Understanding the Radius of a Circle on a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Radius of a Circle on a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Radius of a Circle on a Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Radius of a Circle on a Map: A Comprehensive Guide
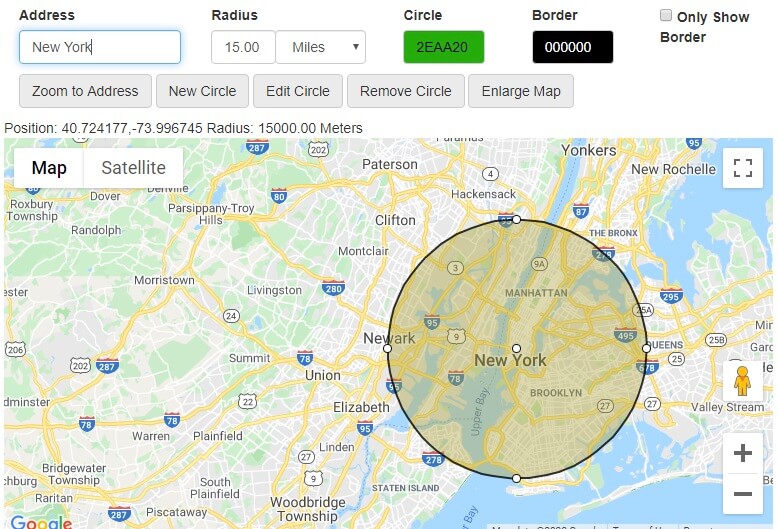
Maps, as visual representations of geographical spaces, often employ circles to depict various features and phenomena. These circles, whether representing the area of influence of a landmark, the range of a signal, or the extent of a natural hazard, are characterized by their radius. This seemingly simple concept plays a crucial role in understanding the scale, scope, and impact of the information presented on a map.
Defining the Radius on a Map:
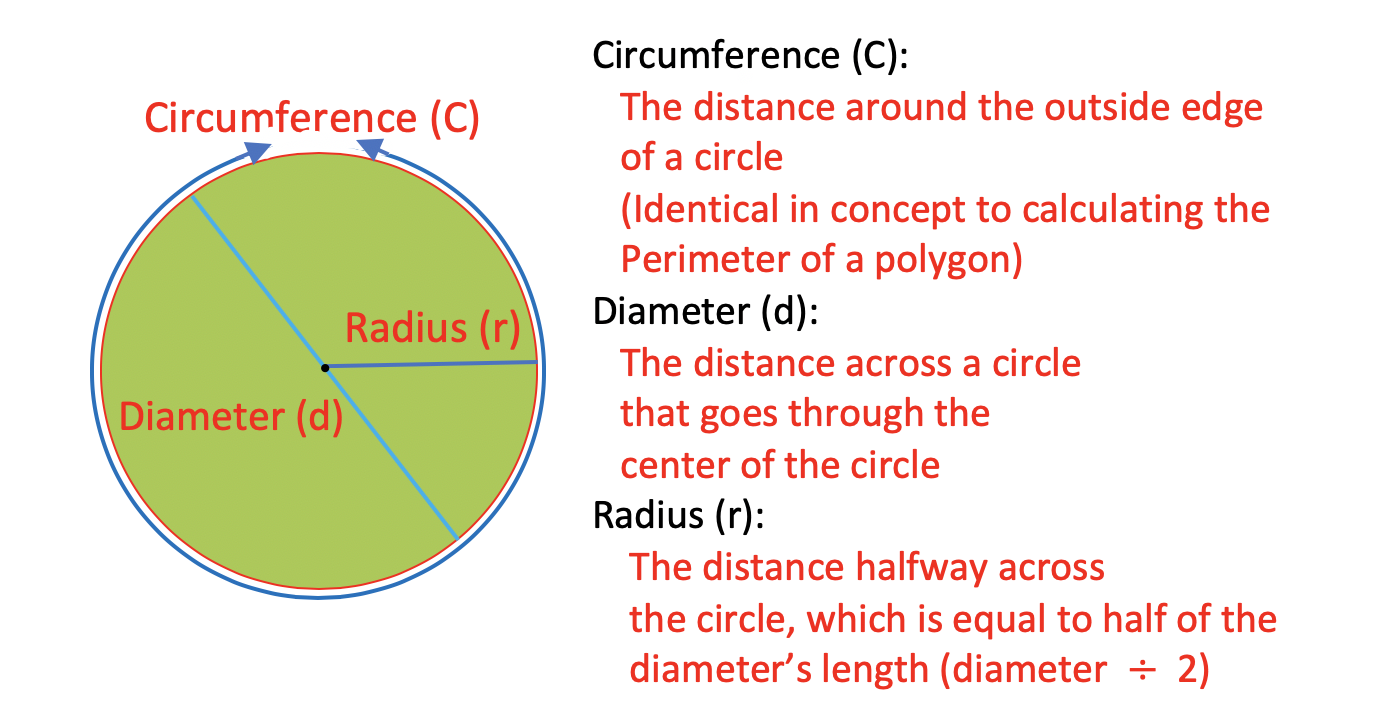
The radius of a circle on a map, much like the radius of any circle, is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. It serves as a key parameter in determining the size and reach of the represented area.
