Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale
- 3.1 Defining Map Scale: A Ratio of Representation
- 3.2 The Importance of Map Scale: Unveiling the Power of Representation
- 3.3 Navigating the Scale Chart: A Guide to Effective Map Interpretation
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Map Scale
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Map Use: Enhancing Your Spatial Awareness
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Scale for Effective Map Interpretation
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale

Maps are powerful tools that allow us to navigate, explore, and understand the world around us. They translate complex spatial relationships into a visual format, enabling us to comprehend vast distances and intricate details. However, the accuracy and utility of any map depend on its scale – the ratio that defines the relationship between the map’s representation and the real-world distance it depicts. This fundamental concept, often expressed in a map scale chart, is essential for interpreting and utilizing map information effectively.
Defining Map Scale: A Ratio of Representation
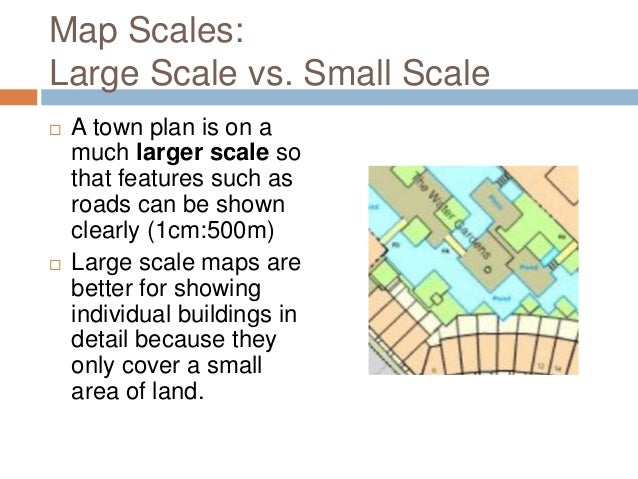
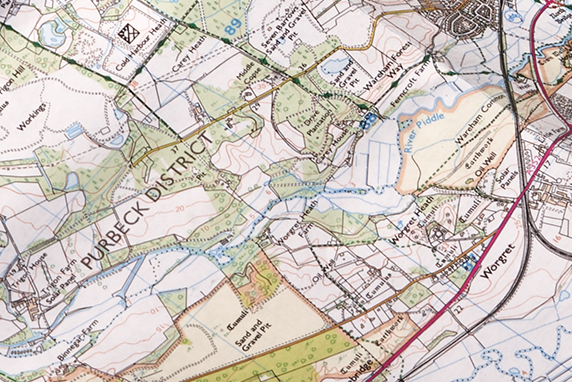
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is crucial because it determines the level of detail and the extent of the area represented on the map. A large-scale map, with a small ratio, depicts a small area in great detail, while a small-scale map, with a large ratio, covers a vast area with less detail.
There are three common ways to express map scale:
1. Verbal Scale: This method uses words to describe the relationship between map distance and ground distance. For example, "1 inch equals 1 mile" indicates that one inch on the map represents one mile on the ground.
2. Representative Fraction (RF): This method expresses the scale as a fraction, where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the corresponding ground distance. For instance, a scale of 1:25,000 means that one unit on the map represents 25,000 units on the ground. This method is particularly useful for calculations and comparisons between different maps.
3. Graphic Scale: This method uses a visual representation of the scale, typically a bar with markings that correspond to specific ground distances. This allows for quick and easy estimation of distances directly on the map without calculations.
The Importance of Map Scale: Unveiling the Power of Representation
Understanding map scale is crucial for several reasons:
-
Accurate Distance Measurement: Map scale allows users to accurately measure distances on the map and translate them to real-world distances. This is essential for navigation, planning routes, and estimating travel time.
-
Effective Interpretation of Detail: Different map scales provide varying levels of detail. Large-scale maps are ideal for studying small areas in detail, while small-scale maps provide a broader overview of larger regions. Choosing the appropriate scale for the task at hand is critical for extracting meaningful information from the map.
