Understanding the Power of Spatial Analysis: A Deep Dive into the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Spatial Analysis: A Deep Dive into the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Spatial Analysis: A Deep Dive into the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Spatial Analysis: A Deep Dive into the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map

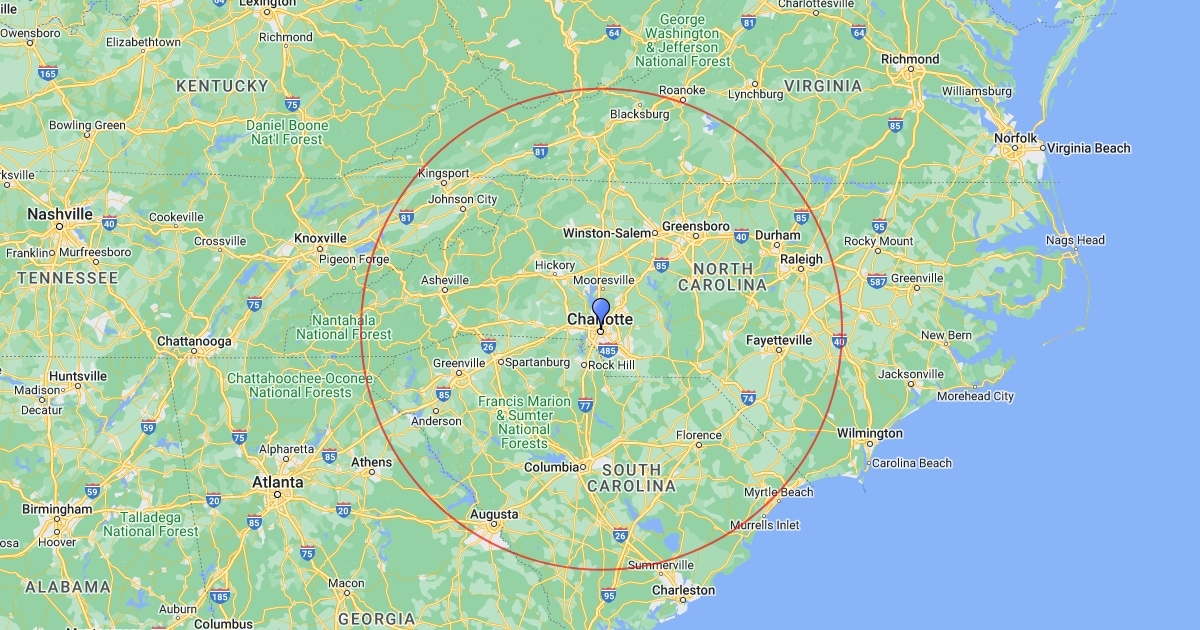
The world around us is a tapestry of interconnected data points, each holding a piece of the story. To truly understand this narrative, we need tools that allow us to visualize and analyze these data points in their spatial context. One such tool, with profound implications for various fields, is the 150 air mile radius dot map.
This seemingly simple visual representation, consisting of dots placed on a map within a 150-mile radius of a designated point, possesses a remarkable ability to unveil hidden patterns, reveal geographic trends, and drive informed decision-making. It is a powerful instrument for spatial analysis, offering insights that would otherwise remain obscured.
Understanding the Concept:
Imagine a central point on a map, representing a city, a business location, or a geographical landmark. The 150 air mile radius dot map creates a circular area around this point, encompassing all locations within a 150-mile aerial distance. This circular region, known as the "buffer zone," becomes the stage for data visualization and analysis.
The Power of Visualization:
The 150 air mile radius dot map’s strength lies in its ability to visually represent spatial relationships. By plotting dots representing various data points within the 150-mile radius, the map transforms abstract information into a tangible, geographically-aware picture. This visual representation allows for quick identification of:
- Spatial clusters: Areas with a high concentration of dots indicate clusters of related data points, revealing potential trends or hotspots.
- Spatial distribution: The map clearly shows the spread and distribution of data points, offering insights into geographical patterns and potential areas of interest.
- Proximity analysis: The map helps identify points that are geographically close to the central point, allowing for analysis of potential relationships and interactions.
Applications and Benefits:
The 150 air mile radius dot map finds its application in numerous fields, empowering professionals to make informed decisions based on spatial insights. Here are some key examples:
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market analysis: Identifying potential customers within a specific geographic radius.
