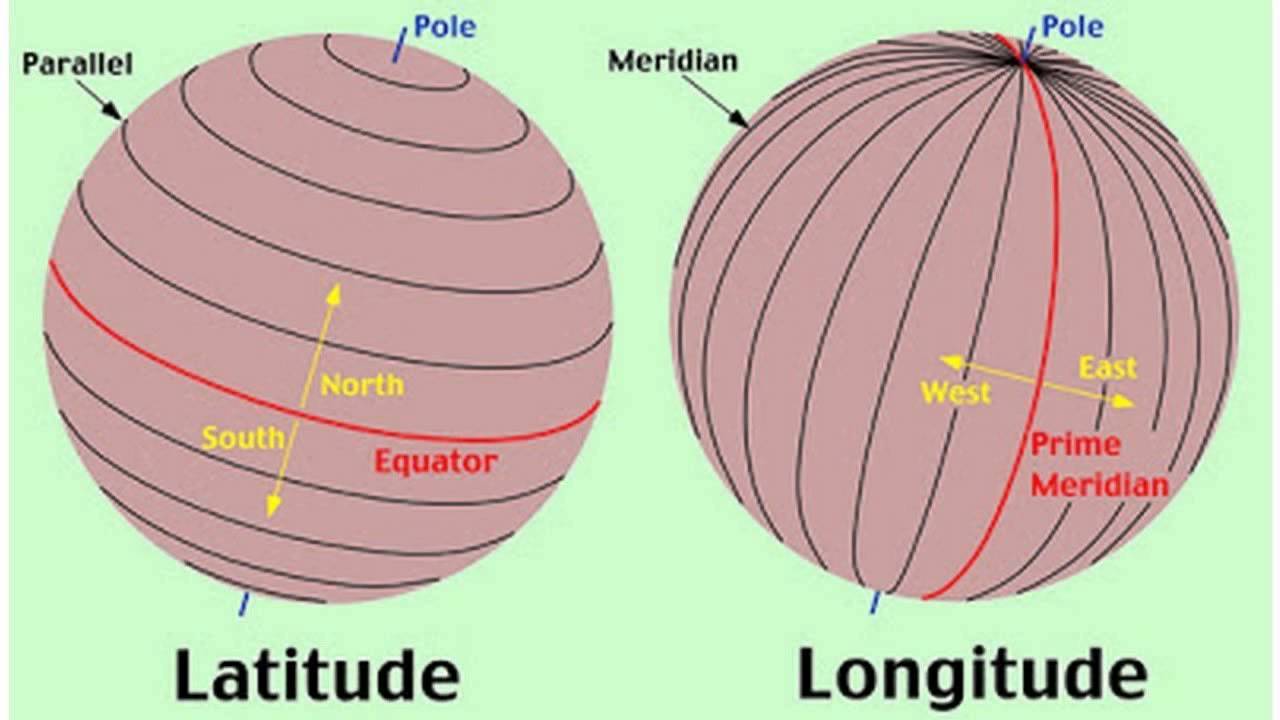
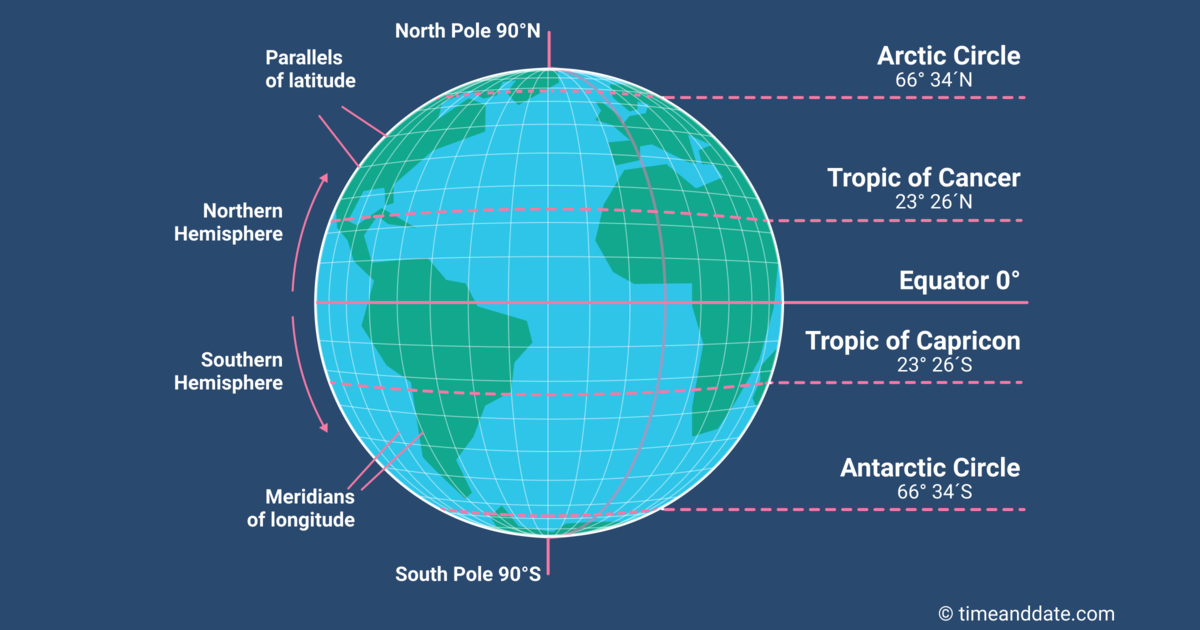
Imagine a globe, a perfect sphere representing our planet. Now, envision a circle drawn around the globe, passing through both the North and South Poles. This circle is the equator, the most important line of latitude, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Every other line of latitude is a smaller circle parallel to the equator, running east to west. These lines, like the equator, are imaginary circles that help us pinpoint our position on Earth. The latitude of a location is its angular distance, measured in degrees, north or south of the equator.
