Understanding the Power of Map Scale Bars: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Distance on Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Map Scale Bars: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Distance on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Map Scale Bars: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Distance on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Map Scale Bars: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Distance on Maps
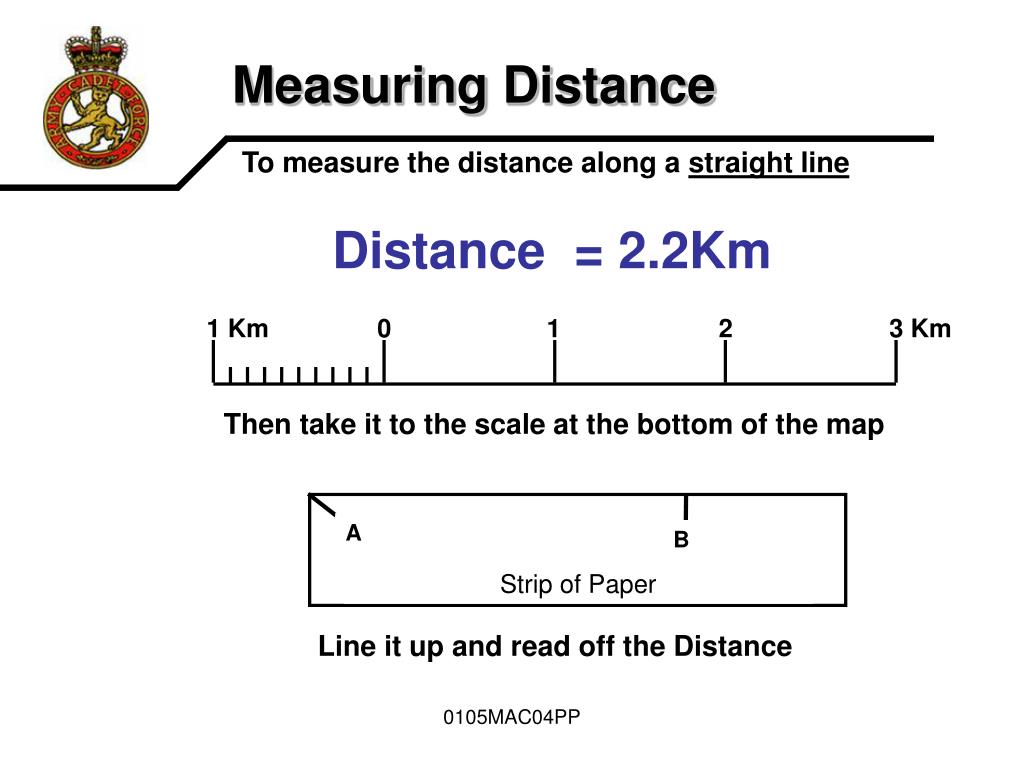
Maps, in their essence, are visual representations of the world, shrinking vast landscapes into manageable formats. However, this reduction necessitates a clear understanding of the relationship between the map’s dimensions and the actual distances they represent. This relationship is precisely what a map scale bar, often referred to as a scale bar, elucidates.
The Essence of Map Scale Bars
A scale bar on a map acts as a visual key, offering a direct translation of distances depicted on the map to their corresponding real-world equivalents. It is essentially a graphical representation of the map’s scale, which defines the ratio between map distance and actual ground distance. This bar typically features marked segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground.
For instance, a scale bar might display segments labeled "1 mile," "2 miles," and "5 miles," indicating that each segment on the map corresponds to the respective distance on the ground. This allows users to directly measure distances on the map by comparing them to the scale bar.
