Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions
Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions
- 3.1 The Essence of Map Scale
- 3.2 Types of Map Scale Representations
- 3.3 Navigating Map Scale Questions
- 3.4 FAQ: Demystifying Map Scale Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Mastering Map Scale Questions
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Power of Map Scale
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions

Maps are powerful tools that condense vast landscapes onto manageable surfaces. They provide a visual representation of the world, enabling us to navigate, analyze, and understand spatial relationships. However, the accuracy and usefulness of a map hinge on one crucial element: its scale. Map scale questions, therefore, are fundamental to interpreting and utilizing maps effectively.
The Essence of Map Scale
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It dictates the level of detail and the extent of the area represented. Understanding map scale is crucial for:
- Determining distances: Knowing the scale allows you to calculate the actual distance between two points on the ground based on the distance measured on the map.
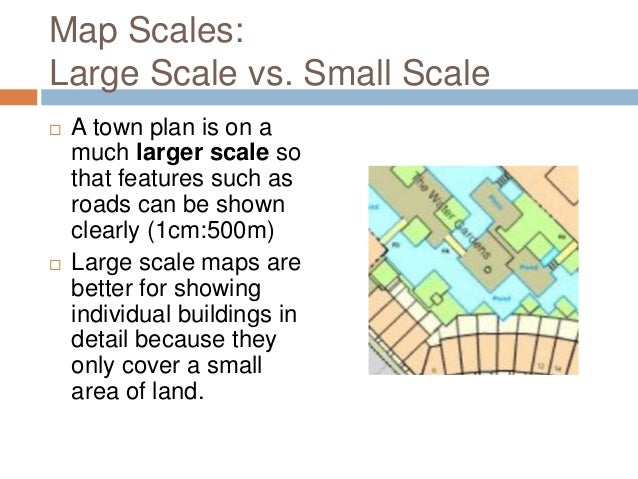
- Interpreting map features: The scale influences the size and clarity of features depicted on the map. A large-scale map (representing a smaller area) will show more detail than a small-scale map (representing a larger area).
- Comparing different maps: By understanding the scale of different maps, you can effectively compare them and choose the most appropriate map for your needs.
Types of Map Scale Representations
Map scale is typically expressed in three ways:
- Verbal Scale: This is the most straightforward representation, stating the relationship between map distance and ground distance in words. For example, "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This is a numerical ratio that expresses the scale as a fraction. For example, a scale of 1:100,000 means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
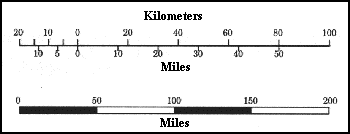
- Graphic Scale: This is a visual representation of the scale, usually in the form of a bar with marked distances. The bar represents a specific distance on the ground, allowing you to directly measure distances on the map.
Navigating Map Scale Questions
Map scale questions often involve calculating distances, converting between different scale representations, or determining the appropriate map for a specific task. To effectively address these questions, it is essential to understand the following concepts:
- Direct Proportionality: The relationship between map distance and ground distance is directly proportional. This means that if the map distance is doubled, the ground distance will also double.
- Conversion Factors: To convert between different units of measurement, use appropriate conversion factors. For example, 1 kilometer equals 1000 meters, and 1 meter equals 100 centimeters.
- Understanding Map Features: Pay attention to the features depicted on the map and their relative sizes. This can help you estimate distances and identify areas of interest.
FAQ: Demystifying Map Scale Questions
1. How do I calculate the actual distance between two points on a map?
To calculate the actual distance, measure the distance between the points on the map using a ruler. Then, use the map scale to determine the corresponding ground distance. For example, if the distance on a map with a scale of 1:50,000 is 5 centimeters, the actual distance is 5 centimeters * 50,000 = 250,000 centimeters, which equates to 2.5 kilometers.
2. How do I determine the appropriate map scale for a specific task?
The appropriate scale depends on the area you are interested in and the level of detail required. For large areas like continents, a small-scale map is suitable. For detailed city maps, a large-scale map is necessary.
3. How do I convert between different map scale representations?
To convert between verbal scale and RF, simply express the verbal scale as a fraction. To convert between RF and graphic scale, use the marked distances on the graphic scale to determine the corresponding ground distance.
4. What are the limitations of map scale?
Map scale is a simplification of reality. It can distort the shapes and sizes of features, especially at smaller scales. Additionally, map projections can introduce further distortions.
Tips for Mastering Map Scale Questions
- Practice: Regularly practice calculating distances and converting between different scale representations.
- Visualize: Try to visualize the relationship between the map and the ground to gain a better understanding of scale.
- Use online tools: There are numerous online tools and calculators available to help you with map scale calculations and conversions.
- Explore different maps: Analyze maps with different scales to observe the differences in detail and representation.
Conclusion: The Power of Map Scale
Map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, influencing the accuracy, detail, and usefulness of maps. By understanding map scale questions and mastering the associated concepts, you can effectively interpret maps, navigate landscapes, and extract valuable information from spatial data. As you delve deeper into the world of maps, remember that understanding scale is not just a technical skill but a key to unlocking the power of visual representation and spatial analysis.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Language of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Scale Questions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
