Understanding the Language of Maps: Delving into Real-World Map Scale
Related Articles: Understanding the Language of Maps: Delving into Real-World Map Scale
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Language of Maps: Delving into Real-World Map Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Language of Maps: Delving into Real-World Map Scale

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our planet, are more than just colorful pictures. They are powerful tools that allow us to navigate, plan journeys, and understand the spatial relationships between places. At the heart of their functionality lies the concept of scale, which essentially translates the vastness of the real world onto a manageable piece of paper or digital screen.
The Essence of Map Scale
Map scale refers to the ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is expressed in various ways, each offering a different perspective on the relationship between the map and reality.
-
Verbal Scale: This straightforward method expresses the scale as a simple statement, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground." This approach is easy to understand but lacks the visual clarity of other methods.
-
Representative Fraction (RF): This method expresses the scale as a fraction, where the numerator represents the map distance and the denominator represents the corresponding ground distance. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map corresponds to 100,000 units on the ground. This method is precise and allows for easy conversion between units.
-
Graphic Scale: This visual representation of scale uses a line divided into segments that correspond to specific distances on the ground. This method is particularly useful for measuring distances directly on the map.
The Importance of Scale in Map Interpretation
Understanding the scale of a map is paramount for accurate interpretation and effective use. Here’s why:
-
Distance Measurement: Scale allows us to calculate distances between points on the map and translate them into real-world measurements. This is crucial for planning trips, calculating travel time, and understanding the relative distances between locations.
-
Area Calculation: Scale enables us to calculate the area of features represented on the map, such as forests, lakes, or urban areas. This information is essential for various applications, including resource management, land use planning, and environmental studies.
-
Feature Representation: The scale of a map determines the level of detail that can be depicted. Large-scale maps, with a smaller ratio, represent smaller areas with greater detail, allowing for the depiction of individual buildings, streets, and even specific landmarks. Conversely, small-scale maps, with a larger ratio, cover broader areas but sacrifice detail, focusing on major features like rivers, mountain ranges, and national boundaries.
Scale and Map Types
The scale of a map is closely tied to its intended purpose and the type of information it conveys.
-
Topographic Maps: These maps focus on depicting the elevation and relief of the terrain. They typically use a large scale, allowing for the representation of contour lines, which indicate changes in elevation. This detailed information is vital for navigation, planning hiking trails, and understanding the landscape.
-
Road Maps: These maps prioritize the depiction of road networks and transportation infrastructure. They often use a smaller scale, focusing on major highways, cities, and regional boundaries. This allows for a broader overview of the road system, making them ideal for planning long journeys.
-
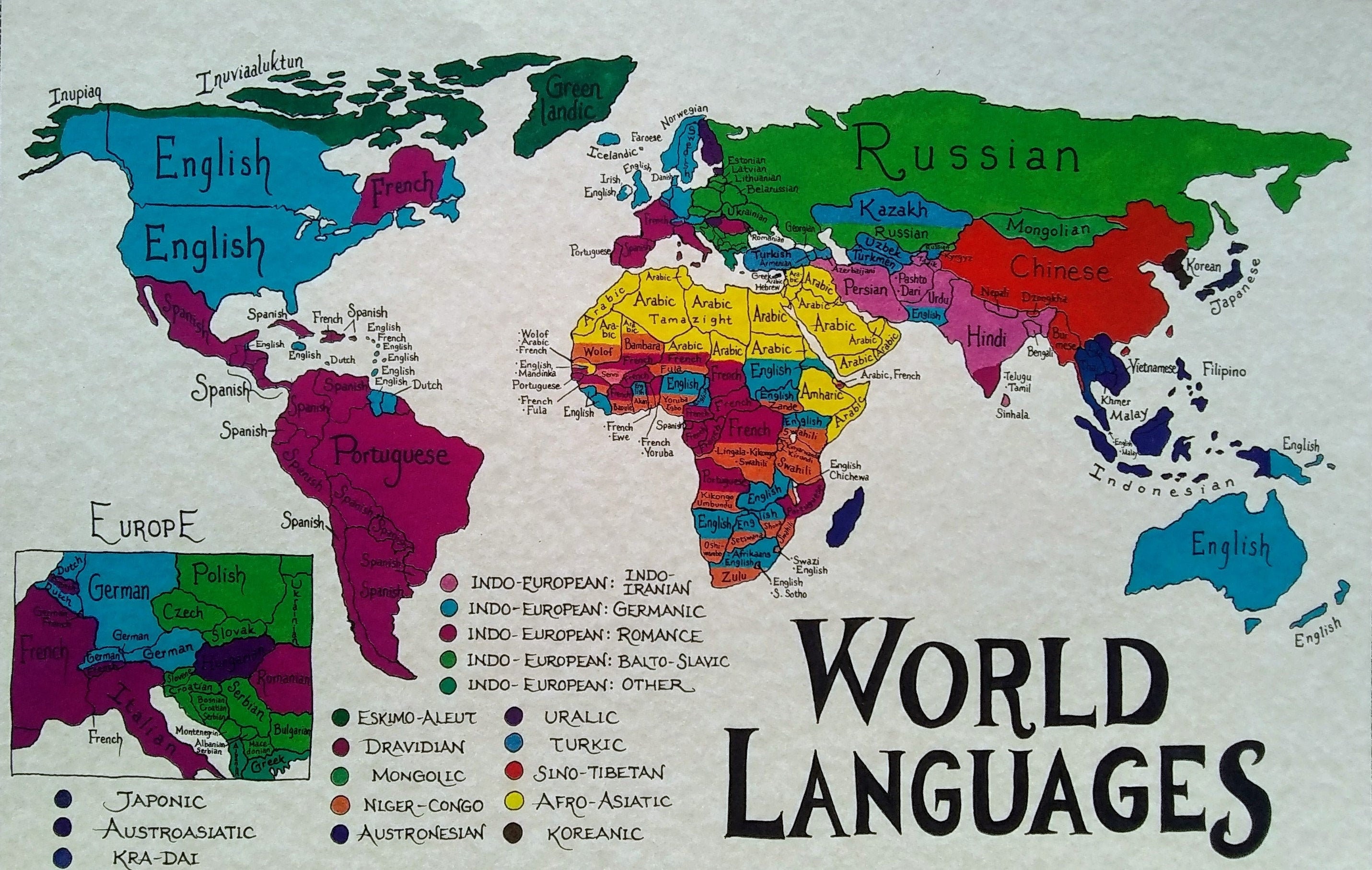
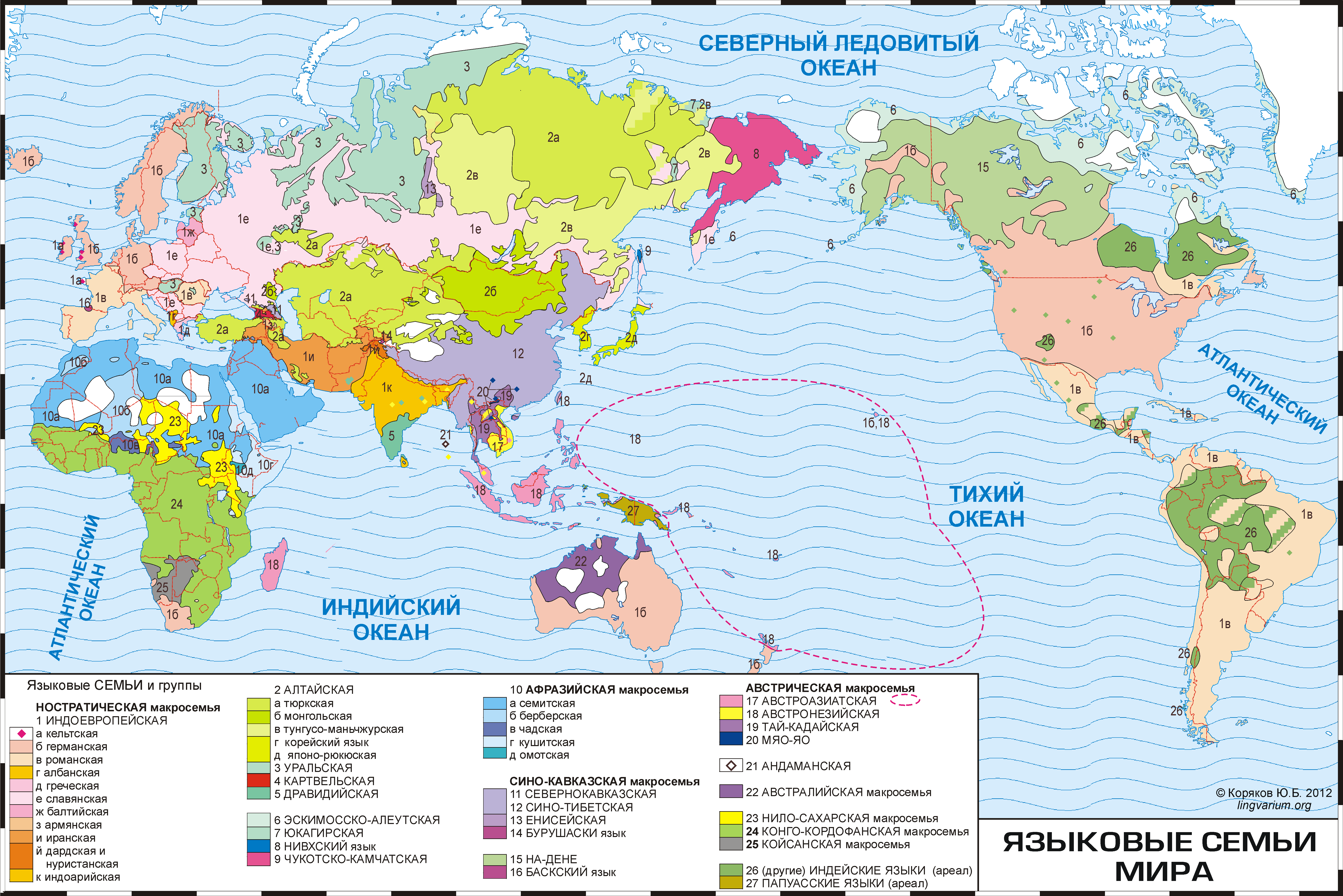