- Competitive analysis: Understanding the distribution of competitors and their market reach.
- Location optimization: Selecting the most strategic location for a new store or office based on customer density and competition.
- Supply chain management: Optimizing logistics routes and distribution networks based on proximity to suppliers and customers.
2. Public Health and Emergency Response:
- Disease outbreak analysis: Identifying geographical clusters of disease cases and potential sources of infection.
- Emergency preparedness: Mapping critical infrastructure and population density within a 150-mile radius of potential disaster zones.
- Resource allocation: Optimizing the deployment of medical resources and emergency personnel based on population distribution and needs.
3. Environmental Studies and Resource Management:
- Wildlife conservation: Mapping wildlife populations and their habitats within a specific radius, aiding in conservation efforts.
- Environmental impact assessment: Analyzing the potential impact of a development project on surrounding ecosystems and resources.
- Water resource management: Identifying areas with high water demand and potential water scarcity within a specific radius.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure planning: Determining the optimal locations for new roads, schools, hospitals, and other infrastructure based on population distribution and existing facilities.
- Land use planning: Identifying areas suitable for different types of development based on proximity to amenities, transportation, and environmental factors.
- Traffic management: Analyzing traffic patterns within a specific radius to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
5. Social Sciences and Demographics:
- Population density analysis: Understanding the distribution of population within a specific radius, revealing areas of high or low density.
- Social service needs assessment: Identifying areas with high concentrations of vulnerable populations, such as the elderly or low-income families, to better allocate social services.
- Migration patterns: Analyzing the movement of people within a specific radius, uncovering trends and drivers of migration.
FAQs about the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map:
1. Why 150 Air Miles?
The 150-mile radius is a commonly used distance in various applications due to its practical relevance. It represents a reasonable distance for travel and communication, encompassing a significant geographic area while remaining manageable for analysis.
2. How is the Radius Calculated?
The radius is calculated using a straight-line distance, measured in air miles, from the central point to the edge of the circular area. This air distance is typically calculated using a geodesic formula, accounting for the curvature of the Earth.
3. What Data Can Be Plotted on the Map?
The 150 air mile radius dot map can accommodate a wide range of data points, including:
- Demographic data: Population density, age distribution, income levels.
- Business data: Company locations, sales figures, customer demographics.
- Health data: Disease incidence rates, hospital locations, emergency response times.
- Environmental data: Pollution levels, wildlife populations, protected areas.
- Transportation data: Road networks, public transportation routes, traffic congestion levels.
4. What Software Can Be Used to Create These Maps?
Various software tools can be used to create 150 air mile radius dot maps, including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software: ArcGIS, QGIS, MapInfo.
- Spreadsheet software: Excel, Google Sheets.
- Mapping websites: Google Maps, Mapbox.
5. What are the Limitations of This Approach?
While powerful, the 150 air mile radius dot map also has limitations:
- Oversimplification: It simplifies complex spatial relationships, potentially overlooking nuanced patterns.
- Limited scope: It only considers data within a specific radius, neglecting information outside the designated area.
- Data availability: The effectiveness of the map depends on the availability and quality of relevant data.
Tips for Using the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map:
- Clearly define the central point: Choose a point that is relevant to your analysis and research question.
- Select appropriate data: Ensure the data used is relevant, accurate, and representative of the geographic area.
- Consider the scale: Adjust the map’s scale to appropriately represent the spatial relationships and data points.
- Use color and symbols effectively: Employ a color scheme and symbols that enhance visual clarity and understanding.
- Interpret the results carefully: Analyze the map’s patterns and trends in conjunction with other data sources and contextual information.
Conclusion:
The 150 air mile radius dot map is a valuable tool for spatial analysis, offering a visual representation of geographic data that can reveal hidden patterns, identify trends, and inform decision-making. Its applications span various fields, from business and marketing to public health, environmental studies, and urban planning. By leveraging this powerful tool, professionals can gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, driving more informed and strategic decisions. However, it is crucial to remember its limitations and use it in conjunction with other data sources and analytical techniques for a comprehensive understanding of the complex world around us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Spatial Analysis: A Deep Dive into the 150 Air Mile Radius Dot Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