Types of Map Scale Bars
Scale bars come in various forms, each suited to specific applications and map types:
-
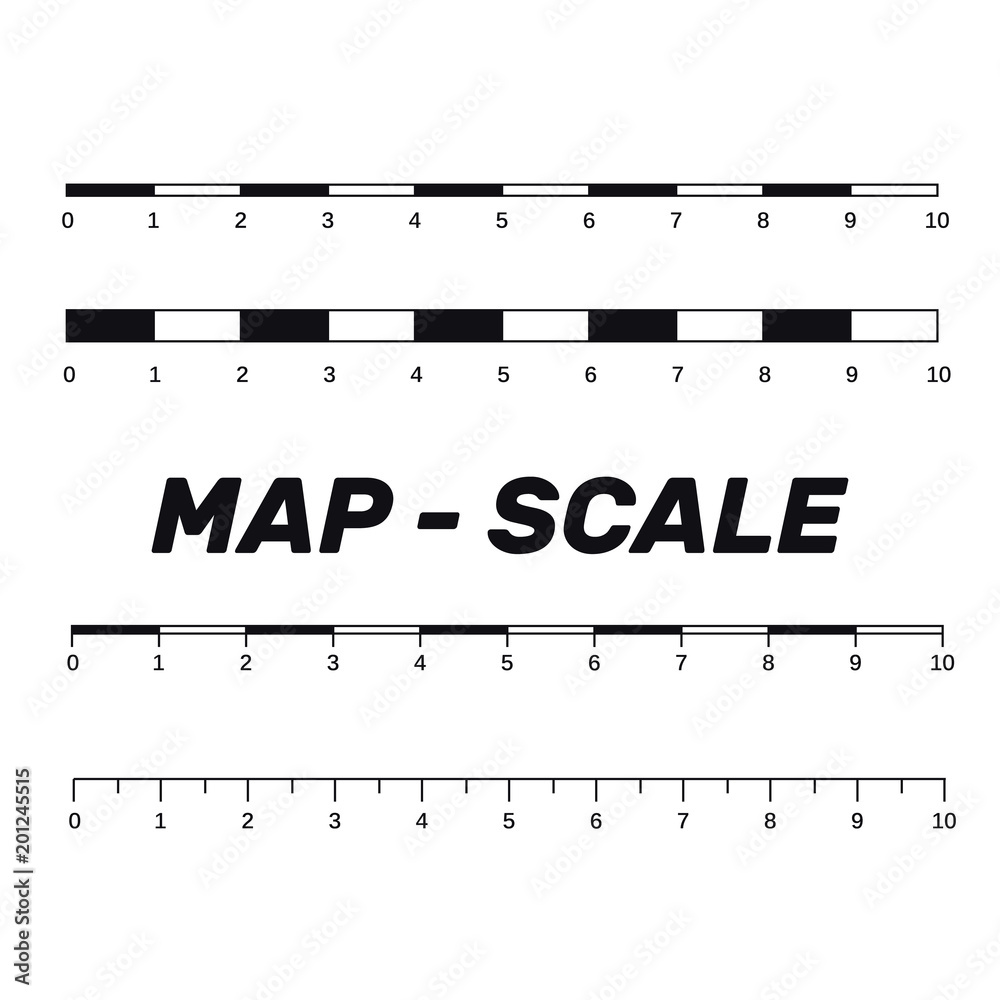
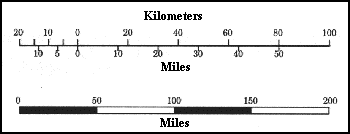
Linear Scale Bars: These are the most common type, consisting of a straight line divided into segments, each representing a specific distance. They offer a simple and straightforward way to measure distances on the map.
-
Verbal Scale Bars: These bars express the scale as a written statement, such as "1 inch equals 1 mile" or "1 centimeter equals 1 kilometer." While less visually intuitive, they provide a clear and concise numerical representation of the scale.
-
Representative Fraction (RF) Scale: This scale is expressed as a ratio, such as 1:100,000. This indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground. This format is commonly used in topographic maps and other technical maps.
The Importance of Map Scale Bars
The significance of map scale bars lies in their ability to bridge the gap between the map’s representation and the actual landscape. They provide a crucial tool for:
-
Accurate Distance Measurement: Scale bars enable users to accurately measure distances on the map, be it for planning a hiking route, determining the distance between two cities, or assessing the area of a particular region.
-
Spatial Understanding: By visually relating map distances to real-world distances, scale bars foster a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships depicted on the map. This is crucial for tasks like navigating unfamiliar terrain, analyzing spatial patterns, or understanding the relative size and distance of geographic features.
-
Map Interpretation: Scale bars are fundamental to map interpretation, ensuring users can accurately interpret the map’s information and draw meaningful conclusions. Without a scale bar, a map’s representation becomes ambiguous, hindering its usefulness.
Using Map Scale Bars Effectively
To effectively utilize a map scale bar, it’s important to follow these guidelines:
-
Identify the Scale Bar: Locate the scale bar on the map. It is usually found in a prominent location, often within the map’s legend or margin.
-
Understand the Units: Pay attention to the units used on the scale bar, whether it be miles, kilometers, or other units.