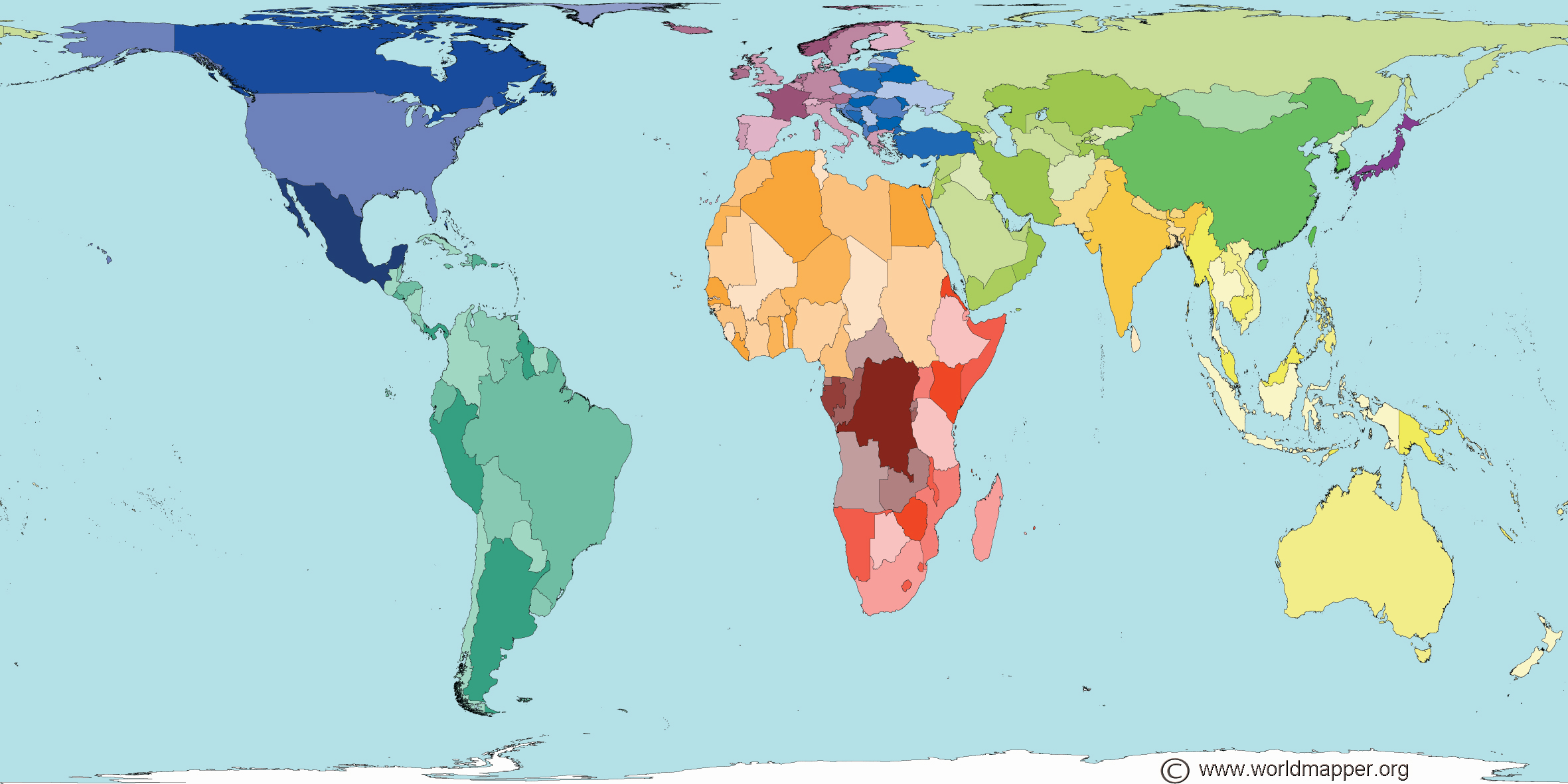
Thematic Maps: These maps highlight a specific theme, such as population density, rainfall patterns, or economic activity. The scale of a thematic map depends on the level of detail required to convey the chosen theme.
Real-World Applications of Map Scale
The concept of map scale extends beyond the realm of traditional paper maps. It plays a crucial role in various modern technologies and applications:
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software uses digital maps with varying scales to analyze spatial data, allowing for the creation of complex models and visualizations. Scale is critical for defining the level of detail required for specific analyses and for accurately representing the relationships between different datasets.
-
Navigation Apps: Smartphone navigation apps utilize map data with varying scales to guide users through unfamiliar environments. The scale dynamically adjusts based on the user’s location and speed, providing the appropriate level of detail for efficient navigation.
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography are essential tools for monitoring the environment and managing resources. The scale of these images determines the resolution and level of detail captured, influencing their suitability for different applications, such as land cover mapping, disaster assessment, and agricultural monitoring.
FAQs on Real-World Map Scale
Q: How do I determine the scale of a map?
A: The scale is usually indicated on the map itself, either verbally, as a representative fraction, or through a graphic scale. If the map lacks a scale, you can determine it by measuring a known distance on the map and comparing it to the corresponding distance on the ground.
Q: Can I use a map with a different scale for a different purpose?
