Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars
- 3.1 A Bridge Between Representation and Reality
- 3.2 Types of Scale Bars and Their Applications
- 3.3 The Importance of Scale Bars in World Maps
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding World Map Scale Bars
- 3.5 Tips for Using Scale Bars Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars
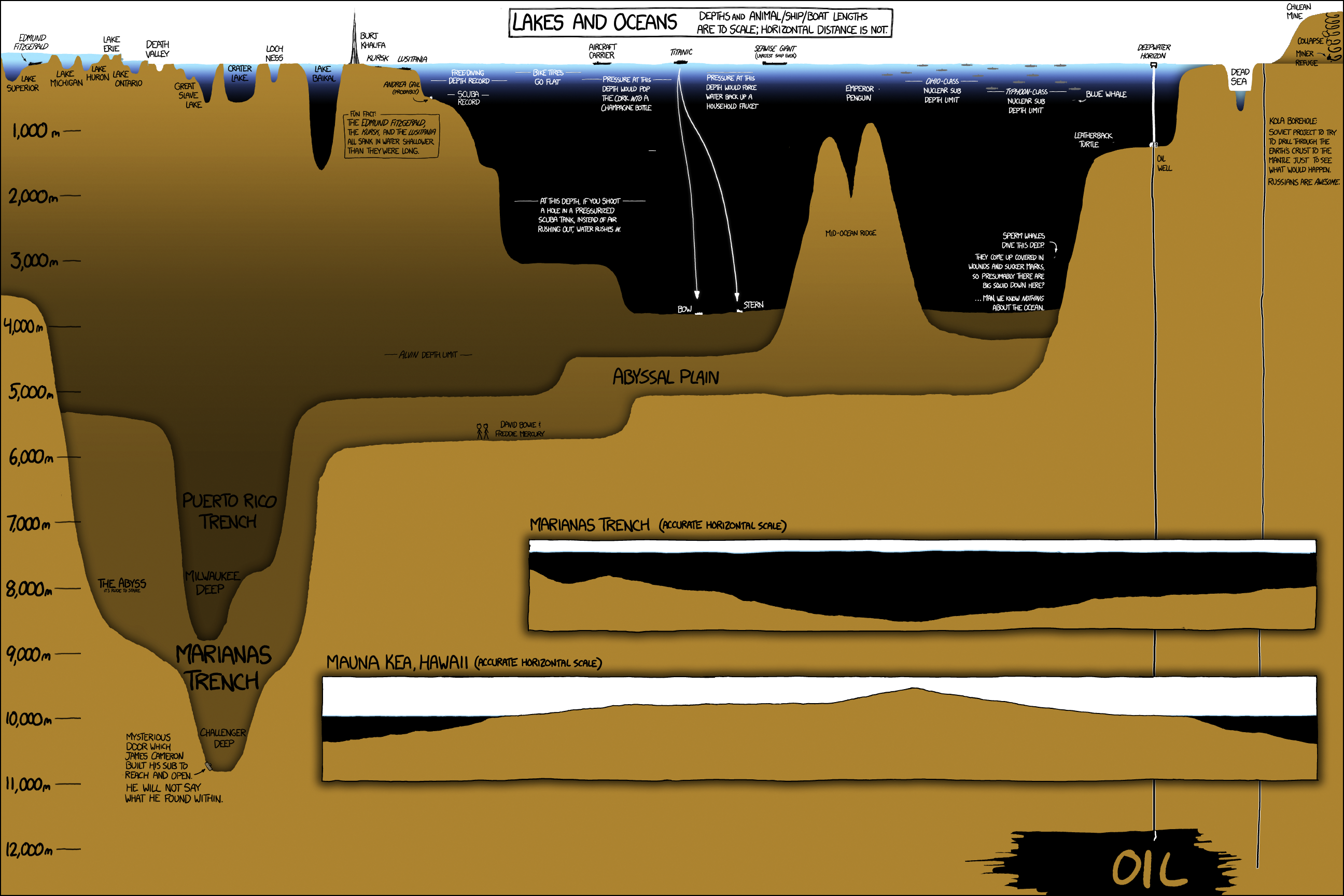
The world, in its vastness, can be daunting to comprehend. Yet, maps, those invaluable tools of cartography, offer a way to navigate its complexities and understand its distances. Central to this understanding lies the scale bar, a seemingly simple yet crucial element that bridges the gap between the two-dimensional representation of the world and its true, three-dimensional form.