-
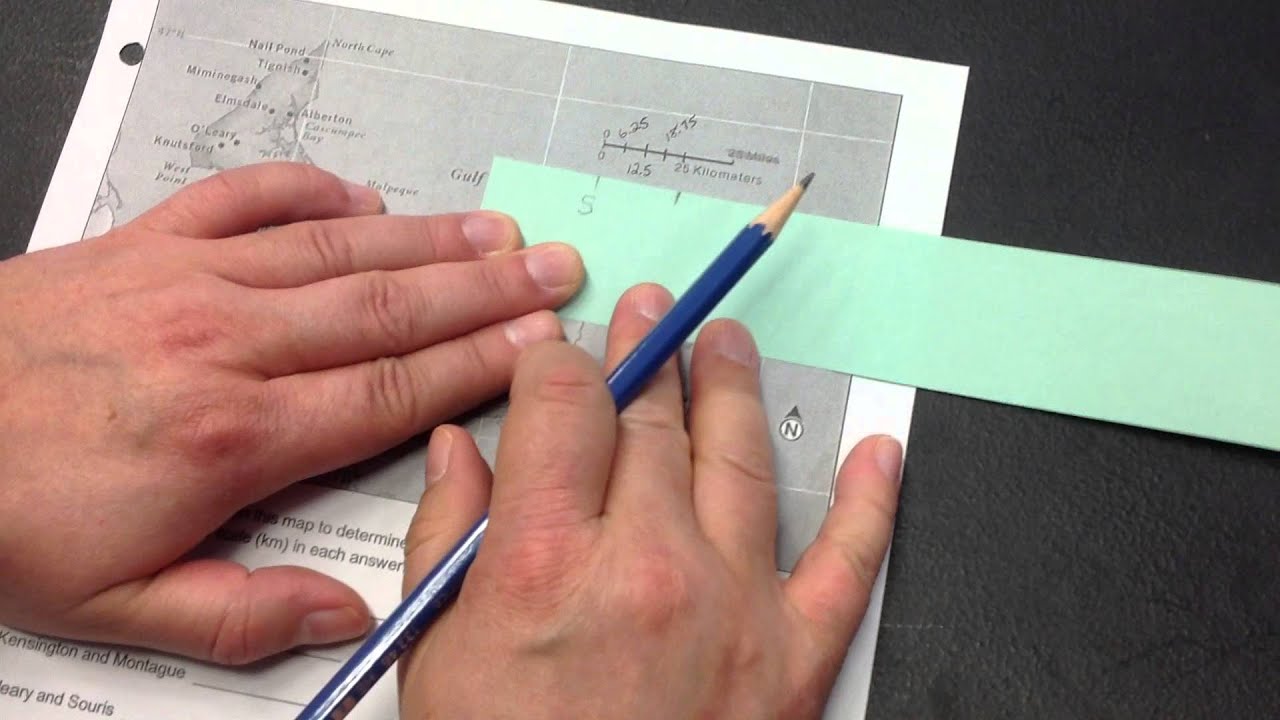
Measure Distances: Use a ruler or another measuring tool to measure distances on the map. Align the tool with the scale bar to determine the corresponding ground distance.
-
Consider Map Distortion: Be mindful that map projections can introduce distortions, particularly in maps depicting large areas. These distortions can affect distance measurements, especially at the map’s edges.
FAQs Regarding Map Scale Bars
1. What is the difference between a scale bar and a map scale?
A scale bar is a visual representation of the map’s scale, while the map scale itself is the ratio between map distance and ground distance. The scale bar provides a direct visual interpretation of the scale, while the map scale is a numerical representation.
2. How do I know which map scale bar to use?
Most maps have only one scale bar. If a map has multiple scale bars, choose the one that best suits the distances you are measuring.
3. Can I use a different measuring tool instead of a ruler?
Yes, you can use any measuring tool that allows you to accurately measure distances on the map. However, it is crucial to ensure the tool’s units align with the units used on the scale bar.
4. How do I interpret a representative fraction (RF) scale?
The RF scale is a ratio expressed as 1:X, where X represents the number of units on the ground corresponding to one unit on the map. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
5. What are the limitations of map scale bars?
Map scale bars are primarily designed for measuring straight-line distances. They may not accurately reflect distances along curved paths or across areas where map distortions are significant.
Tips for Using Map Scale Bars Effectively
-
Always check the scale bar: Before using a map, always locate and examine the scale bar to understand the map’s scale and the units used.
-
Use a clear ruler: Ensure the ruler you use is clear and marked with accurate units to avoid measurement errors.
-
Consider map distortion: Be aware of potential distortions in the map’s projection, particularly when measuring distances over large areas or along curved paths.
-
Practice makes perfect: Familiarity with map scale bars comes with practice. Regularly use scale bars to measure distances on various maps to develop a comfortable understanding of their application.
Conclusion
Map scale bars are essential tools for understanding and interpreting maps. They bridge the gap between the map’s representation and the real world, allowing users to accurately measure distances, analyze spatial relationships, and gain a deeper understanding of the information presented. By mastering the use of scale bars, individuals can enhance their map reading skills and utilize maps more effectively for various purposes, from navigation and planning to research and analysis.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Map Scale Bars: A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring Distance on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