Importance and Applications of the Radius:
The concept of radius on a map finds applications in diverse fields, contributing significantly to various analyses and decision-making processes.
1. Geographical Analysis and Spatial Planning:
- Defining Zones of Influence: Circles with varying radii can be used to delineate areas of influence around specific points of interest, such as hospitals, schools, or commercial centers. This helps in understanding the accessibility and reach of these facilities, aiding in spatial planning and resource allocation.
- Determining Service Areas: The radius of a circle can define the service area of a particular business or organization, allowing for targeted marketing and efficient resource deployment.
- Analyzing Spatial Patterns: By comparing radii of circles representing different phenomena, such as population density or crime rates, spatial patterns and trends can be identified, leading to informed policy decisions.
2. Environmental Monitoring and Disaster Management:
- Mapping Natural Hazards: Circles can depict the potential impact zone of natural disasters like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or floods. The radius of these circles, determined by factors like the magnitude of the event and terrain characteristics, provides crucial information for evacuation planning and disaster preparedness.
- Monitoring Environmental Impact: Circles with radii representing the spread of pollution or contamination can help visualize the extent of environmental damage and inform remediation efforts.
3. Navigation and Transportation:
- Defining Flight Paths and Airspace: Circles with varying radii are used to demarcate airspace restrictions and flight paths, ensuring safe and efficient air traffic management.
- Mapping Transportation Networks: Circles can represent the service area of public transportation routes, allowing for efficient planning and optimization of transportation networks.
4. Data Visualization and Communication:
- Illustrating Data Distributions: Circles with radii proportional to data values can effectively visualize spatial data, such as population density or economic activity. This provides a clear and intuitive understanding of the distribution and magnitude of the data.
- Communicating Complex Information: Circles can simplify complex information by visually representing relationships and spatial patterns, making it easier for audiences to understand and interpret.
Factors Influencing the Radius:
The radius of a circle on a map is not a fixed value but is influenced by several factors, including:
- Scale of the Map: The larger the scale of the map, the smaller the radius will appear, and vice versa.
- Projection Used: Different map projections can distort distances and shapes, affecting the accuracy of the represented radius.
- Data Source and Accuracy: The accuracy of the data used to determine the radius will influence its reliability.
- Purpose of the Map: The intended use of the map will influence the choice of radius, ensuring the information is conveyed effectively and serves its purpose.
FAQs Regarding Radius on a Map:
1. How is the radius of a circle on a map determined?
The radius is typically determined by the distance from the center of the circle to its circumference, measured using appropriate units like kilometers, miles, or nautical miles. The specific method of determination depends on the data source and the purpose of the map.
2. Can the radius of a circle on a map be inaccurate?
Yes, the radius can be inaccurate due to factors like map projection distortions, data inaccuracies, or the simplification of complex phenomena. It is important to consider these limitations when interpreting information based on the radius.
3. How can I determine the real-world distance represented by a radius on a map?
The real-world distance can be determined by using the map’s scale and converting the radius measurement to the corresponding units. For example, if the map scale is 1:10,000 and the radius is 2 cm, the real-world distance would be 200 meters.
4. What are some common applications of circles with radii on maps?
Circles with radii are commonly used to represent areas of influence, service areas, natural hazard zones, pollution spread, flight paths, and data distributions.
5. How can I use the radius of a circle on a map to make informed decisions?
By understanding the factors influencing the radius and the data it represents, you can use it to assess the reach of services, plan for disaster preparedness, analyze spatial patterns, and make informed decisions based on the information presented on the map.
Tips for Using Radius on a Map Effectively:
- Understand the map’s scale and projection: This will help you interpret the radius accurately and avoid misinterpretations.
- Consider the data source and accuracy: Evaluate the reliability of the data used to determine the radius.
- Use multiple sources of information: Combine the information from the radius with other data sources to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Be aware of limitations: Recognize that the radius is a simplification and may not fully represent the complexity of the real-world phenomenon.
Conclusion:
The radius of a circle on a map, though seemingly simple, plays a vital role in conveying spatial information and facilitating informed decision-making across diverse fields. Understanding its definition, applications, and influencing factors is crucial for effective interpretation and utilization of maps in various contexts. By considering the limitations and employing best practices, the radius can be a powerful tool for analyzing spatial data, planning for the future, and managing resources effectively.