-
Comparison and Analysis: Comparing maps with different scales allows for the analysis of spatial relationships and the identification of patterns across different geographic areas. For example, comparing a large-scale map of a city with a small-scale map of a country can reveal the city’s location and its relationship to the broader regional context.
-
Spatial Reasoning and Visualization: Understanding map scale fosters spatial reasoning skills, allowing users to visualize and interpret spatial information effectively. This is essential for understanding geographic concepts, analyzing data, and making informed decisions based on spatial information.
Navigating the Scale Chart: A Guide to Effective Map Interpretation
A map scale chart is a visual representation of the map’s scale, typically located in the map’s legend or margin. It provides a reference point for understanding the relationship between map distance and ground distance. Here’s how to effectively use a map scale chart:
-
Identify the Scale Type: Determine whether the chart uses a verbal scale, a representative fraction, or a graphic scale.
-
Locate the Corresponding Ground Distance: Identify the specific ground distance represented by the scale chart. This information is usually provided in the chart itself or in the map legend.
-
Measure the Map Distance: Use a ruler or other measuring tool to measure the distance between two points on the map.
-
Calculate the Actual Distance: Use the scale chart to convert the measured map distance into the corresponding ground distance. For example, if the scale is 1:25,000 and the measured map distance is 2 cm, the actual ground distance is 2 cm x 25,000 = 50,000 cm, or 500 meters.
-
Interpret the Level of Detail: Understand the relationship between the scale and the level of detail displayed on the map. A larger scale (smaller ratio) indicates a more detailed representation, while a smaller scale (larger ratio) provides a broader overview with less detail.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Map Scale
1. What is the difference between a large-scale map and a small-scale map?
A large-scale map depicts a small area with a high level of detail, while a small-scale map covers a larger area with less detail. The scale ratio reflects this difference: a large-scale map has a smaller ratio (e.g., 1:10,000), while a small-scale map has a larger ratio (e.g., 1:1,000,000).
2. How do I choose the appropriate map scale for my needs?
Consider the purpose of your map and the level of detail required. If you need to study a specific area in detail, choose a large-scale map. If you need a broader overview of a larger region, select a small-scale map.
3. Can I convert between different map scales?
Yes, you can convert between different scales using simple calculations. For example, to convert a scale of 1:25,000 to 1:50,000, you would double the map distance. However, converting between scales can affect the level of detail and may not always be accurate.
4. Why are some maps distorted?
Maps are representations of a three-dimensional Earth on a two-dimensional surface. This process inevitably leads to distortion, especially for large-scale maps covering vast areas. Different map projections are designed to minimize specific types of distortion, but some distortion is always present.
5. How can I improve my map reading skills?
Practice reading maps with different scales, focusing on interpreting the scale chart and understanding the level of detail. Familiarize yourself with common map symbols and legends. Use online resources and interactive maps to enhance your understanding of map concepts.
Tips for Effective Map Use: Enhancing Your Spatial Awareness
-
Read the Map Legend: Carefully review the map legend to understand the symbols, colors, and other conventions used on the map.
-
Pay Attention to Scale: Always check the map scale to understand the level of detail and the area represented.
-
Use a Ruler: Employ a ruler or other measuring tool to accurately determine distances on the map.
-
Consider the Purpose: Determine the specific information you need from the map and choose the appropriate scale and type of map for your task.
-
Explore Different Maps: Compare maps with different scales and projections to gain a comprehensive understanding of the area.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Scale for Effective Map Interpretation
Map scale is a fundamental concept that underpins the accuracy, detail, and utility of any map. By understanding the relationship between map distance and ground distance, we can effectively interpret and utilize map information for navigation, planning, analysis, and spatial reasoning. The map scale chart serves as a vital guide, enabling us to unlock the power of maps and navigate the world with greater understanding and precision.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