A: While it’s possible to use a map with a different scale than intended, it’s important to be aware of the limitations. A map with a scale too small for your needs might not provide sufficient detail, while a map with a scale too large might be cumbersome and overwhelming.
Q: How does scale affect the accuracy of a map?
A: The accuracy of a map is influenced by various factors, including the scale, the quality of data used to create the map, and the projection system employed. Generally, larger-scale maps tend to be more accurate in representing small-scale features, while smaller-scale maps provide a more generalized representation of larger areas.
Tips for Using Real-World Map Scale
- Always check the scale: Before using a map, ensure you understand the scale and its implications for your intended use.
- Consider your needs: Choose a map with a scale appropriate for your specific needs, whether it’s for planning a hiking trip, navigating a city, or analyzing environmental data.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool: For accurate distance measurements, use a ruler or other measuring tool in conjunction with the map’s scale.
- Understand the limitations: Be aware that maps are simplifications of reality and that the level of detail is limited by the scale.
Conclusion
Map scale is a fundamental concept that underpins our ability to understand and interact with the world around us. From navigating through unfamiliar cities to analyzing complex environmental data, the scale of a map determines its suitability for different tasks and the level of detail it can convey. By understanding the language of map scale, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power of maps as tools for exploration, analysis, and decision-making.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Language of Maps: Delving into Real-World Map Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