A Bridge Between Representation and Reality
A scale bar, often found at the bottom or side of a world map, serves as a visual key to interpreting distances. It provides a tangible, measurable reference point, enabling viewers to translate the distances depicted on the map to their real-world counterparts. This conversion is essential for understanding the true extent of geographical features, the distances between locations, and the relative sizes of different countries and continents.
Imagine a world map without a scale bar. The continents would appear as mere shapes, their vastness and distances incomprehensible. A scale bar, however, introduces a sense of proportion, allowing us to grasp the true magnitude of the world and its components.
Types of Scale Bars and Their Applications
Scale bars come in various forms, each with its own unique purpose and application:
-
Linear Scale Bars: These are the most common type, consisting of a straight line divided into segments representing specific distances. They are typically labeled with units like kilometers or miles, offering a direct conversion from map distance to real-world distance.
-
Graphic Scale Bars: These scale bars utilize a graphical representation, often resembling a ruler, with markings indicating specific distances. They are particularly useful for maps with varying scales, as they provide a visual representation of the scale at different points on the map.
-
Verbal Scale Bars: These scale bars express the relationship between map distance and real-world distance in words, such as "1 centimeter equals 10 kilometers." While less visually intuitive, they offer a precise numerical representation of the scale.
-
Representative Fraction (RF) Scale: This type of scale, expressed as a fraction (e.g., 1:100,000), indicates that one unit of measurement on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world. While not a scale bar in the traditional sense, it provides a numerical representation of the map’s scale.
The Importance of Scale Bars in World Maps
The significance of scale bars extends beyond simply understanding distances. They play a critical role in:
-
Accurate Measurement: Scale bars enable precise measurement of distances between locations, facilitating navigation, planning journeys, and conducting geographical research.
-
Comparative Analysis: By providing a reference point for distance, scale bars allow for meaningful comparisons of the sizes and distances between different geographical features. This is crucial for understanding the relative importance and influence of different regions.
-
Data Interpretation: Scale bars are essential for interpreting data presented on maps, such as population density, resource distribution, or environmental trends. They allow for a more accurate understanding of the spatial distribution of these data points.
-
Visual Communication: Scale bars enhance the clarity and effectiveness of world maps by providing a visual anchor for understanding distances and proportions. This ensures that viewers can accurately interpret the information presented on the map.
FAQs Regarding World Map Scale Bars
1. How do I use a scale bar to measure distance?
To measure distance using a scale bar, place a ruler along the line on the map representing the distance you want to measure. Then, align the ruler with the scale bar and note the corresponding distance on the scale bar.
2. Why do different world maps have different scale bars?
World maps are often created at different scales, reflecting their intended purpose and level of detail. A map focusing on a specific region might have a larger scale than a map showcasing the entire globe.
3. Can I create my own scale bar for a world map?
Yes, you can create your own scale bar using a ruler and a piece of paper. Measure the distance on the map you want to represent and then use the scale you desire to create a corresponding scale bar.
4. What are the limitations of scale bars?
Scale bars only accurately represent distances on the flat surface of the map. They do not account for the curvature of the Earth, which can introduce distortion, particularly for larger distances.
5. How do I understand the distortion caused by the Earth’s curvature on a world map?
The distortion caused by the Earth’s curvature is unavoidable on flat maps. Different map projections, such as Mercator or Robinson, attempt to minimize distortion in different ways. Understanding the specific projection used for a map is crucial for interpreting distances accurately.
Tips for Using Scale Bars Effectively
-
Pay attention to the units of measurement: Ensure you are using the correct units (kilometers, miles, etc.) when interpreting distances.
-
Consider the map’s scale: A smaller scale map will have a larger distance represented by the same segment on the scale bar than a larger scale map.
-
Use a ruler for accurate measurements: Avoid using estimations when measuring distances on a map.
-
Be aware of distortion: Remember that scale bars only represent distances on a flat surface. Distortion can occur due to the Earth’s curvature, especially for large distances.
Conclusion
The scale bar, seemingly a simple element on a world map, plays a pivotal role in unlocking the secrets of distance. It provides a bridge between the two-dimensional representation of the world and its vast, three-dimensional reality. By understanding the principles behind scale bars and their various types, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between maps, distances, and our understanding of the world. As we continue to explore and interact with our planet, the scale bar will remain an invaluable tool for navigating its complexities and appreciating its grandeur.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Distance: A Deep Dive into World Map Scale Bars. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
