Unraveling the Earth’s Story: The Importance of Map Scale in Geology
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth’s Story: The Importance of Map Scale in Geology
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth’s Story: The Importance of Map Scale in Geology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Earth’s Story: The Importance of Map Scale in Geology

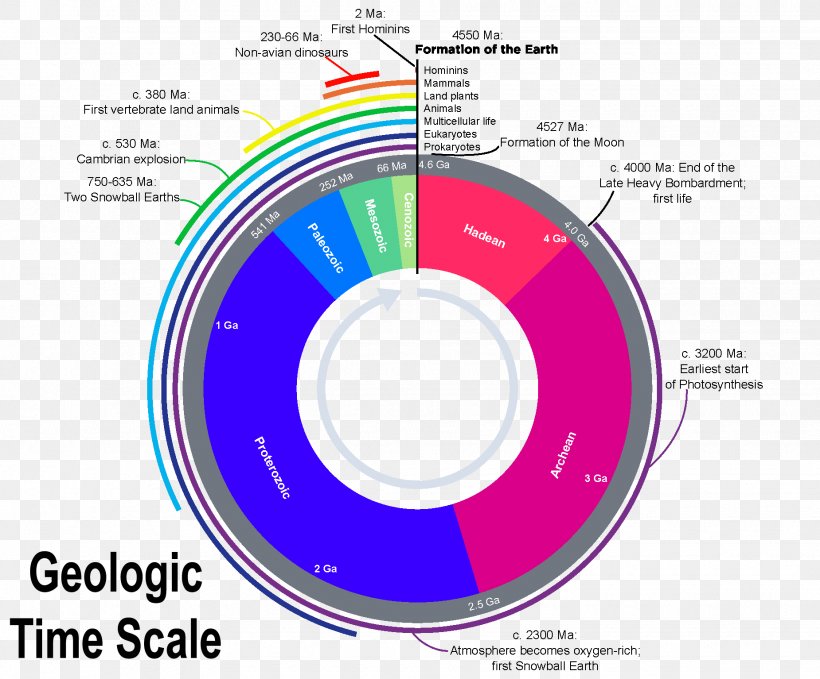
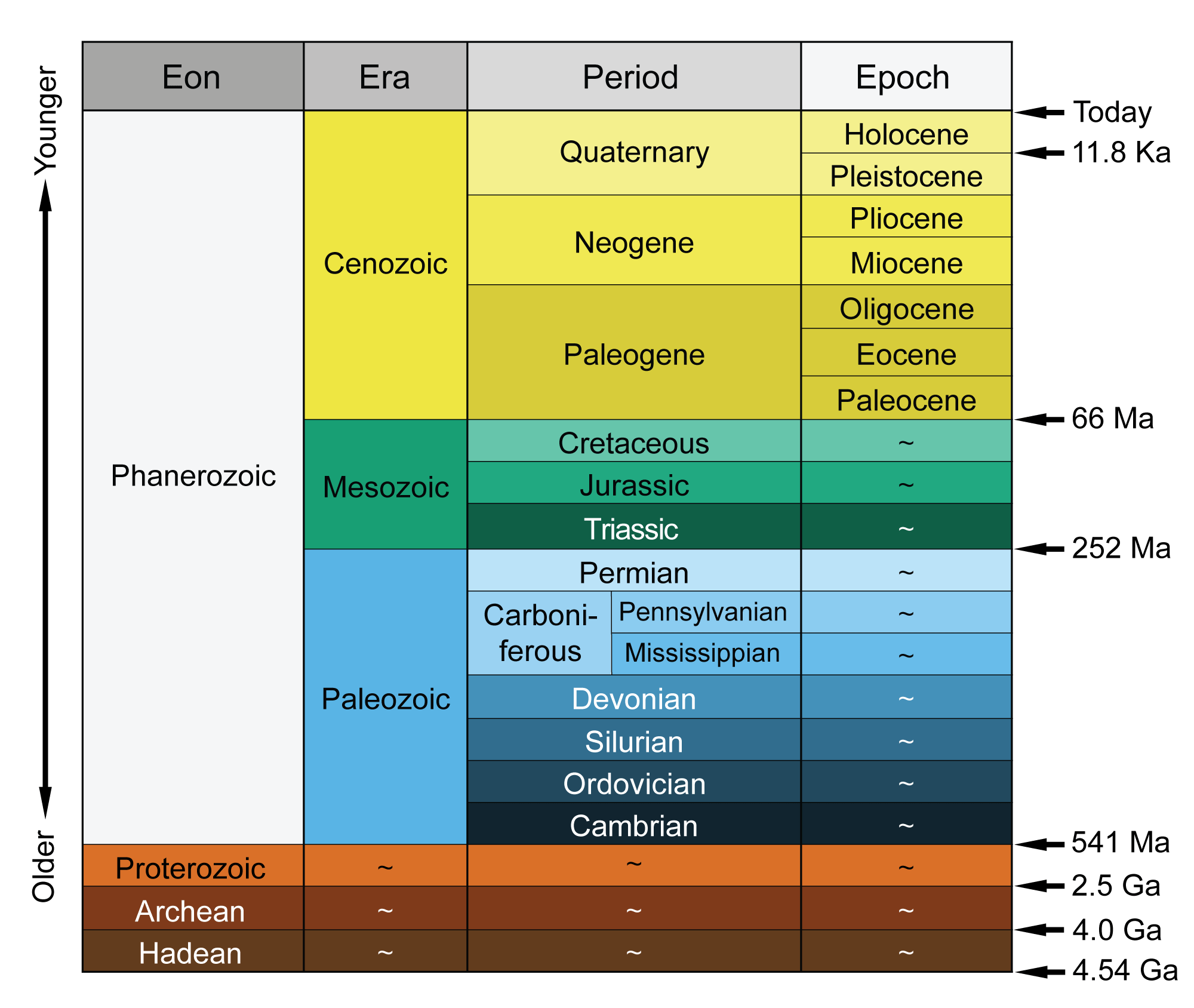
The Earth’s surface is a tapestry woven with diverse geological features, each holding clues to the planet’s tumultuous history. Understanding these features, from towering mountains to hidden faults, requires a precise and comprehensive method of representation: geological maps. However, the effectiveness of these maps hinges on a crucial concept: map scale.
