Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Chevrolet Silverado: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Chevrolet Silverado: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Chevrolet Silverado: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Chevrolet Silverado: A Comprehensive Guide
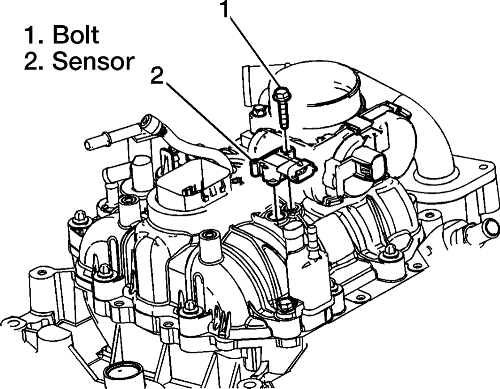
The Chevrolet Silverado, a mainstay of the American pickup truck landscape, relies on a complex array of sensors and systems to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Among these, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a critical role in regulating engine operation and delivering a smooth driving experience.
The Role of the MAP Sensor:
The MAP sensor is a crucial component in the engine control system, responsible for measuring the pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure, is directly related to the density of the air entering the engine. The sensor translates this pressure into an electrical signal that is sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
How the MAP Sensor Works:
The MAP sensor typically employs a diaphragm-based design. A sealed chamber within the sensor is exposed to the intake manifold pressure. As pressure changes, the diaphragm flexes, altering the resistance within an internal electrical circuit. This change in resistance is interpreted by the ECU as a voltage signal, directly proportional to the manifold absolute pressure.
The Importance of the MAP Sensor:
The MAP sensor’s role extends beyond simply measuring pressure. Its readings are vital for the ECU to make critical decisions about engine operation, including:
- Fuel Injection Timing: The ECU utilizes the MAP sensor readings to determine the optimal fuel injection timing. Higher manifold pressure indicates denser air, necessitating a richer fuel mixture for efficient combustion.
- Ignition Timing: Similar to fuel injection, the MAP sensor data helps the ECU adjust ignition timing. Higher pressure suggests a denser air-fuel mixture, requiring a slightly delayed ignition to avoid premature detonation (knocking).
- Air-Fuel Ratio Control: The MAP sensor provides crucial information for the ECU to maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio. This ensures efficient combustion, minimizing fuel consumption and harmful emissions.
- Throttle Position Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor readings in conjunction with throttle position sensor data to regulate throttle response and maintain smooth acceleration.
Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor:
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to various issues, negatively impacting engine performance and fuel efficiency. Common symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include:
- Engine Stalling or Hesitation: An inaccurate pressure reading can disrupt the engine’s fuel and ignition timing, causing stalling or hesitation during acceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Incorrect fuel-air mixture due to a faulty MAP sensor can result in increased fuel consumption.
- Rough Idle: A malfunctioning sensor can lead to inconsistent engine idling, resulting in a rough or uneven idle.
- Check Engine Light: The ECU will typically illuminate the check engine light when it detects a fault in the MAP sensor circuit.
- Reduced Power: A faulty MAP sensor can limit engine power output due to incorrect fuel and ignition timing.
Troubleshooting a Faulty MAP Sensor:
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a systematic approach:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the MAP sensor for any physical damage, loose connections, or signs of corrosion.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect the intake manifold and associated hoses for leaks, as these can affect the sensor’s readings.
- Use a Diagnostic Scanner: A scan tool can retrieve error codes related to the MAP sensor, providing valuable insights into the issue.
- Voltage Check: Using a multimeter, measure the voltage output from the MAP sensor under various engine conditions. Compare these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any discrepancies.
- Pressure Test: A pressure gauge can be used to verify the accuracy of the MAP sensor’s pressure readings.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor:
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is generally straightforward and can be performed by a skilled DIYer or a qualified mechanic. The process typically involves:
- Locate the MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor is usually located on the intake manifold, near the throttle body. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for precise location.
- Disconnect Electrical Connections: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the MAP sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Depending on the vehicle model, the MAP sensor may be secured by a bolt or a clip. Remove the sensor carefully.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor in the same location, ensuring the gasket is properly seated.
- Reconnect Electrical Connections: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new MAP sensor.
- Clear Error Codes: After installation, use a scan tool to clear any stored error codes related to the MAP sensor.
FAQs about the MAP Sensor in Chevrolet Silverado:
Q: What are the common causes of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Common causes include physical damage, corrosion, leaks in the intake manifold, and internal sensor failure.
Q: Can I drive my Silverado with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While driving with a faulty MAP sensor is possible, it is not recommended. The engine may experience performance issues, increased fuel consumption, and potentially damage other components.
Q: How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
A: The MAP sensor generally has a lifespan of several years. However, regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent premature failure.
Q: Can I clean the MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning the MAP sensor is not recommended, as it can damage the delicate internal components. It is best to replace a faulty sensor.
Q: How much does a new MAP sensor cost?
A: The cost of a new MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle model and brand. It is typically affordable, ranging from a few dollars to a few hundred dollars.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor:
- Regularly inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage or corrosion.
- Ensure the intake manifold and associated hoses are free of leaks.
- Perform routine engine maintenance, including air filter replacement, to prevent excessive dirt buildup.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or cleaners near the MAP sensor.
Conclusion:
The MAP sensor plays a critical role in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency in Chevrolet Silverado vehicles. By understanding its function, recognizing symptoms of a faulty sensor, and performing timely maintenance, Silverado owners can ensure smooth and reliable operation of their trucks. A properly functioning MAP sensor contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience, enhanced fuel economy, and reduced emissions.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Chevrolet Silverado: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
