Understanding the Language of Maps: Decoding the Scale
Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: Decoding the Scale
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Language of Maps: Decoding the Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Language of Maps: Decoding the Scale

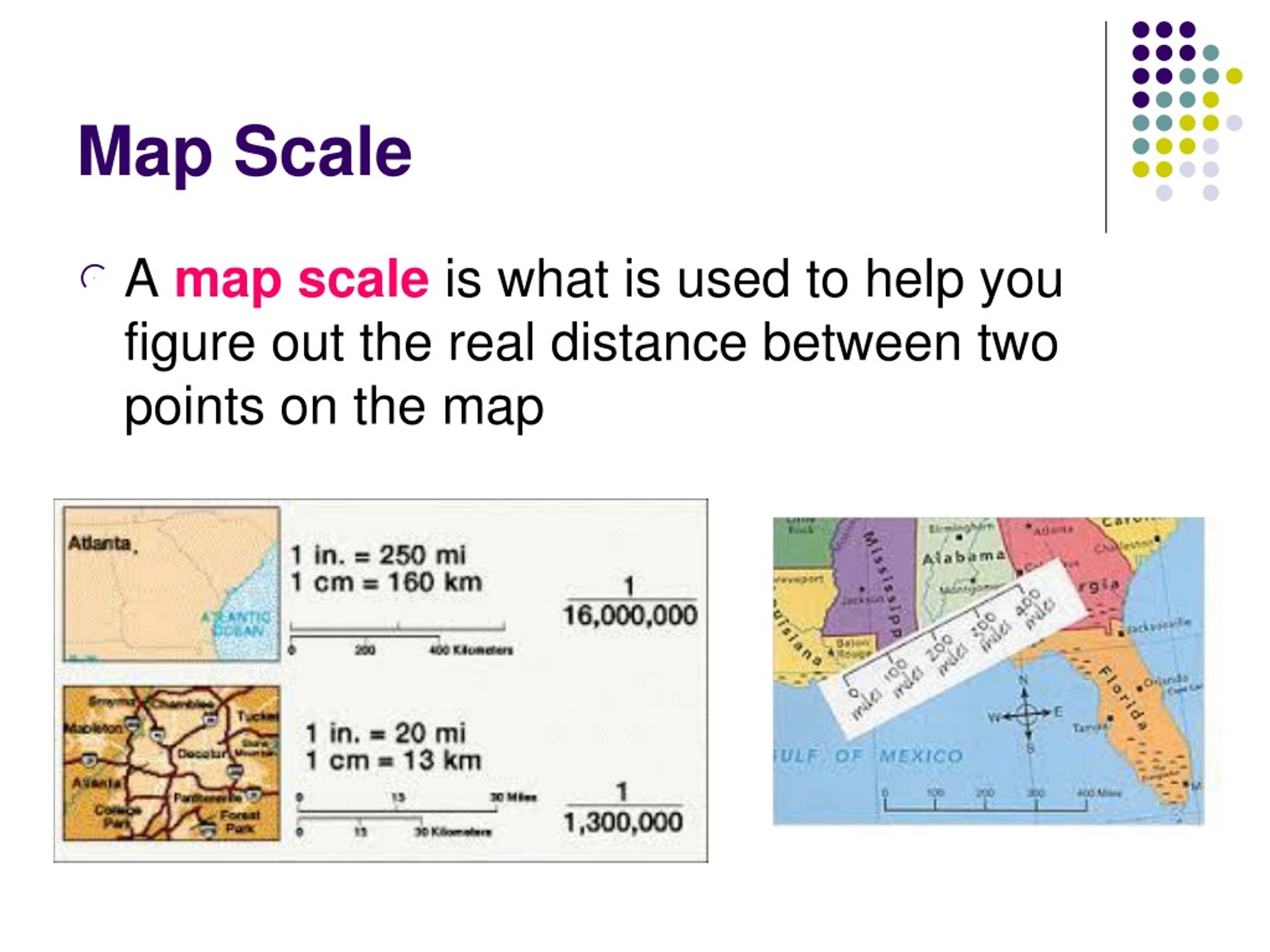
Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our world, are more than just colorful pictures. They are powerful tools that allow us to navigate, analyze, and understand spatial relationships. At the heart of every map lies a crucial element: the scale. A map’s scale dictates the relationship between distances on the map and their corresponding distances in the real world. It is the key to interpreting the map’s information accurately.
A common way to express a map’s scale is through a ratio, often presented as a verbal statement, such as "2 inches equals 25 miles." This particular scale signifies that every two inches measured on the map represents a distance of 25 miles on the ground. This ratio serves as a vital translation tool, enabling us to convert distances measured on the map into real-world distances and vice versa.
