Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Guide for Automotive Enthusiasts
Related Articles: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Guide for Automotive Enthusiasts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Guide for Automotive Enthusiasts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Guide for Automotive Enthusiasts

The intricate dance of internal combustion engines relies on a delicate balance of air and fuel. Ensuring this balance is a critical component called the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This sensor plays a crucial role in modern vehicles, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with vital information about the pressure inside the engine’s intake manifold. This data is then used to calculate the precise amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion, impacting performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The Role of the MAP Sensor in Engine Management
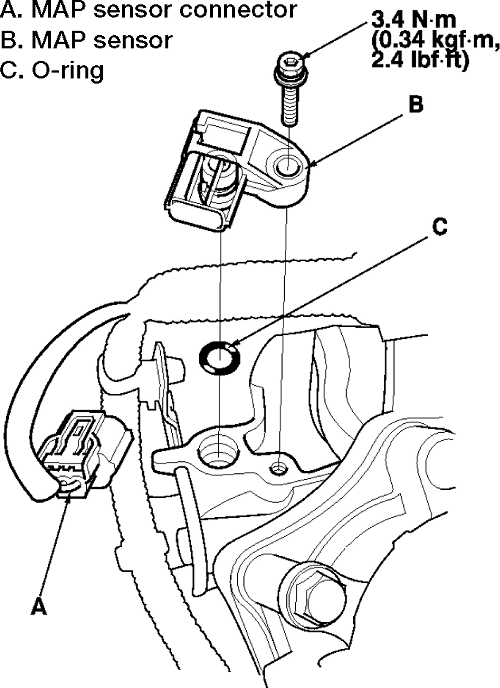
The MAP sensor, a small, cylindrical device typically located in the intake manifold, measures the pressure of air entering the engine. This pressure is directly related to the amount of air being drawn into the cylinders. The sensor converts this pressure reading into an electrical signal that the ECU interprets.
How the MAP Sensor Works
The MAP sensor employs a diaphragm, a thin, flexible membrane that reacts to changes in pressure. As the pressure in the intake manifold increases, the diaphragm flexes, altering the resistance of a variable resistor. This change in resistance is then translated into an electrical signal that the ECU receives.
The Importance of a Functioning MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can have significant consequences for engine performance and fuel efficiency. If the sensor provides inaccurate readings, the ECU will miscalculate the amount of fuel needed, leading to:
- Poor Fuel Economy: An incorrect fuel-air mixture can result in excessive fuel consumption, wasting money and increasing emissions.
- Engine Misfire: A lean fuel mixture (too much air, not enough fuel) can cause the engine to misfire, resulting in rough idle, hesitation, and potential damage to the engine.
- Reduced Power: A rich fuel mixture (too much fuel, not enough air) can lead to decreased engine power and sluggish acceleration.
- Check Engine Light: The ECU will detect the faulty sensor and illuminate the check engine light, prompting a diagnostic scan to identify the problem.
Common Symptoms of a Failing MAP Sensor
- Check Engine Light Illumination: The most common sign of a failing MAP sensor is the check engine light illuminating, accompanied by a diagnostic code indicating a problem with the MAP sensor circuit.
- Rough Idle: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can cause the engine to idle erratically, with the RPM fluctuating.
- Hesitation or Stalling: The engine may hesitate during acceleration or stall when idling, especially during cold starts.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Increased fuel consumption is a common symptom of a faulty MAP sensor, as the engine is not receiving the correct fuel-air mixture.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust: Excessive fuel being injected into the cylinders due to a faulty MAP sensor can cause black smoke to be emitted from the exhaust.
Diagnosing a MAP Sensor Issue
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for any physical damage, loose connections, or signs of corrosion.
- Diagnostic Code Reading: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored diagnostic codes related to the MAP sensor circuit.
- Pressure Testing: Use a pressure gauge to check the actual pressure in the intake manifold and compare it to the readings provided by the MAP sensor.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output from the MAP sensor and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Replacing a MAP Sensor
Replacing a MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward process:
- Locate the Sensor: Identify the MAP sensor, typically located in the intake manifold.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector leading to the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Use a wrench to loosen and remove the mounting bolts holding the sensor in place.
- Install the New Sensor: Carefully install the new MAP sensor, ensuring a tight fit and secure connection.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored diagnostic codes related to the MAP sensor.
FAQs about MAP Sensors
Q: Can I clean a MAP sensor?
A: While it is not recommended to clean a MAP sensor, it is possible to clean the sensor’s electrical connector and the surrounding area to ensure proper electrical contact.
Q: What is the average lifespan of a MAP sensor?
A: MAP sensors typically last for a considerable period, often exceeding 100,000 miles. However, factors like environmental conditions, engine wear, and quality of the sensor can influence its lifespan.
Q: Can I drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: It is not advisable to drive with a faulty MAP sensor. While the vehicle may still run, the engine will operate inefficiently, potentially causing damage and compromising fuel efficiency.
Q: What are the signs of a bad MAP sensor?
A: The most common signs of a bad MAP sensor include a check engine light, rough idle, hesitation or stalling, poor fuel economy, and black smoke from the exhaust.
Tips for Maintaining a MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Performing routine engine maintenance, such as oil changes and air filter replacements, helps maintain the overall health of the engine, including the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Environments: Exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, and dirt can damage the MAP sensor.
- Quality Components: Using high-quality aftermarket MAP sensors from reputable manufacturers can ensure longevity and reliable performance.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in modern vehicles, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Understanding its function and the potential consequences of a malfunctioning sensor is crucial for maintaining the health and longevity of your vehicle. By recognizing the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor and addressing the issue promptly, you can prevent potential damage and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Guide for Automotive Enthusiasts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