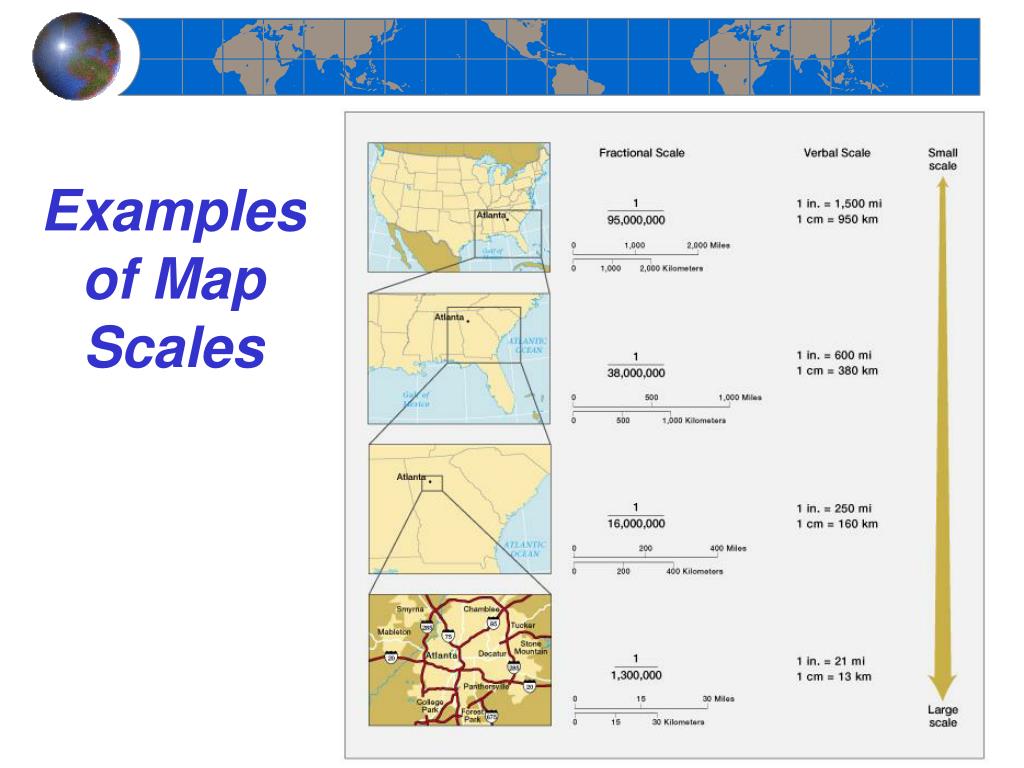
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio is crucial for accurately depicting geological features and understanding their spatial relationships. A large-scale map, with a smaller ratio, represents a smaller area in greater detail, while a small-scale map, with a larger ratio, encompasses a broader region at a lower level of detail.
The Significance of Scale in Geological Mapping
The choice of map scale directly influences the level of detail and the types of geological features that can be effectively represented. Understanding this relationship is paramount for interpreting geological maps and drawing meaningful conclusions about the Earth’s history and structure.