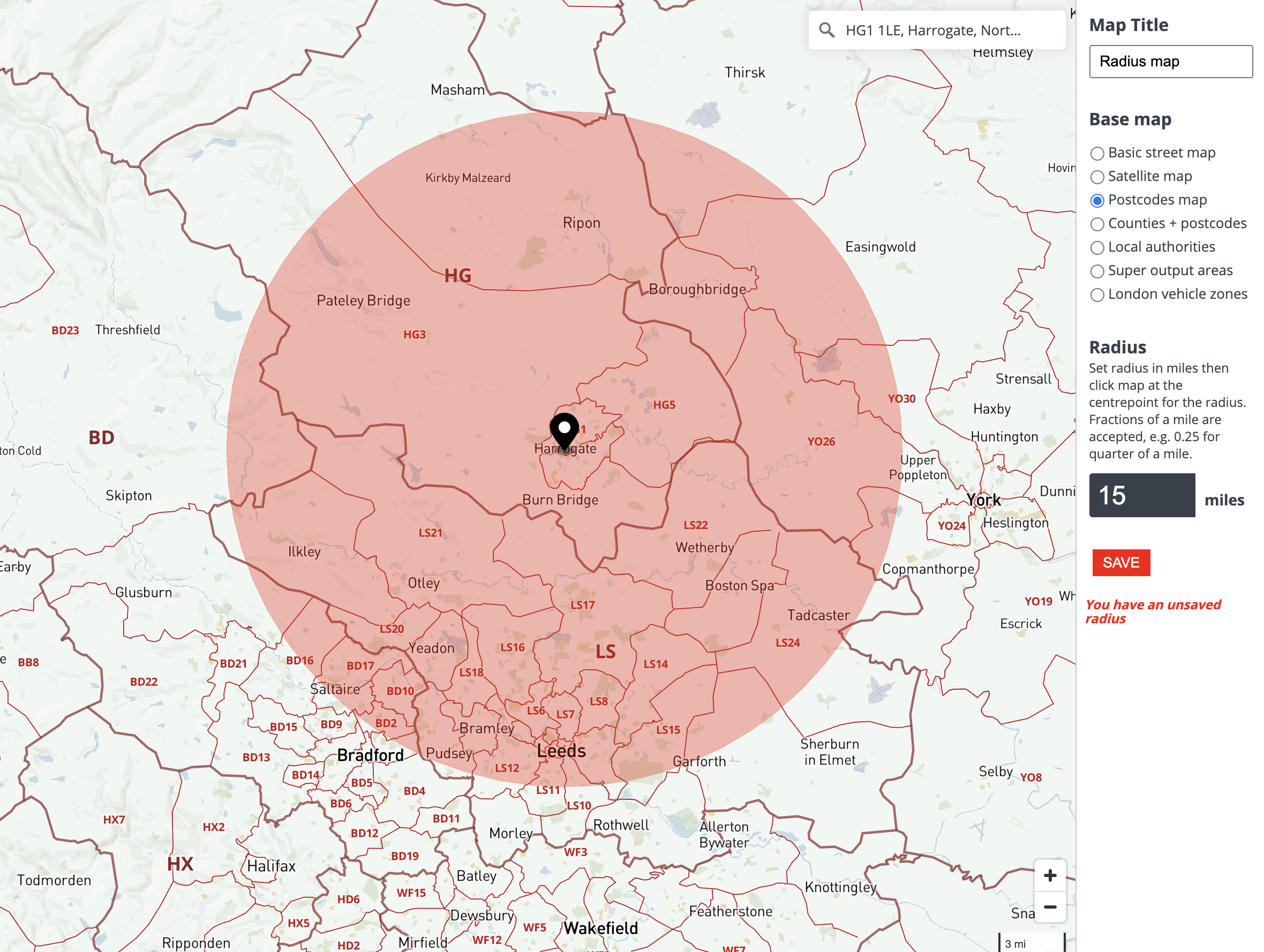
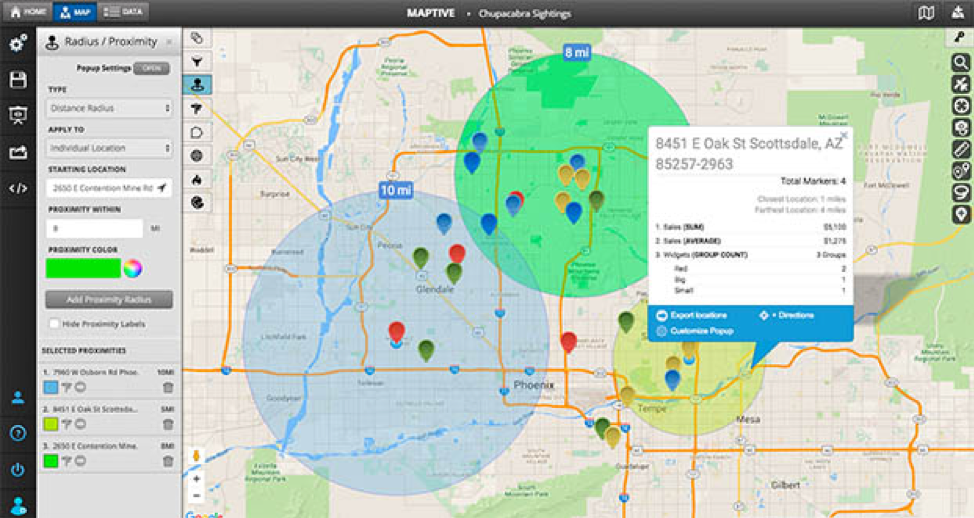

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Radius of a Circle on a Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