The Significance of Scale in Map Interpretation
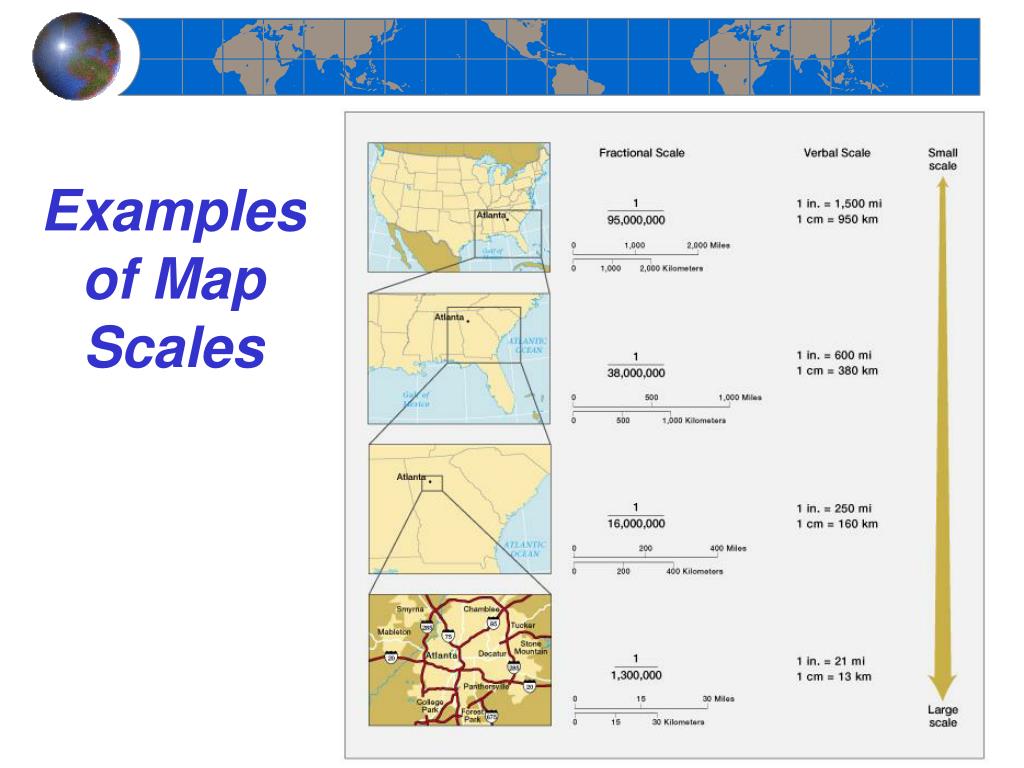
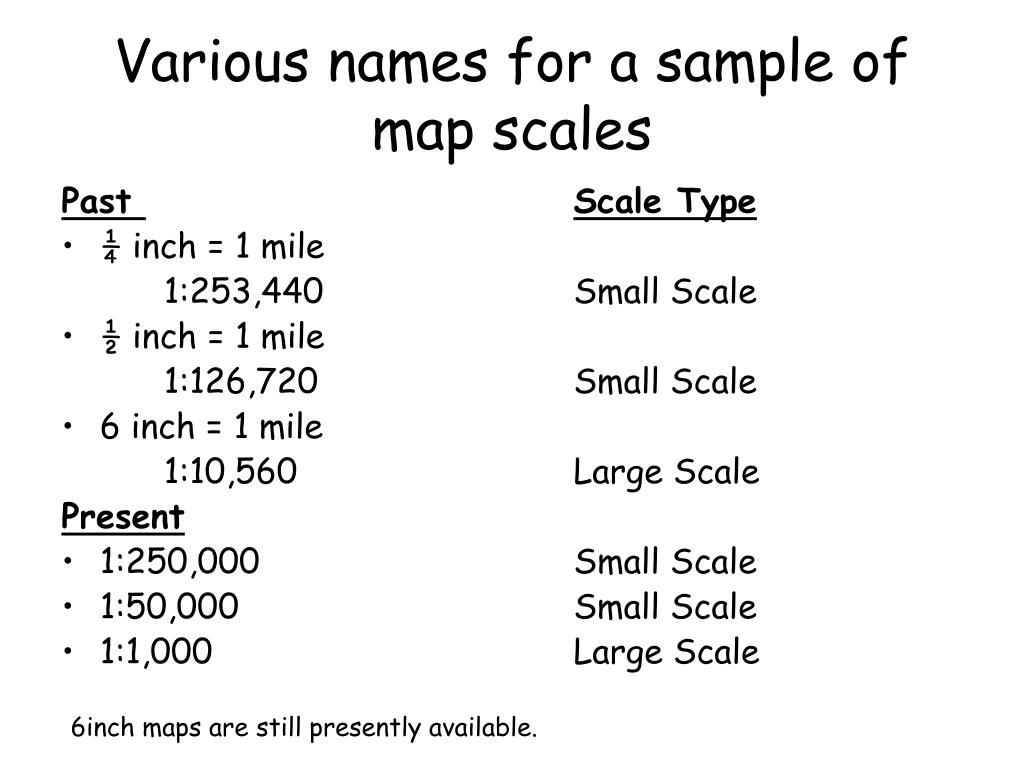
The scale of a map plays a pivotal role in its effectiveness. A large-scale map, where a small distance on the map corresponds to a small distance on the ground, provides detailed information about a specific area. This makes them ideal for urban planning, surveying, and other activities requiring precise measurements.