Large-Scale Maps: Unveiling Fine-Grained Details
Large-scale maps, often used for detailed studies of specific areas, allow geologists to accurately depict:
- Precise locations of geological formations: These maps can pinpoint the boundaries of rock units, identify individual layers within a sequence, and show the distribution of different types of rocks.
- Structural features: Detailed representations of folds, faults, and other structural features are crucial for understanding the deformation history of a region and its impact on the landscape.
- Mineral deposits and resource potential: Large-scale maps are essential for identifying and delineating mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and other valuable resources.
- Geomorphological features: These maps can effectively depict the intricate details of landforms, such as canyons, valleys, and coastal features, providing insights into the processes that shaped the landscape.
Small-Scale Maps: Capturing the Big Picture
Small-scale maps, encompassing vast regions, offer a broader perspective on geological phenomena, allowing geologists to:
- Identify regional geological trends: These maps reveal the distribution of major rock units, tectonic structures, and geological provinces, providing insights into the overall geological framework of a region.
- Understand the relationship between geological features and regional processes: Small-scale maps can illustrate the influence of plate tectonics, erosion, and climate on the landscape.
- Assess the potential for resource exploration: By identifying areas with specific geological characteristics, small-scale maps can guide exploration efforts for resources like oil, gas, and minerals.
The Interplay of Scale and Geological Interpretation
Choosing the appropriate map scale is critical for conducting meaningful geological investigations. It is not merely a matter of representing the Earth’s surface but rather a tool for understanding the processes that shaped it.
- Large-scale maps: Best suited for detailed studies of specific areas, focusing on local geological variations and structures.
- Small-scale maps: Ideal for regional-scale investigations, providing a broader perspective on the geological framework of a larger region.
A Practical Example: Understanding the Impact of Scale on Geological Interpretation
Imagine a geologist studying a region with a complex history of faulting and folding. Using a large-scale map, they can meticulously trace the individual faults, identify the direction and magnitude of displacement, and analyze the relationship between faults and folds. This detailed information can help them understand the sequence of tectonic events that shaped the region.
However, if the geologist uses a small-scale map, they may only be able to identify the major faults and folds, missing the intricate details of individual structures. While this might provide a general understanding of the region’s tectonic history, it would lack the precision necessary for detailed analysis.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Map Scale Geology
Advances in technology have revolutionized geological mapping, enabling the creation of high-resolution maps at various scales.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows geologists to integrate data from different sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and field observations, to create detailed geological maps.
- Remote Sensing: Techniques like satellite imagery and aerial photography provide a comprehensive overview of the Earth’s surface, enabling the identification of geological features across large areas.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): DEMs provide detailed topographic information, allowing geologists to create accurate representations of the terrain and understand its relationship to geological structures.
These technological advancements allow geologists to create increasingly sophisticated and accurate geological maps, regardless of the scale.
FAQs on Map Scale Geology
1. What is the difference between large-scale and small-scale maps?
- Large-scale maps: Represent a smaller area in greater detail, with a smaller ratio between map distance and ground distance.
- Small-scale maps: Represent a larger area at a lower level of detail, with a larger ratio between map distance and ground distance.
2. How do I choose the appropriate map scale for my geological study?
The choice of map scale depends on the specific objectives of your study. Consider the size of the area you are investigating, the level of detail required, and the types of geological features you are interested in.
3. What are some common map scale notations?
Map scales can be expressed in different ways:
- Verbal scale: States the ratio in words, e.g., "1 centimeter represents 1 kilometer."
- Representative fraction (RF): Expresses the ratio as a fraction, e.g., 1:100,000.
- Graphic scale: A visual representation of the scale using a line marked with distances.
4. How can I convert between different map scales?
To convert between different map scales, you can use the following formula:
- Scale 1 / Scale 2 = Distance on Map 1 / Distance on Map 2
Tips for Understanding Map Scale in Geology
- Always pay attention to the map scale: It is the key to interpreting the information presented on the map.
- Use a ruler or scale bar: Measure distances on the map to understand the actual distances on the ground.
- Consider the purpose of the map: Different map scales are designed for different purposes.
- Compare maps at different scales: This can help you understand the relationship between local and regional geological features.
Conclusion: The Importance of Map Scale in Unveiling Earth’s Secrets
Map scale is not just a technical aspect of geological mapping but a fundamental concept that influences our understanding of the Earth’s history and structure. By carefully considering the appropriate scale for their investigations, geologists can effectively depict geological features, analyze their relationships, and draw meaningful conclusions about the processes that shaped our planet. As technology continues to advance, the role of map scale in geological studies will only become more critical, enabling us to unravel the Earth’s secrets with increasing precision and depth.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth’s Story: The Importance of Map Scale in Geology. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