- The equator, being at 0 degrees latitude, is the reference point.
- Locations north of the equator have positive latitude values, ranging from 0 to 90 degrees at the North Pole.
- Locations south of the equator have negative latitude values, ranging from 0 to -90 degrees at the South Pole.
The Significance of Latitude
Latitude is a fundamental concept in geography, influencing various aspects of our planet:
- Climate: Latitude significantly affects climate patterns. Regions near the equator receive direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in warmer temperatures and tropical climates. As you move further north or south, the angle of sunlight decreases, leading to colder temperatures and seasonal variations.
- Daylight Hours: Latitude determines the length of daylight hours at different locations. The equator experiences nearly equal day and night throughout the year. As you move towards the poles, the difference in day and night length becomes more pronounced, with extreme variations during the summer and winter solstices.
- Navigation: Latitude is crucial for navigation, allowing sailors and pilots to determine their position on Earth. By measuring the angle of the sun or stars relative to the horizon, they can calculate their latitude and thus their location.
- Understanding Time Zones: Latitude plays a role in defining time zones. The Earth’s rotation creates a 24-hour day, and time zones are created to account for the varying positions of the sun at different longitudes. While longitude primarily determines the time zone, latitude influences the length of daylight hours and thus the timing of sunrise and sunset.
- Global Mapping and Data Analysis: Lines of latitude are foundational to mapping systems. They serve as a grid system, enabling us to accurately represent locations and geographical features on maps. Latitude is also critical in analyzing global datasets, such as weather patterns, population distribution, and resource availability.
Exploring the Lines of Latitude
Beyond the equator, several other lines of latitude hold significance:
- Tropics: The Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South) mark the boundaries of the tropics, regions characterized by consistently warm temperatures and significant rainfall.
- Arctic and Antarctic Circles: The Arctic Circle (66.5 degrees North) and the Antarctic Circle (66.5 degrees South) mark the boundaries of the polar regions, experiencing prolonged periods of darkness and daylight during the winter and summer solstices, respectively.
- Other Notable Lines: Other lines of latitude, such as the 30th and 40th parallels, have cultural and geographical significance. For instance, the 30th parallel North runs through several major cities in the United States, while the 40th parallel North is known as the "Golden Gate" and is associated with fertile land and pleasant climates.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Latitude
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude and longitude are both essential coordinates for defining locations on Earth. Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, running horizontally from east to west. Longitude, on the other hand, measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, running vertically from north to south. Together, latitude and longitude create a grid system that allows us to pinpoint any location on Earth.
Q: How is latitude measured?
A: Latitude is typically measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. The equator is at 0 degrees latitude, and the North Pole is at 90 degrees North. Locations north of the equator have positive latitude values, while locations south of the equator have negative latitude values.
Q: Why is latitude important for climate?
A: Latitude significantly affects climate patterns due to the angle of sunlight reaching different parts of the Earth. Regions near the equator receive direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in warmer temperatures. As you move further north or south, the angle of sunlight decreases, leading to colder temperatures and seasonal variations.
Q: How does latitude influence time zones?
A: Latitude indirectly influences time zones by affecting the length of daylight hours. While longitude primarily determines the time zone, latitude affects the timing of sunrise and sunset.
Q: What are some examples of the importance of latitude in everyday life?
A: Latitude is essential for various aspects of our lives, from navigation and climate understanding to mapping and data analysis. For instance, sailors use latitude to determine their position at sea, while farmers use it to understand the best time to plant crops.
Tips: Navigating the World of Latitude
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the Earth as a sphere helps understand how lines of latitude wrap around the globe.
- Remember the equator: The equator is the starting point for measuring latitude, and it divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- Think about the sun: The angle of sunlight hitting the Earth directly affects temperature and daylight hours, which are influenced by latitude.
- Explore the world: Travel to different latitudes and observe the variations in climate, daylight hours, and cultural practices.
Conclusion: The Importance of Lines Running East to West
Lines of latitude, running horizontally from east to west, are not merely imaginary lines on a map. They are fundamental geographical concepts that define our position on Earth, influence climate patterns, and guide navigation. Understanding latitude is essential for comprehending the diverse features and dynamics of our planet. By appreciating the significance of these horizontal lines, we gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and our place within it.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Horizontal Lines on Maps: A Guide to Latitude and its Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