Conversely, a small-scale map, where a large distance on the map represents a large distance on the ground, offers a broad overview of a larger region. These maps are useful for illustrating geographical features, analyzing regional trends, or planning long-distance travel.
Dissecting the Ratio: Understanding the Relationship
The ratio "2 inches equals 25 miles" can be broken down into two distinct parts:
- The Map Distance: This is the distance measured on the map itself, represented in inches in this example.
- The Real-World Distance: This is the corresponding distance on the ground, represented in miles in this example.
The scale ratio establishes a direct relationship between these two distances. It acts as a conversion factor, allowing us to translate between the map representation and the real world.
Practical Applications: Using the Scale to Measure Distances
To utilize the scale effectively, one must understand its application in measuring distances on a map. If a map has a scale of "2 inches equals 25 miles," then:
- To find the real-world distance: Measure the distance between two points on the map in inches. Then, divide the measured distance by 2 (the map distance in the ratio) and multiply the result by 25 (the real-world distance in the ratio). This will give you the actual distance between those points in miles.
- To find the map distance: Divide the real-world distance (in miles) by 25 (the real-world distance in the ratio) and multiply the result by 2 (the map distance in the ratio). This will give you the corresponding distance on the map in inches.
Beyond the Ratio: Exploring Other Scale Representations
While the ratio form is prevalent, map scales can be expressed in other ways:
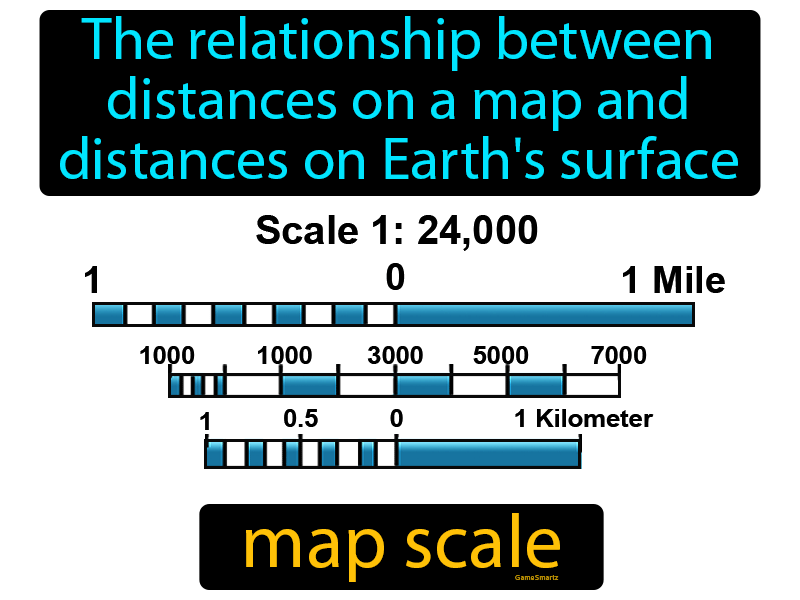
- Representative Fraction (RF): This form expresses the scale as a fraction, where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the real-world distance. For example, the scale "2 inches equals 25 miles" can be expressed as 1:1,584,000. This fraction indicates that one unit on the map represents 1,584,000 units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: This method uses a line segment divided into smaller units, representing specific distances on the ground. The user can measure a distance on the map and compare it to the graphic scale to determine the actual distance.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Why are different map scales used?
A: Different map scales are used to suit specific purposes. Large-scale maps are ideal for detailed information, while small-scale maps are suitable for broader overviews.
Q: How do I choose the right map scale?
A: The choice of map scale depends on the intended use of the map. If you need precise measurements for a small area, a large-scale map is preferred. If you need a general overview of a large region, a small-scale map would be more appropriate.
Q: Can I change the scale of a map?
A: While you can digitally enlarge or reduce a map, this does not change its inherent scale. Changing the size of the map will alter the appearance of the features but will not change the ratio between the map and the real world.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- Always check the map’s scale: Ensure you understand the scale before attempting to measure distances or interpret the information.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool: This will ensure accurate measurements, especially when working with large-scale maps.
- Be mindful of the units: Ensure the map’s scale and your measurements are in the same units.
- Understand the limitations of scale: Remember that even a large-scale map can only represent a limited amount of detail.
Conclusion: The Importance of Scale in Mapping
The scale of a map is a fundamental element that dictates its accuracy, usefulness, and interpretation. By understanding the scale, we can effectively navigate, analyze, and understand the spatial relationships depicted on maps. Whether it’s planning a hiking route, studying urban development, or analyzing regional trends, the scale remains a crucial tool in our understanding of the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Language of Maps: Decoding the Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
